Python+matplotlib绘制多子图的方法详解
目录
- 本文速览
- 1、matplotlib.pyplot api 方式添加子图
- 2、面向对象方式添加子图
- 3、matplotlib.pyplot add_subplot方式添加子图
- 4、matplotlib.gridspec.GridSpec方式添加子图
- 5、子图中绘制子图
- 6、任意位置绘制子图(plt.axes)
本文速览
matplotlib.pyplot api 绘制子图
面向对象方式绘制子图
matplotlib.gridspec.GridSpec绘制子图
任意位置添加子图
关于pyplot和面向对象两种绘图方式可参考之前文章:matplotlib.pyplot api verus matplotlib object-oriented
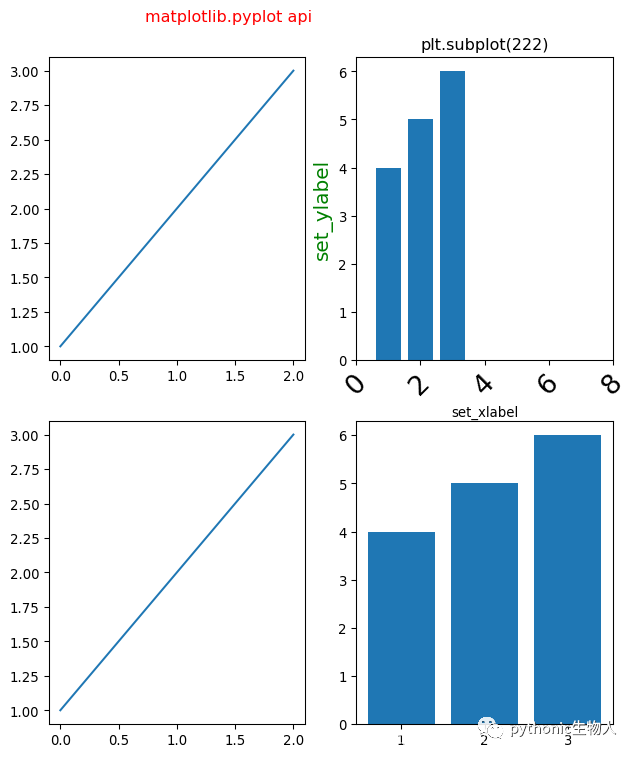
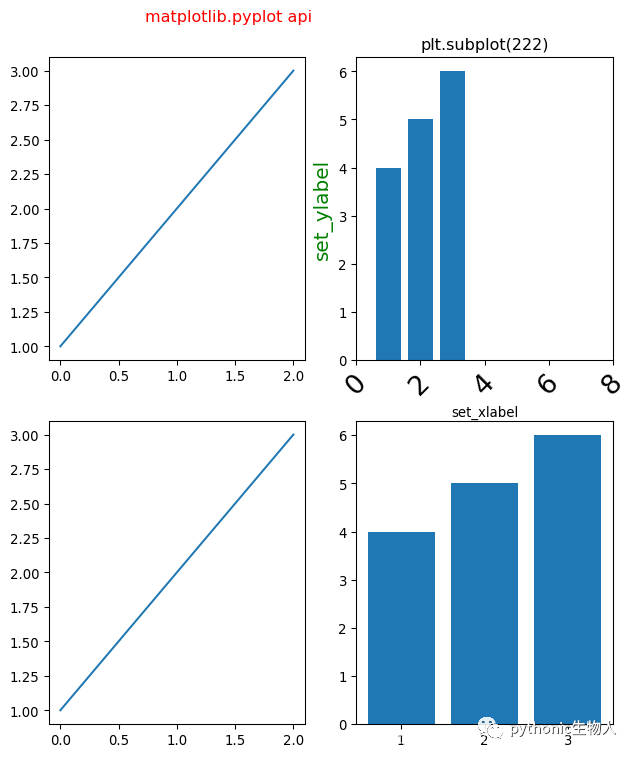
1、matplotlib.pyplot api 方式添加子图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
my_dpi=96
plt.figure(figsize=(480/my_dpi,480/my_dpi),dpi=my_dpi)
plt.subplot(221)
plt.plot([1,2,3])
plt.subplot(222)
plt.bar([1,2,3],[4,5,6])
plt.title('plt.subplot(222)')#注意比较和上面面向对象方式的差异
plt.xlabel('set_xlabel')
plt.ylabel('set_ylabel',fontsize=15,color='g')#设置y轴刻度标签
plt.xlim(0,8)#设置x轴刻度范围
plt.xticks(range(0,10,2)) # 设置x轴刻度间距
plt.tick_params(axis='x', labelsize=20, rotation=45)#x轴标签旋转、字号等
plt.subplot(223)
plt.plot([1,2,3])
plt.subplot(224)
plt.bar([1,2,3],[4,5,6])
plt.suptitle('matplotlib.pyplot api',color='r')
fig.tight_layout(rect=(0,0,1,0.9))
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.125,
bottom=-0.51,
right=1.3,
top=0.88,
wspace=0.2,
hspace=0.2
)
#plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
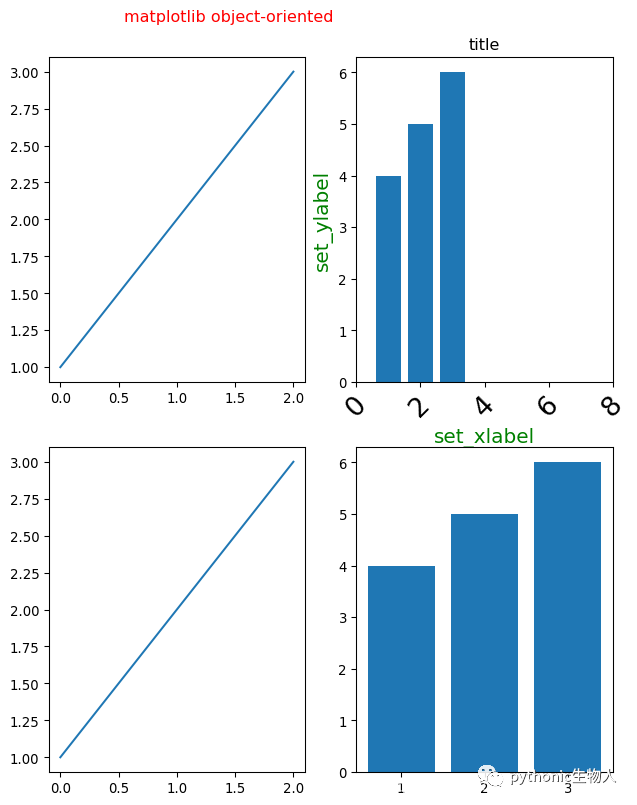
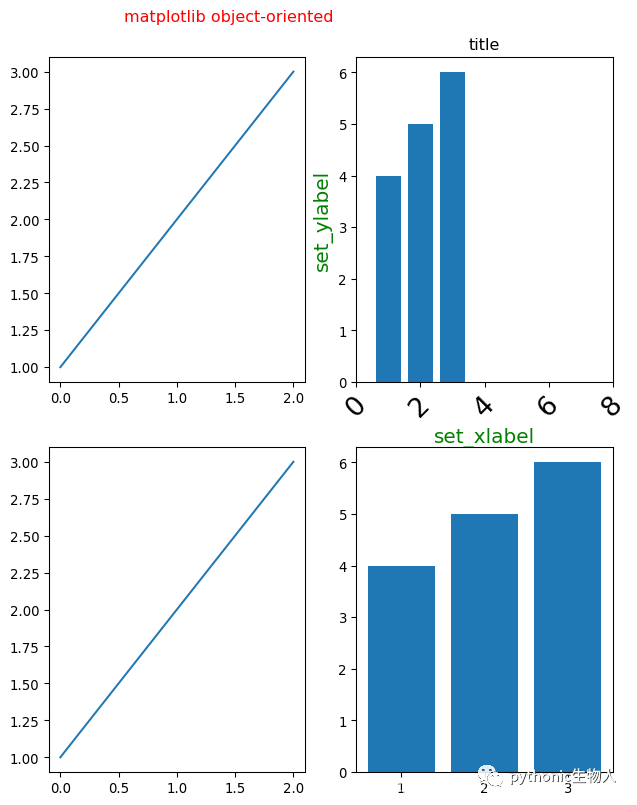
2、面向对象方式添加子图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
my_dpi=96
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2,2,figsize=(480/my_dpi,480/my_dpi),dpi=my_dpi,
sharex=False,#x轴刻度值共享开启
sharey=False,#y轴刻度值共享关闭
)
#fig为matplotlib.figure.Figure对象
#axs为matplotlib.axes.Axes,把fig分成2x2的子图
axs[0][0].plot([1,2,3])
axs[0][1].bar([1,2,3],[4,5,6])
axs[0][1].set(title='title')#设置axes及子图标题
axs[0][1].set_xlabel('set_xlabel',fontsize=15,color='g')#设置x轴刻度标签
axs[0][1].set_ylabel('set_ylabel',fontsize=15,color='g')#设置y轴刻度标签
axs[0][1].set_xlim(0,8)#设置x轴刻度范围
axs[0][1].set_xticks(range(0,10,2)) # 设置x轴刻度间距
axs[0][1].tick_params(axis='x', #可选'y','both'
labelsize=20, rotation=45)#x轴标签旋转、字号等
axs[1][0].plot([1,2,3])
axs[1][1].bar([1,2,3],[4,5,6])
fig.suptitle('matplotlib object-oriented',color='r')#设置fig即整整张图的标题
#修改子图在整个figure中的位置(上下左右)
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.125,
bottom=-0.61,
right=1.3,#防止右边子图y轴标题与左边子图重叠
top=0.88,
wspace=0.2,
hspace=0.2
)
# 参数介绍
'''
## The figure subplot parameters. All dimensions are a fraction of the figure width and height.
#figure.subplot.left: 0.125 # the left side of the subplots of the figure
#figure.subplot.right: 0.9 # the right side of the subplots of the figure
#figure.subplot.bottom: 0.11 # the bottom of the subplots of the figure
#figure.subplot.top: 0.88 # the top of the subplots of the figure
#figure.subplot.wspace: 0.2 # the amount of width reserved for space between subplots,
# expressed as a fraction of the average axis width
#figure.subplot.hspace: 0.2 # the amount of height reserved for space between subplots,
# expressed as a fraction of the average axis height
'''
plt.show()
3、matplotlib.pyplot add_subplot方式添加子图
my_dpi=96
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(480/my_dpi,480/my_dpi),dpi=my_dpi)
fig.add_subplot(221)
plt.plot([1,2,3])
fig.add_subplot(222)
plt.bar([1,2,3],[4,5,6])
plt.title('fig.add_subplot(222)')
fig.add_subplot(223)
plt.plot([1,2,3])
fig.add_subplot(224)
plt.bar([1,2,3],[4,5,6])
plt.suptitle('matplotlib.pyplot api:add_subplot',color='r')

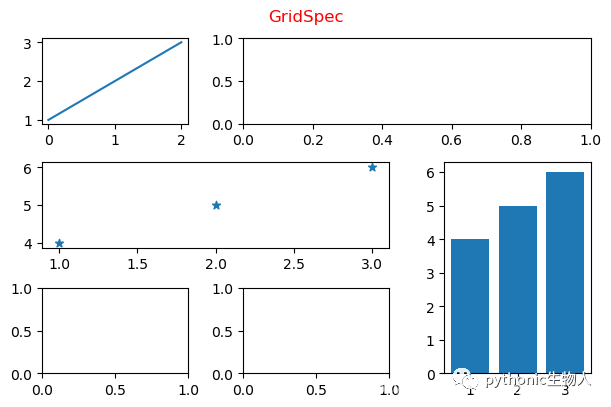
4、matplotlib.gridspec.GridSpec方式添加子图
语法:matplotlib.gridspec.GridSpec(nrows, ncols, figure=None, left=None, bottom=None, right=None, top=None, wspace=None, hspace=None, width_ratios=None, height_ratios=None)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.gridspec import GridSpec
fig = plt.figure(dpi=100,
constrained_layout=True,#类似于tight_layout,使得各子图之间的距离自动调整【类似excel中行宽根据内容自适应】
)
gs = GridSpec(3, 3, figure=fig)#GridSpec将fiure分为3行3列,每行三个axes,gs为一个matplotlib.gridspec.GridSpec对象,可灵活的切片figure
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 0:1])
plt.plot([1,2,3])
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 1:3])#gs[0, 0:3]中0选取figure的第一行,0:3选取figure第二列和第三列
#ax3 = fig.add_subplot(gs[1, 0:2])
plt.subplot(gs[1, 0:2])#同样可以使用基于pyplot api的方式
plt.scatter([1,2,3],[4,5,6],marker='*')
ax4 = fig.add_subplot(gs[1:3, 2:3])
plt.bar([1,2,3],[4,5,6])
ax5 = fig.add_subplot(gs[2, 0:1])
ax6 = fig.add_subplot(gs[2, 1:2])
fig.suptitle("GridSpec",color='r')
plt.show()

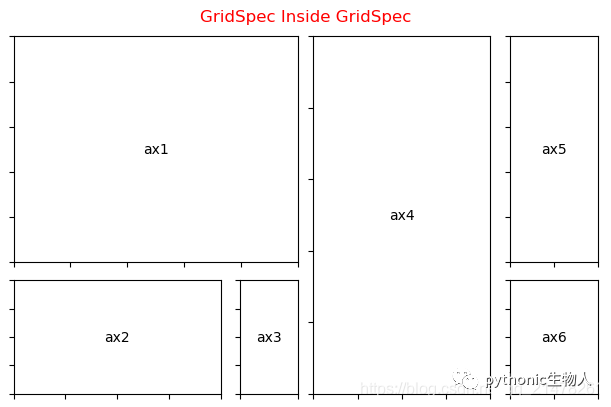
5、子图中绘制子图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec
def format_axes(fig):
for i, ax in enumerate(fig.axes):
ax.text(0.5, 0.5, "ax%d" % (i+1), va="center", ha="center")
ax.tick_params(labelbottom=False, labelleft=False)
# 子图中再绘制子图
fig = plt.figure(dpi=100,
constrained_layout=True,
)
gs0 = GridSpec(1, 2, figure=fig)#将figure切片为1行2列的两个子图
gs00 = gridspec.GridSpecFromSubplotSpec(3, 3, subplot_spec=gs0[0])#将以上第一个子图gs0[0]再次切片为3行3列的9个axes
#gs0[0]子图自由切片
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs00[:-1, :])
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs00[-1, :-1])
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(gs00[-1, -1])
gs01 = gs0[1].subgridspec(3, 3)#将以上第二个子图gs0[1]再次切片为3行3列的axes
#gs0[1]子图自由切片
ax4 = fig.add_subplot(gs01[:, :-1])
ax5 = fig.add_subplot(gs01[:-1, -1])
ax6 = fig.add_subplot(gs01[-1, -1])
plt.suptitle("GridSpec Inside GridSpec",color='r')
format_axes(fig)
plt.show()
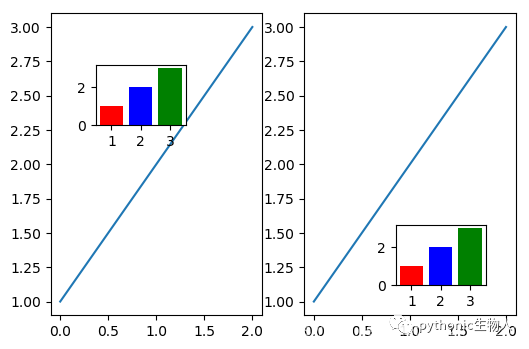
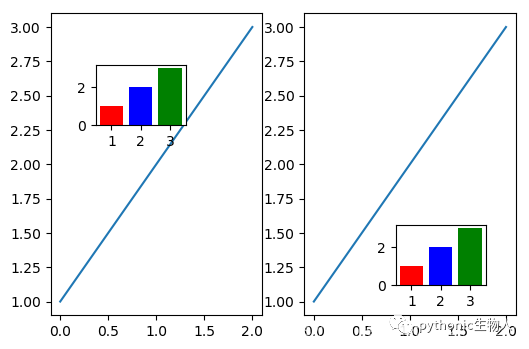
6、任意位置绘制子图(plt.axes)
plt.subplots(1,2,dpi=100) plt.subplot(121) plt.plot([1,2,3]) plt.subplot(122) plt.plot([1,2,3]) plt.axes([0.7, 0.2, 0.15, 0.15], ## [left, bottom, width, height]四个参数(fractions of figure)可以非常灵活的调节子图中子图的位置 ) plt.bar([1,2,3],[1,2,3],color=['r','b','g']) plt.axes([0.2, 0.6, 0.15, 0.15], ) plt.bar([1,2,3],[1,2,3],color=['r','b','g'])
以上就是Python+matplotlib绘制多子图的方法详解的详细内容,更多关于Python matplotlib多子图的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!
赞 (0)

