C++中cout输出中文信息乱码问题及解决
目录
- cout输出中文信息乱码问题
- 问题描述
- 解决办法
- C++ 输出cout
- 输出
- 输出
- 附录
cout输出中文信息乱码问题
问题描述
在实例化学生类对象时,对学生的姓名采用了形如“张三”这样的汉字信息,在输出学生姓名时出现了乱码问题(如下图):
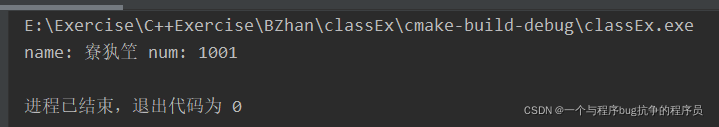
解决办法
采用<windows.h>头文件中的SetConsoleOutputCP(CP_UTF8)函数来设置在显示器打印时的编码格式就解决了乱码问题。
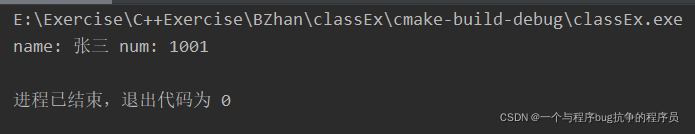
完整代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <windows.h>
using namespace std;
class Student {
public:
string name;
int num;
Student(const string &name, int num) : name(name), num(num) {}
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const Student &student) {
os << "name: " << student.name << " num: " << student.num;
return os;
}
};
int main() {
SetConsoleOutputCP(CP_UTF8);
Student s("张三", 1001);
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}
C++ 输出cout
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
/*
<<运算符 (可以进行 混合 拼接输出)
*/
const char *s = "hhhhh"; //字符串是const char*类型的,所以将字符串赋值给 char* 类型要加const关键字
cout << "the length of the s is " << strlen(s) << endl; // strlen()是cstring库中的函数
char str[10] = "ddddd";
cout << "hello" << endl;
cout << s << str << endl; //可以进行拼接输出
// 如何打印字符串地址的值?
//对于其他类型的指针,c++将其对应于void*,并打印地址的数值表示。如果要获得字符串的地址,则必须将其强制类型转换成其他类型
cout << &str[0] << endl; //invalid
cout << (float *)s << endl; //valid
cout << (void *)str << endl; //valid
cout << (int *)"hello" << endl; //valid
cout << "-------------------------------------------\n";
/*
put()方法 (可以进行 混合 拼接输出)
用于显示字符 (也可以将int型的赋给它,它会将int转换成char,从而显示与该ascll码相对应的字符)
*/
cout.put('d');
cout.put('\n');
cout.put('d').put('b').put('\n'); //可以进行拼接输出
cout.put(65);
cout.put(65.9); //put 浮点数65.9强制类型转换成整型数65(向下取整)
cout.put('\n');
cout << "-------------------------------------------\n";
/*
write()方法 (可以进行 混合 拼接输出)
第一个参数提供了要显示的字符串的地址,第二个参数指出要显示多少个字符
*/
const char *state1 = "Florida";
const char *state2 = "Kansas";
//state1、state3用于提供state2前面和后面的数据,以便程序员知道程序错误存取state2时发生的情况
const char *state3 = "Euphoria";
int len = strlen(state2);
cout << "Increasing loop index:\n";
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= len; i++)
{
cout.write(state2, i);
cout << endl;
}
// concatenate output
cout << "Decreasing loop index:\n";
for (i = len; i > 0; i--)
cout.write(state2, i) << endl;
// exceed string length
cout << "Exceeding string length:\n";
//我们发现:连续定义的字符串时连续存储的,中间用一个空格隔开 !!这可能因为编译器之间的差别而有所不同
cout.write(state2, len + 5).write("\n", 1).write(state2, len + 4) << endl;
/*
write()也可以用于数值数据,您可以将数字的地址强制转换成char*,然后传递给他
但这不会将数字转换为相应的字符,而是传输内存中储存的位表示。例如4字节的long值将作为四个独立的字节被传输,
输出设备将把每个字节作为ASCLL码进行解释,最终显示出来的是四个字符的组合(有可能是乱码)
*/
long val = 1094795585; // 二进制数01000001010000010100000101000001所对应的十进制数(每个字节都是65)
cout.write((char *)&val, sizeof(long)).write("\n", 1);
cout << "-------------------------------------------\n";
/*
刷新输出缓存区
*/
cout << "Hello, good-looking! " << flush;
cout << "Wait just a moment, please." << endl; //endl 刷新缓冲区,并插入一个换行符
flush(cout);
cout << flush; //ostream类对<<插入运算符进行了重载,使得下述表达式将被替换位函数调用flush(cout);
return 0;
}
输出
the length of the s is 5
hello
hhhhhddddd
ddddd
0x406045
0x61feee
0x406063
-------------------------------------------
d
db
AA
-------------------------------------------
Increasing loop index:
K
Ka
Kan
Kans
Kansa
Kansas
Decreasing loop index:
Kansas
Kansa
Kans
Kan
Ka
K
Exceeding string length:
Kansas Euph
Kansas Eup
AAAA
-------------------------------------------
Hello, good-looking! Wait just a moment, please.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n = 10;
cout << "n\n";
cout << n << " (decimal)\n";
cout << hex << n << " (hexadecimal)\n";
cout << oct << n << " (octal)\n";
dec(cout); // ostream类重载了<<运算符,这使得上述用法与函数调用dec(cout)等价
cout << n << " (decimal)\n";
cout << "-------------------------------------------\n";
//width() 只影响接下来显示的一个项目,然后字段宽度将恢复为默认值 0
int w = cout.width(2); //width(int i)返回的是修改前字段宽度的值,而不是刚设置的值
//fill(char c) 它更改的填充字符将一直有效,直到再次更改它为止
cout.fill('*');
cout << "default field width = " << w << ":\n"; //C++的原则:显示所有的数据比保持列的整洁更重要。输入上面设置了字段宽度为2,但这里依旧能将字符串“default field width = ”显示全
cout.width(5);
cout << "N"
<< ":\n";
for (long i = 1; i <= 100; i *= 10)
{
cout.width(5);
cout << i << ":\n";
}
cout << "-------------------------------------------\n";
//设置浮点数的精度
float price1 = 20.40;
float price2 = 1.9 + 8.0 / 9.0;
cout << "\"Furry Friends\" is $" << price1 << "!\n";
cout << "\"Fiery Fiends\" is $" << price2 << "!\n";
cout.precision(2); //修改输出浮点数的精度为2,设置后一直有效,直到再次更改它为止
cout << "\"Furry Friends\" is $" << price1 << "!\n";
cout << "\"Fiery Fiends\" is $" << price2 << "!\n";
cout.precision(6);
cout.setf(ios_base::showpoint); //showpoint是ios_base类声明中定义的类级静态常量,在成员函数的定义外面使用要加上作用域运算符(::)
cout << "\"Furry Friends\" is $" << price1 << "!\n";
cout << "\"Fiery Fiends\" is $" << price2 << "!\n";
cout.precision(2);
cout << "\"Furry Friends\" is $" << price1 << "!\n";
cout << "\"Fiery Fiends\" is $" << price2 << "!\n";
cout << "-------------------------------------------\n";
int temperature = 63;
cout << "Today's water temperature: ";
cout.setf(ios_base::showpos); // show plus sign
cout << temperature << endl;
cout << "For our programming friends, that's\n";
cout << std::hex << temperature << endl; // use hex
cout.setf(ios_base::uppercase); // use uppercase in hex
cout.setf(ios_base::showbase); // use 0X prefix for hex
cout << "or\n";
cout << temperature << endl;
cout << "How " << true << "! oops -- How ";
cout.setf(ios_base::boolalpha);
cout << true << "!\n";
cin.get();
return 0;
}
输出
n
10 (decimal)
a (hexadecimal)
12 (octal)
10 (decimal)
-------------------------------------------
default field width = 0:
****N:
****1:
***10:
**100:
-------------------------------------------
"Furry Friends" is $20.4!
"Fiery Fiends" is $2.78889!
"Furry Friends" is $20!
"Fiery Fiends" is $2.8!
"Furry Friends" is $20.4000!
"Fiery Fiends" is $2.78889!
"Furry Friends" is $20.!
"Fiery Fiends" is $2.8!
-------------------------------------------
Today's water temperature: +63
For our programming friends, that's
3f
or
0X3F
How 0X1! oops -- How true!
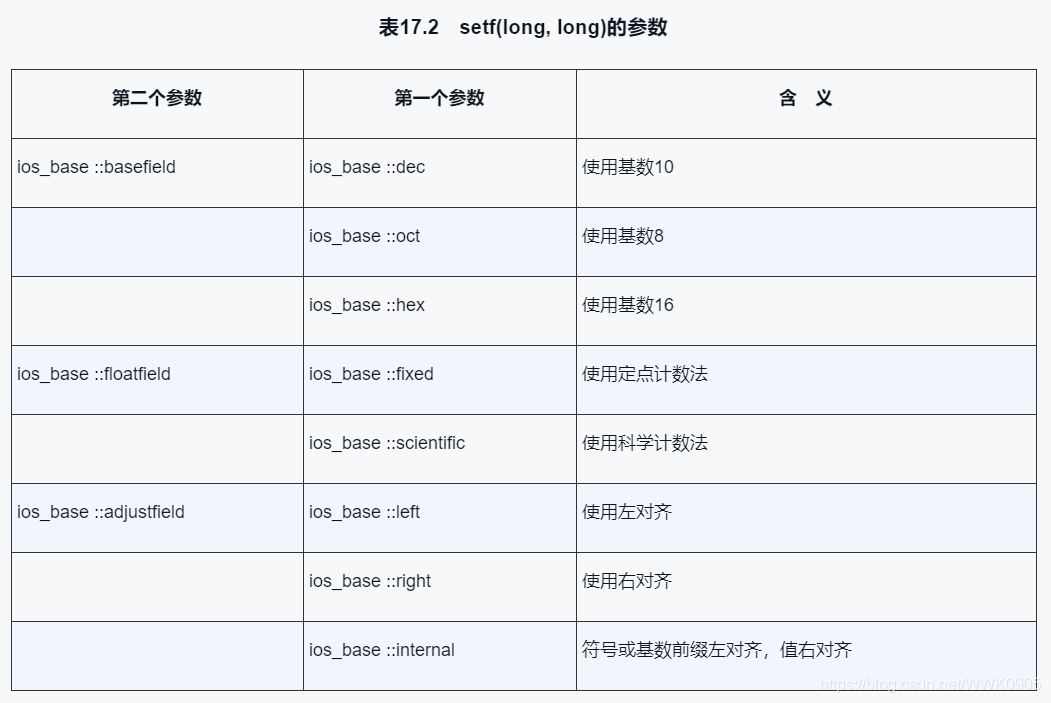
附录
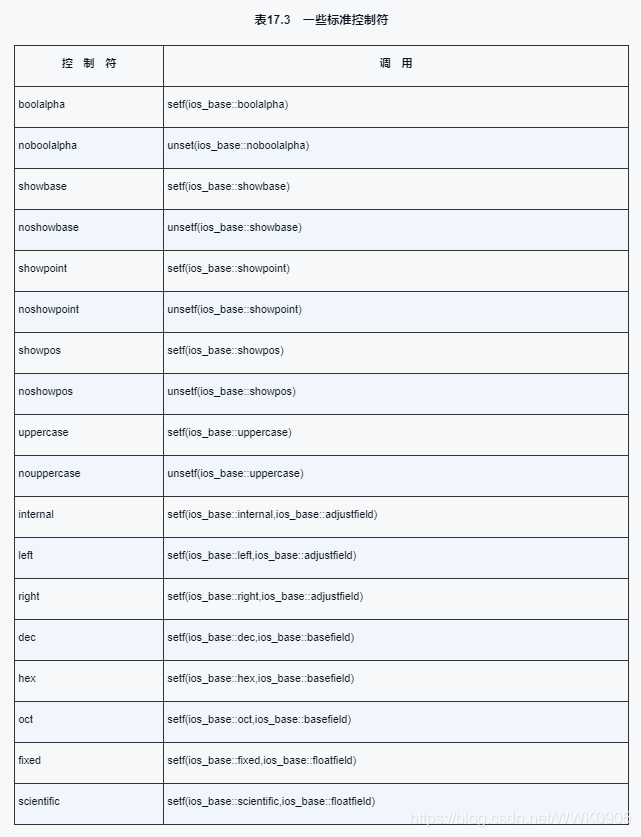
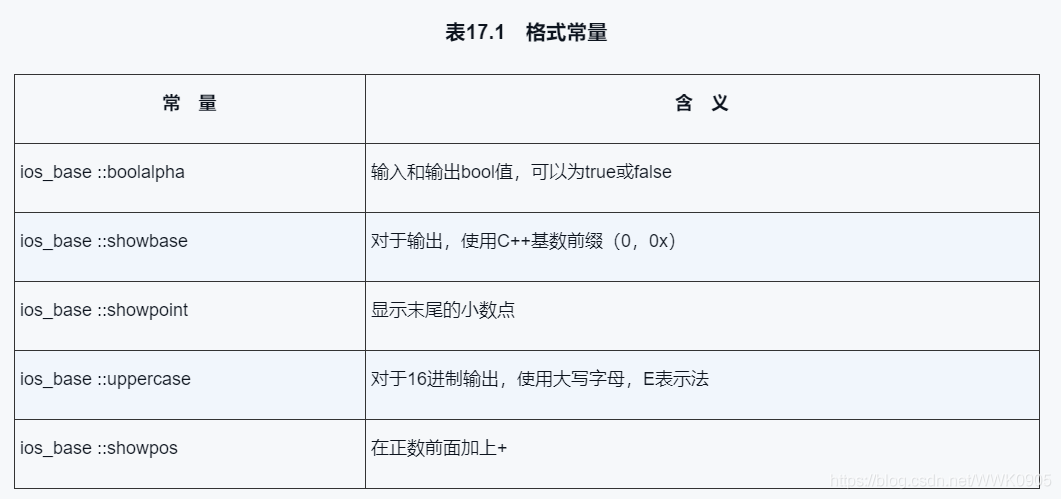
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

