详解SpringMVC学习系列之国际化
在系列(7)中我们讲了数据的格式化显示,Spring在做格式化展示的时候已经做了国际化处理,那么如何将我们网站的其它内容(如菜单、标题等)做国际化处理呢?这就是本篇要将的内容—>国际化。
一.基于浏览器请求的国际化实现:
首先配置我们项目的springservlet-config.xml文件添加的内容如下:
<bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource"> <!-- 国际化信息所在的文件名 --> <property name="basename" value="messages" /> <!-- 如果在国际化资源文件中找不到对应代码的信息,就用这个代码作为名称 --> <property name="useCodeAsDefaultMessage" value="true" /> </bean>
在com.demo.web.controllers包中添加GlobalController.java内容如下:
package com.demo.web.controllers;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContext;
import com.demo.web.models.FormatModel;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/global")
public class GlobalController {
@RequestMapping(value="/test", method = {RequestMethod.GET})
public String test(HttpServletRequest request,Model model){
if(!model.containsAttribute("contentModel")){
//从后台代码获取国际化信息
RequestContext requestContext = new RequestContext(request);
model.addAttribute("money", requestContext.getMessage("money"));
model.addAttribute("date", requestContext.getMessage("date"));
FormatModel formatModel=new FormatModel();
formatModel.setMoney(12345.678);
formatModel.setDate(new Date());
model.addAttribute("contentModel", formatModel);
}
return "globaltest";
}
}
这里展示模型还用系列(7)中的作为演示。
在项目中的源文件夹resources中添加messages.properties、messages_zh_CN.properties、messages_en_US.properties三个文件,其中messages.properties、messages_zh_CN.properties里面的"money", "date",为中文,messages_en_US.properties里面的为英文。
在views文件夹中添加globaltest.jsp视图,内容如下:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<%@taglib prefix="spring" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" %>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
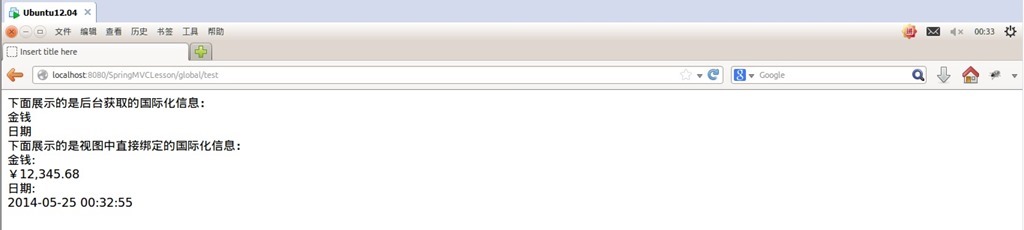
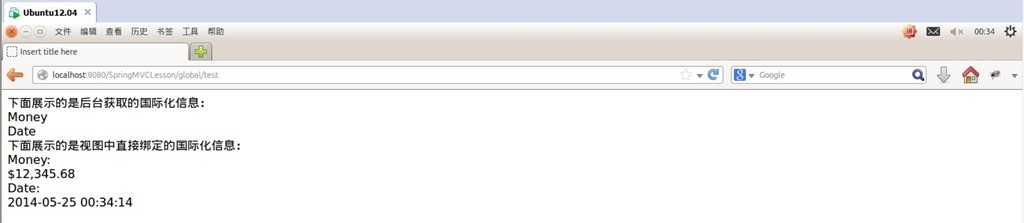
下面展示的是后台获取的国际化信息:<br/>
${money}<br/>
${date}<br/>
下面展示的是视图中直接绑定的国际化信息:<br/>
<spring:message code="money"/>:<br/>
<spring:eval expression="contentModel.money"></spring:eval><br/>
<spring:message code="date"/>:<br/>
<spring:eval expression="contentModel.date"></spring:eval><br/>
</body>
</html>
运行测试:
更改浏览器语言顺序,刷新页面:
二.基于Session的国际化实现:
在项目的springservlet-config.xml文件添加的内容如下(第一种时添加的内容要保留):
<mvc:interceptors> <!-- 国际化操作拦截器 如果采用基于(请求/Session/Cookie)则必需配置 --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.LocaleChangeInterceptor" /> </mvc:interceptors> <bean id="localeResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.SessionLocaleResolver" />
更改globaltest.jsp视图为如下内容:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<%@taglib prefix="spring" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" %>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
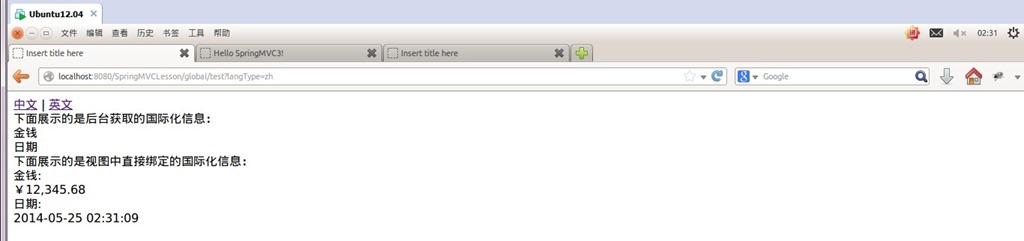
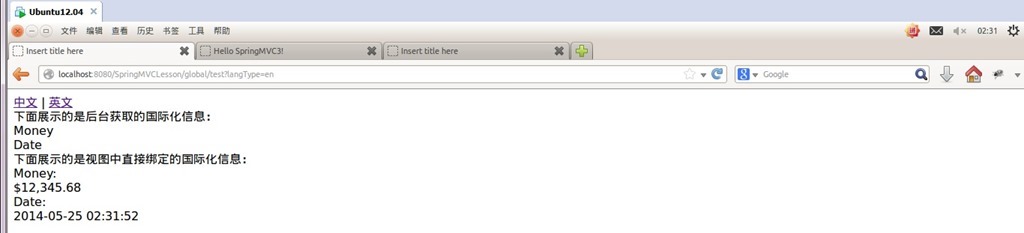
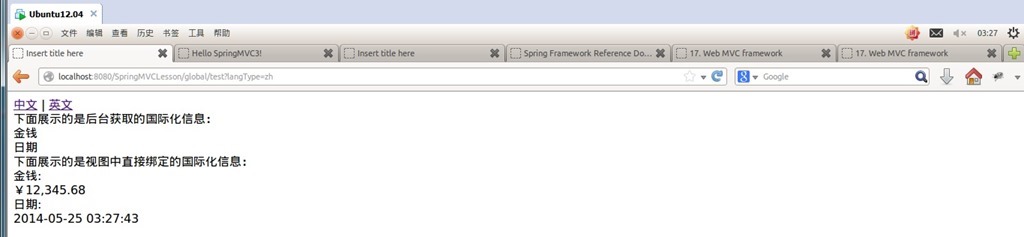
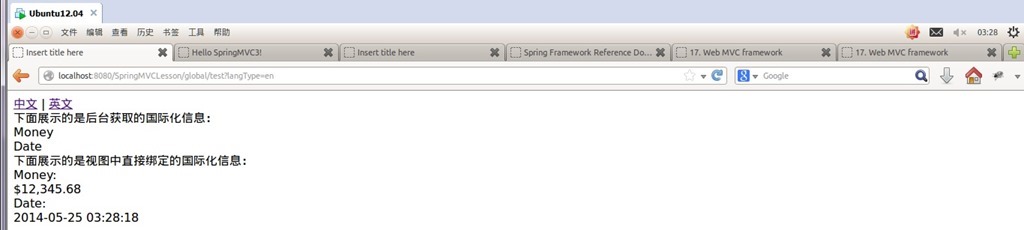
<a href="test?langType=zh" rel="external nofollow" >中文</a> | <a href="test?langType=en" rel="external nofollow" >英文</a><br/>
下面展示的是后台获取的国际化信息:<br/>
${money}<br/>
${date}<br/>
下面展示的是视图中直接绑定的国际化信息:<br/>
<spring:message code="money"/>:<br/>
<spring:eval expression="contentModel.money"></spring:eval><br/>
<spring:message code="date"/>:<br/>
<spring:eval expression="contentModel.date"></spring:eval><br/>
</body>
</html>
更改GlobalController.java为如下内容:
package com.demo.web.controllers;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Locale;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.SessionLocaleResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContext;
import com.demo.web.models.FormatModel;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/global")
public class GlobalController {
@RequestMapping(value="/test", method = {RequestMethod.GET})
public String test(HttpServletRequest request,Model model, @RequestParam(value="langType", defaultValue="zh") String langType){
if(!model.containsAttribute("contentModel")){
if(langType.equals("zh")){
Locale locale = new Locale("zh", "CN");
request.getSession().setAttribute(SessionLocaleResolver.LOCALE_SESSION_ATTRIBUTE_NAME,locale);
}
else if(langType.equals("en")){
Locale locale = new Locale("en", "US");
request.getSession().setAttribute(SessionLocaleResolver.LOCALE_SESSION_ATTRIBUTE_NAME,locale);
}
else
request.getSession().setAttribute(SessionLocaleResolver.LOCALE_SESSION_ATTRIBUTE_NAME,LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
//从后台代码获取国际化信息
RequestContext requestContext = new RequestContext(request);
model.addAttribute("money", requestContext.getMessage("money"));
model.addAttribute("date", requestContext.getMessage("date"));
FormatModel formatModel=new FormatModel();
formatModel.setMoney(12345.678);
formatModel.setDate(new Date());
model.addAttribute("contentModel", formatModel);
}
return "globaltest";
}
}
运行测试:
三.基于Cookie的国际化实现:
把实现第二种方法时在项目的springservlet-config.xml文件中添加的
<bean id="localeResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.SessionLocaleResolver" />
注释掉,并添加以下内容:
<bean id="localeResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.CookieLocaleResolver" />
更改GlobalController.java为如下内容:
package com.demo.web.controllers;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Locale;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.CookieLocaleResolver;
//import org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.SessionLocaleResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContext;
import com.demo.web.models.FormatModel;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/global")
public class GlobalController {
@RequestMapping(value="/test", method = {RequestMethod.GET})
public String test(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Model model, @RequestParam(value="langType", defaultValue="zh") String langType){
if(!model.containsAttribute("contentModel")){
/*if(langType.equals("zh")){
Locale locale = new Locale("zh", "CN");
request.getSession().setAttribute(SessionLocaleResolver.LOCALE_SESSION_ATTRIBUTE_NAME,locale);
}
else if(langType.equals("en")){
Locale locale = new Locale("en", "US");
request.getSession().setAttribute(SessionLocaleResolver.LOCALE_SESSION_ATTRIBUTE_NAME,locale);
}
else
request.getSession().setAttribute(SessionLocaleResolver.LOCALE_SESSION_ATTRIBUTE_NAME,LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());*/
if(langType.equals("zh")){
Locale locale = new Locale("zh", "CN");
//request.getSession().setAttribute(SessionLocaleResolver.LOCALE_SESSION_ATTRIBUTE_NAME,locale);
(new CookieLocaleResolver()).setLocale (request, response, locale);
}
else if(langType.equals("en")){
Locale locale = new Locale("en", "US");
//request.getSession().setAttribute(SessionLocaleResolver.LOCALE_SESSION_ATTRIBUTE_NAME,locale);
(new CookieLocaleResolver()).setLocale (request, response, locale);
}
else
//request.getSession().setAttribute(SessionLocaleResolver.LOCALE_SESSION_ATTRIBUTE_NAME,LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
(new CookieLocaleResolver()).setLocale (request, response, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
//从后台代码获取国际化信息
RequestContext requestContext = new RequestContext(request);
model.addAttribute("money", requestContext.getMessage("money"));
model.addAttribute("date", requestContext.getMessage("date"));
FormatModel formatModel=new FormatModel();
formatModel.setMoney(12345.678);
formatModel.setDate(new Date());
model.addAttribute("contentModel", formatModel);
}
return "globaltest";
}
}
运行测试:
关于<bean id="localeResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.CookieLocaleResolver" />3个属性的说明(可以都不设置而用其默认值):
<bean id="localeResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.CookieLocaleResolver"> <!-- 设置cookieName名称,可以根据名称通过js来修改设置,也可以像上面演示的那样修改设置,默认的名称为 类名+LOCALE(即:org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.CookieLocaleResolver.LOCALE--> <property name="cookieName" value="lang"/> <!-- 设置最大有效时间,如果是-1,则不存储,浏览器关闭后即失效,默认为Integer.MAX_INT--> <property name="cookieMaxAge" value="100000"> <!-- 设置cookie可见的地址,默认是“/”即对网站所有地址都是可见的,如果设为其它地址,则只有该地址或其后的地址才可见--> <property name="cookiePath" value="/"> </bean>
四.基于URL请求的国际化的实现:
首先添加一个类,内容如下:
import java.util.Locale;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver;
public class MyAcceptHeaderLocaleResolver extends AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver {
private Locale myLocal;
public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request) {
return myLocal;
}
public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Locale locale) {
myLocal = locale;
}
}
然后把实现第二种方法时在项目的springservlet-config.xml文件中添加的
<bean id="localeResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.SessionLocaleResolver" />
注释掉,并添加以下内容:
<bean id="localeResolver" class="xx.xxx.xxx.MyAcceptHeaderLocaleResolver"/>
“xx.xxx.xxx”是刚才添加的MyAcceptHeaderLocaleResolver 类所在的包名。
保存之后就可以在请求的URL后附上 locale=zh_CN 或 locale=en_US 如 http://xxxxxxxx?locale=zh_CN 来改变语言了,具体这里不再做演示了。
国际化部分的内容到此结束。
代码下载:SpringMVCi18n_jb51.rar
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。

