SpringBoot实战之处理异常案例详解
前段时间写了一篇关于实现统一响应信息的博文,根据文中实战操作,能够解决正常响应的一致性,但想要实现优雅响应,还需要优雅的处理异常响应,所以有了这篇内容。
作为后台服务,能够正确的处理程序抛出的异常,并返回友好的异常信息是非常重要的,毕竟我们大部分代码都是为了 处理异常情况。而且,统一的异常响应,有助于客户端理解服务端响应,并作出正确处理,而且能够提升接口的服务质量。
SpringBoot提供了异常的响应,可以通过/error请求查看效果:

这是从浏览器打开的场景,也就是请求头不包括content-type: applicaton/json,大白板一个,和友好完全不搭边。
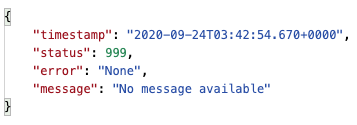
这是请求头包括content-type: applicaton/json时的响应,格式还行,但是我们还需要加工一下,实现自定义的异常码和异常信息。
本文主要是针对RESTful请求的统一响应,想要实现的功能包括:
- 自动封装异常,返回统一响应
- 异常信息国际化
定义异常响应类
当程序发送错误时,不应该将晦涩的堆栈报告信息返回给API客户端,从某种意义讲,这是一种不礼貌的和不负责任的行为。
我们在SpringBoot 实战:一招实现结果的优雅响应中,定义了一个响应类,为什么还要再定义一个异常响应类呢?其实是为了语义明确且职责单一。类图如下:
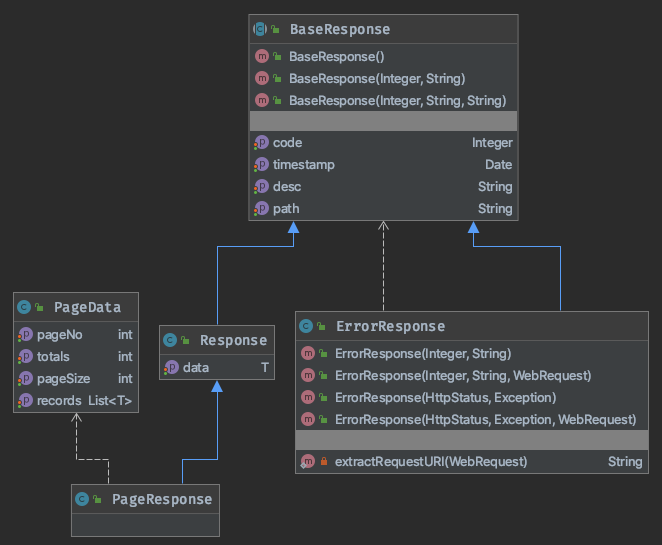
具体代码如下:
基础类BaseResponse:
@Data
public abstract class BaseResponse {
private Integer code;
private String desc;
private Date timestamp = new Date();
private String path;
public BaseResponse() {
}
public BaseResponse(final Integer code, final String desc) {
this.code = code;
this.desc = desc;
}
public BaseResponse(final Integer code, final String desc, final String path) {
this.code = code;
this.desc = desc;
this.path = path;
}
}
异常类ErrorResponse:
@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = true)
@Data
public class ErrorResponse extends BaseResponse {
public ErrorResponse(final Integer code, final String desc) {
super(code, desc);
}
public ErrorResponse(final Integer code, final String desc, final WebRequest request) {
super(code, desc, extractRequestURI(request));
}
public ErrorResponse(final HttpStatus status, final Exception e) {
super(status.value(), status.getReasonPhrase() + ": " + e.getMessage());
}
public ErrorResponse(final HttpStatus status, final Exception e, final WebRequest request) {
super(status.value(), status.getReasonPhrase() + ": " + e.getMessage(), extractRequestURI(request));
}
private static String extractRequestURI(WebRequest request) {
final String requestURI;
if (request instanceof ServletWebRequest) {
ServletWebRequest servletWebRequest = (ServletWebRequest) request;
requestURI = servletWebRequest.getRequest().getRequestURI();
} else {
requestURI = request.getDescription(false);
}
return requestURI;
}
}
定义异常枚举类
为了能够规范响应码和响应信息,我们可以定义一个枚举类。
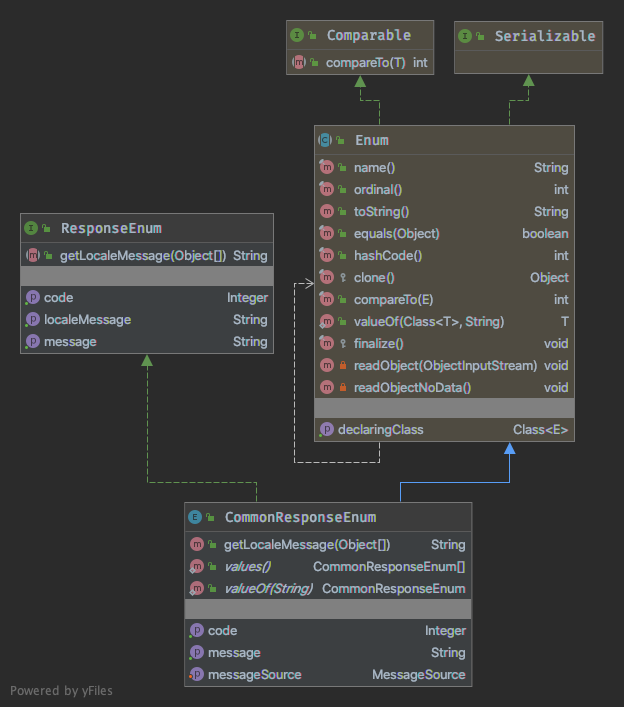
枚举接口ResponseEnum:
public interface ResponseEnum {
Integer getCode();
String getMessage();
default String getLocaleMessage() {
return getLocaleMessage(null);
}
String getLocaleMessage(Object[] args);
}
枚举类CommonResponseEnum:
public enum CommonResponseEnum implements ResponseEnum {
BAD_REQUEST(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value(), "Bad Request"),
NOT_FOUND(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND.value(), "Not Found"),
METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED(HttpStatus.METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED.value(), "Method Not Allowed"),
NOT_ACCEPTABLE(HttpStatus.NOT_ACCEPTABLE.value(), "Not Acceptable"),
REQUEST_TIMEOUT(HttpStatus.REQUEST_TIMEOUT.value(), "Request Timeout"),
UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE(HttpStatus.UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE.value(), "Unsupported Media Type"),
INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(), "Server Error"),
SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE(HttpStatus.SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE.value(), "Service Unavailable"),
ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT(4000, "Illegal Argument"),
DATA_NOT_FOUND(4004, "Data Not Found"),
USER_NOT_FOUND(4104, "User Not Found"),
MENU_NOT_FOUND(4204, "Menu Not Found"),
INTERNAL_ERROR(9999, "Server Error"),
;
private final Integer code;
private final String message;
private MessageSource messageSource;
CommonResponseEnum(final Integer code, final String message) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
}
@Override
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
@Override
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
@Override
public String getLocaleMessage(Object[] args) {
return messageSource.getMessage("response.error." + code, args, message, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
}
public void setMessageSource(final MessageSource messageSource) {
this.messageSource = messageSource;
}
@Component
public static class ReportTypeServiceInjector {
private final MessageSource messageSource;
public ReportTypeServiceInjector(final MessageSource messageSource) {
this.messageSource = messageSource;
}
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct() {
for (final CommonResponseEnum anEnum : CommonResponseEnum.values()) {
anEnum.setMessageSource(messageSource);
}
}
}
}
需要注意的是,我们在异常枚举类中定义了ReportTypeServiceInjector类,这个类的作用是为枚举类注入MessageSource对象,是为了实现异常信息的国际化。这部分功能Spring已经封装好了,我们只需要在resources目录中定义一组messages.properties文件就可以了,比如:
message.properties定义默认描述:
response.error.4000=[DEFAULT] Illegal Arguments response.error.4004=[DEFAULT] Not Found
messages_zh_CN.properties定义中文描述:
response.error.4004=对应数据未找到
response.error.9999=系统异常,请求参数: {0}
messages_en_US.properties定义英文描述:
response.error.4004=Not Found
自定义异常类
Java和Spring中提供了很多可用的异常类,可以满足大部分场景,但是有时候我们希望异常类可以携带更多信息,所以还是需要自定义异常类:
- 可以携带我们想要的信息;
- 有更加明确语义;
- 附带效果,可以知道这是手动抛出的业务异常。
上代码:
@Data
@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = true)
public class CodeBaseException extends RuntimeException {
private final ResponseEnum anEnum;
private final Object[] args;// 打印参数
private final String message;// 异常信息
private final Throwable cause;// 异常栈
public CodeBaseException(final ResponseEnum anEnum) {
this(anEnum, null, anEnum.getMessage(), null);
}
public CodeBaseException(final ResponseEnum anEnum, final String message) {
this(anEnum, null, message, null);
}
public CodeBaseException(final ResponseEnum anEnum, final Object[] args, final String message) {
this(anEnum, args, message, null);
}
public CodeBaseException(final ResponseEnum anEnum, final Object[] args, final String message, final Throwable cause) {
this.anEnum = anEnum;
this.args = args;
this.message = message;
this.cause = cause;
}
}
自定义异常信息处理类
前期准备工作完成,接下来定义异常信息处理类。
Spring自带的异常信息处理类往往不能满足我们实际的业务需求,这就需要我们定义符合具体情况的异常信息处理类,在自定义异常信息处理类中,我们可以封装更为详细的异常报告。我们可以扩展Spring提供的ResponseEntityExceptionHandler类定义自己的异常信息处理类,站在巨人的肩膀上,快速封装自己需要的类。
通过源码可以看到,ResponseEntityExceptionHandler类的核心方法是public final ResponseEntity<Object> handleException(Exception ex, WebRequest request),所有的异常都在这个方法中根据类型进行处理,我们只需要实现具体的处理方法即可:
@RestControllerAdvice
@Slf4j
public class UnifiedExceptionHandlerV2 extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
private static final String ENV_PROD = "prod";
private final MessageSource messageSource;
private final Boolean isProd;
public UnifiedExceptionHandlerV2(@Value("${spring.profiles.active:dev}") final String activeProfile, final MessageSource messageSource) {
this.messageSource = messageSource;
this.isProd = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(activeProfile.split(","))).contains(ENV_PROD);
}
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleExceptionInternal(final Exception e, final Object body, final HttpHeaders headers, final HttpStatus status, final WebRequest request) {
log.info("请求异常:" + e.getMessage(), e);
if (HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.equals(status)) {
request.setAttribute(WebUtils.ERROR_EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE, e, WebRequest.SCOPE_REQUEST);
}
return new ResponseEntity<>(new ErrorResponse(status, e), headers, HttpStatus.OK);
}
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleBindException(final BindException ex, final HttpHeaders headers, final HttpStatus status, final WebRequest request) {
log.info("参数绑定异常", ex);
final ErrorResponse response = wrapperBindingResult(status, ex.getBindingResult());
return new ResponseEntity<>(response, headers, HttpStatus.OK);
}
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleMethodArgumentNotValid(final MethodArgumentNotValidException ex, final HttpHeaders headers, final HttpStatus status, final WebRequest request) {
log.info("参数校验异常", ex);
final ErrorResponse response = wrapperBindingResult(status, ex.getBindingResult());
return new ResponseEntity<>(response, headers, HttpStatus.OK);
}
@ExceptionHandler(value = CodeBaseException.class)
@ResponseBody
public ErrorResponse handleBusinessException(CodeBaseException e) {
log.error("业务异常:" + e.getMessage(), e);
final ResponseEnum anEnum = e.getAnEnum();
return new ErrorResponse(anEnum.getCode(), anEnum.getLocaleMessage(e.getArgs()));
}
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public ErrorResponse handleExceptionInternal(Exception e) {
log.error("未捕捉异常:" + e.getMessage(), e);
final Integer code = INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.getCode();
return new ErrorResponse(code, getLocaleMessage(code, e.getMessage()));
}
/**
* 包装绑定异常结果
*
* @param status HTTP状态码
* @param bindingResult 参数校验结果
* @return 异常对象
*/
private ErrorResponse wrapperBindingResult(HttpStatus status, BindingResult bindingResult) {
final List<String> errorDesc = new ArrayList<>();
for (ObjectError error : bindingResult.getAllErrors()) {
final StringBuilder msg = new StringBuilder();
if (error instanceof FieldError) {
msg.append(((FieldError) error).getField()).append(": ");
}
msg.append(error.getDefaultMessage() == null ? "" : error.getDefaultMessage());
errorDesc.add(msg.toString());
}
final String desc = isProd ? getLocaleMessage(status.value(), status.getReasonPhrase()) : String.join(", ", errorDesc);
return new ErrorResponse(status.value(), desc);
}
private String getLocaleMessage(Integer code, String defaultMsg) {
try {
return messageSource.getMessage("" + code, null, defaultMsg, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.warn("本地化异常消息发生异常: {}", code);
return defaultMsg;
}
}
}
如果感觉Spring的ResponseEntityExceptionHandler类不够灵活,也可以完全自定义异常处理类:
@RestControllerAdvice
@Slf4j
public class UnifiedExceptionHandler {
private static final String ENV_PROD = "prod";
private final MessageSource messageSource;
private final Boolean isProd;
public UnifiedExceptionHandler(@Value("${spring.profiles.active:dev}") final String activeProfile, final MessageSource messageSource) {
this.messageSource = messageSource;
this.isProd = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(activeProfile.split(","))).contains(ENV_PROD);
}
@ExceptionHandler({
MissingServletRequestParameterException.class,// 缺少servlet请求参数异常处理方法
ServletRequestBindingException.class,// servlet请求绑定异常
TypeMismatchException.class,// 类型不匹配
HttpMessageNotReadableException.class,// 消息无法检索
MissingServletRequestPartException.class// 缺少servlet请求部分
})
public ErrorResponse badRequestException(Exception e, WebRequest request) {
log.info(e.getMessage(), e);
return new ErrorResponse(BAD_REQUEST.getCode(), e.getMessage(), request);
}
@ExceptionHandler({
NoHandlerFoundException.class// 没有发现处理程序异常
})
public ErrorResponse noHandlerFoundException(Exception e, WebRequest request) {
log.info(e.getMessage(), e);
return new ErrorResponse(NOT_FOUND.getCode(), e.getMessage(), request);
}
@ExceptionHandler({
HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException.class// 不支持的HTTP请求方法异常信息处理方法
})
public ErrorResponse httpRequestMethodNotSupportedException(Exception e, WebRequest request) {
log.info(e.getMessage(), e);
return new ErrorResponse(METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED.getCode(), e.getMessage(), request);
}
@ExceptionHandler({
HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException.class// 不接受的HTTP媒体类型异常处方法
})
public ErrorResponse httpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException(Exception e, WebRequest request) {
log.info(e.getMessage(), e);
return new ErrorResponse(NOT_ACCEPTABLE.getCode(), e.getMessage(), request);
}
@ExceptionHandler({
HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException.class// 不支持的HTTP媒体类型异常处理方法
})
public ErrorResponse httpMediaTypeNotSupportedException(Exception e, WebRequest request) {
log.info(e.getMessage(), e);
return new ErrorResponse(UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE.getCode(), e.getMessage(), request);
}
@ExceptionHandler({
AsyncRequestTimeoutException.class// 异步请求超时异常
})
public ErrorResponse asyncRequestTimeoutException(Exception e, WebRequest request) {
log.info(e.getMessage(), e);
return new ErrorResponse(SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE.getCode(), e.getMessage(), request);
}
@ExceptionHandler({
MissingPathVariableException.class,// 请求路径参数缺失异常处方法
HttpMessageNotWritableException.class,// HTTP消息不可写
ConversionNotSupportedException.class,// 不支持转换
})
public ErrorResponse handleServletException(Exception e, WebRequest request) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
return new ErrorResponse(INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.getCode(), e.getMessage(), request);
}
@ExceptionHandler({
BindException.class// 参数绑定异常
})
@ResponseBody
public ErrorResponse handleBindException(BindException e, WebRequest request) {
log.error("参数绑定异常", e);
return wrapperBindingResult(e.getBindingResult(), request);
}
/**
* 参数校验异常,将校验失败的所有异常组合成一条错误信息
*/
@ExceptionHandler({
MethodArgumentNotValidException.class// 方法参数无效
})
@ResponseBody
public ErrorResponse handleValidException(MethodArgumentNotValidException e, WebRequest request) {
log.error("参数校验异常", e);
return wrapperBindingResult(e.getBindingResult(), request);
}
/**
* 包装绑定异常结果
*/
private ErrorResponse wrapperBindingResult(BindingResult bindingResult, WebRequest request) {
final List<String> errorDesc = new ArrayList<>();
for (ObjectError error : bindingResult.getAllErrors()) {
final StringBuilder msg = new StringBuilder();
if (error instanceof FieldError) {
msg.append(((FieldError) error).getField()).append(": ");
}
msg.append(error.getDefaultMessage() == null ? "" : error.getDefaultMessage());
errorDesc.add(msg.toString());
}
final String desc = isProd ? getLocaleMessage(BAD_REQUEST.getCode(), "") : String.join(", ", errorDesc);
return new ErrorResponse(BAD_REQUEST.getCode(), desc, request);
}
/**
* 业务异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = CodeBaseException.class)
@ResponseBody
public ErrorResponse handleBusinessException(CodeBaseException e, WebRequest request) {
log.error("业务异常:" + e.getMessage(), e);
final ResponseEnum anEnum = e.getAnEnum();
return new ErrorResponse(anEnum.getCode(), anEnum.getLocaleMessage(e.getArgs()), request);
}
/**
* 未定义异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public ErrorResponse handleExceptionInternal(Exception e, WebRequest request) {
log.error("未捕捉异常:" + e.getMessage(), e);
final Integer code = INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.getCode();
return new ErrorResponse(code, getLocaleMessage(code, e.getMessage()), request);
}
private String getLocaleMessage(Integer code, String defaultMsg) {
try {
return messageSource.getMessage("" + code, null, defaultMsg, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.warn("本地化异常消息发生异常: {}", code);
return defaultMsg;
}
}
}
从上面两个类可以看出,比较核心的是这么几个注解:
- @ExceptionHandle:负责处理controller标注的类中抛出的异常的注解
- @RestControllerAdvice:能够将@ExceptionHandler标注的方法集中到一个地方进行处理的注解,这个注解是复合注解,实现了
@ControllerAdvice和@ResponseBody的功能。
借用谭朝红博文中的图片(蓝色箭头表示正常的请求和响应,红色箭头表示发生异常的请求和响应):
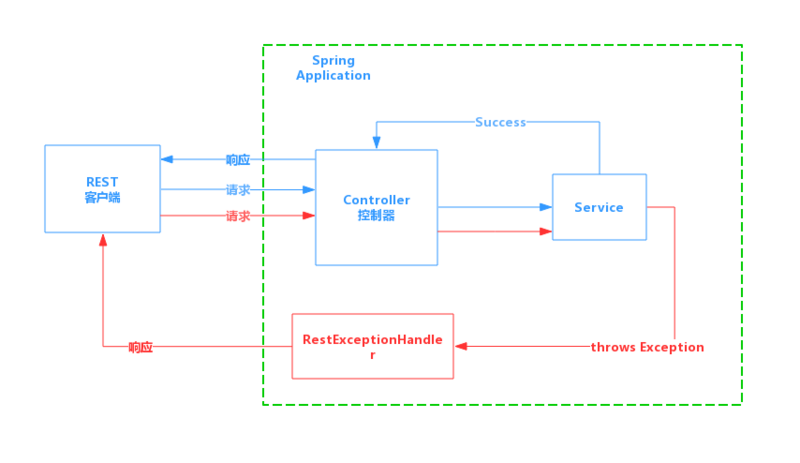
写个Demo测试一下
接下来我们写个demo测试一下是否能够实现异常的优雅响应:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("index")
@Slf4j
public class IndexController {
private final IndexService indexService;
public IndexController(final IndexService indexService) {
this.indexService = indexService;
}
@GetMapping("hello1")
public Response<String> hello1() {
Response<String> response = new Response<>();
try {
response.setCode(200);
response.setDesc("请求成功");
response.setData(indexService.hello());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("hello1方法请求异常", e);
response.setCode(500);
response.setDesc("请求异常:" + e.getMessage());
} finally {
log.info("执行controller的finally结构");
}
return response;
}
@GetMapping("hello2")
public Response<String> hello2(@RequestParam("ex") String ex) {
switch (ex) {
case "ex1":
throw new CodeBaseException(CommonResponseEnum.USER_NOT_FOUND, "用户信息不存在");
case "ex2":
throw new CodeBaseException(CommonResponseEnum.MENU_NOT_FOUND, "菜单信息不存在");
case "ex3":
throw new CodeBaseException(CommonResponseEnum.ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT, "请求参数异常");
case "ex4":
throw new CodeBaseException(CommonResponseEnum.DATA_NOT_FOUND, "数据不存在");
}
throw new CodeBaseException(INTERNAL_ERROR, new Object[]{ex}, "请求异常", new RuntimeException("运行时异常信息"));
}
}
启动服务之后,传入不同参数获取不同的异常信息:
// 请求 /index/hello2?ex=ex1
{
"code": 4104,
"desc": "User Not Found",
"timestamp": "2020-10-10T05:58:39.433+00:00",
"path": "/index/hello2"
}
// 请求 /index/hello2?ex=ex2
{
"code": 4204, "desc": "Menu Not Found",
"timestamp": "2020-10-10T06:00:34.141+00:00",
"path": "/index/hello2"
}
// 请求 /index/hello2?ex=ex3
{
"code": 4000,
"desc": "[DEFAULT] Illegal Arguments",
"timestamp": "2020-10-10T06:00:44.233+00:00",
"path": "/index/hello2"
}
// 请求 /index/hello2?ex=ex4
{
"code": 4004,
"desc": "对应数据未找到",
"timestamp": "2020-10-10T06:00:54.178+00:00",
"path": "/index/hello2"
}
附上文中的代码:https://github.com/howardliu-cn/effective-spring/tree/main/spring-exception-handler,收工。
推荐阅读
- SpringBoot 实战:一招实现结果的优雅响应
- SpringBoot 实战:如何优雅的处理异常
- SpringBoot 实战:通过 BeanPostProcessor 动态注入 ID 生成器
- SpringBoot 实战:自定义 Filter 优雅获取请求参数和响应结果
- SpringBoot 实战:优雅的使用枚举参数
- SpringBoot 实战:优雅的使用枚举参数(原理篇)
- SpringBoot 实战:在 RequestBody 中优雅的使用枚举参数
到此这篇关于SpringBoot实战之处理异常案例详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot实战之处理异常内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

