Spring IOC创建对象的两种方式
IOC创建对象的方式
一、 使用无参构造创建对象(默认方式)
创建实体类
注意:属性必须要有set方法,来完成注入
public class User {
private String name;
public User() {
System.out.println("执行了User类的无参构造方法~");
}
public User(String name){
this.name = name;
System.out.println("执行了User类的有参构造方法");
}
//使用无参构造方法时,必须要设置set方法,因为注入时 需要通过set方法注入
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
配置Bean
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user" class="com.test.pojo.User">
<property name="name" value="gyp"/>
</bean>
</beans>
测试类
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
User user = context.getBean("user", User.class);
System.out.println(user);
}
}
结果:

二、使用有参构造创建对象
- 通过下标注入
- 通过名字注入 【推荐】
- 通过类型注入
有参构造,不需要set方法注入
通过下标方式注入(通过index来选择,给有参构造的第几个参数注入)
(1)配置Bean
<bean id="user" class="com.test.pojo.User">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="gyp"/>
</bean>
(2)测试结果
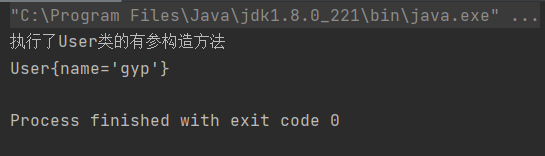
通过名字注入
(1)配置Bean
<bean id="user" class="com.test.pojo.User">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="gyp"/>
</bean>
(2)测试结果
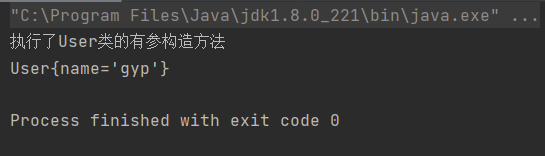
通过类型注入(不建议使用!因为当类里面有两个相同类型的属性时,无法给属性注入)
(1)配置Bean
<bean id="user" class="com.test.pojo.User">
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="gyp"/>
</bean>
(2)测试结果

总结:在加载配置文件的时候,IOC就已经创建好了对象!
到此这篇关于Spring IOC创建对象的两种方式的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Spring IOC创建对象内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!
赞 (0)

