Android中初始化Codec2的具体流程
目录
- 1、MediaCodec调用流程
- 2、CCodec调用流程
- 小结:
- 3、整体时序图
1、MediaCodec调用流程
首先,我们先看下MediaCodec::CreateByType函数里面做了什么:
sp<MediaCodec> MediaCodec::CreateByType(
const sp<ALooper> &looper, const AString &mime, bool encoder, status_t *err, pid_t pid,
uid_t uid) {
sp<AMessage> format;
return CreateByType(looper, mime, encoder, err, pid, uid, format);
}
sp<MediaCodec> MediaCodec::CreateByType(
const sp<ALooper> &looper, const AString &mime, bool encoder, status_t *err, pid_t pid,
uid_t uid, sp<AMessage> format) {
Vector<AString> matchingCodecs;
MediaCodecList::findMatchingCodecs(
mime.c_str(),
encoder,
0,
format,
&matchingCodecs);
if (err != NULL) {
*err = NAME_NOT_FOUND;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < matchingCodecs.size(); ++i) {
sp<MediaCodec> codec = new MediaCodec(looper, pid, uid);
AString componentName = matchingCodecs[i];
status_t ret = codec->init(componentName);
if (err != NULL) {
*err = ret;
}
if (ret == OK) {
return codec;
}
ALOGD("Allocating component '%s' failed (%d), try next one.",
componentName.c_str(), ret);
}
return NULL;
}
CreateByType调用CreateByType的重载函数。
CreateByType(
const sp<ALooper> &looper, const AString &mime, bool encoder, status_t *err, pid_t pid,
uid_t uid, sp<AMessage> format)
里面主要是做了下面两件事:
1、查找支持的Codec。
2、根据matchingCodecs创建MediaCodec 对应的解码器调用init。
MediaCodec::init再根据创建来的名字调用mGetCodecBase这个 function
status_t MediaCodec::init(const AString &name) {
mResourceManagerProxy->init();
mInitName = name;
mCodecInfo.clear();
bool secureCodec = false;
const char *owner = "";
mCodec = mGetCodecBase(name, owner);
if (mIsVideo) {
if (mCodecLooper == NULL) {
mCodecLooper = new ALooper;
mCodecLooper->setName("CodecLooper");
mCodecLooper->start(false, false, ANDROID_PRIORITY_AUDIO);
}
mCodecLooper->registerHandler(mCodec);
} else {
mLooper->registerHandler(mCodec);
}
mLooper->registerHandler(this);
mCodec->setCallback(
std::unique_ptr<CodecBase::CodecCallback>(
new CodecCallback(new AMessage(kWhatCodecNotify, this))));
mBufferChannel = mCodec->getBufferChannel();
mBufferChannel->setCallback(
std::unique_ptr<CodecBase::BufferCallback>(
new BufferCallback(new AMessage(kWhatCodecNotify, this))));
sp<AMessage> msg = new AMessage(kWhatInit, this);
if (mCodecInfo) {
msg->setObject("codecInfo", mCodecInfo);
// name may be different from mCodecInfo->getCodecName() if we stripped
// ".secure"
}
msg->setString("name", name);
}
mGetCodecBase指向的是下列函数:
创建一个父类的对象,具体这父类对象是走Codec2还是ACodec的决定在下列函数中:
sp<CodecBase> MediaCodec::GetCodecBase(const AString &name, const char *owner) {
if (owner) {
if (strcmp(owner, "default") == 0) {
return new ACodec;
} else if (strncmp(owner, "codec2", 6) == 0) {
return CreateCCodec();
}
}
if (name.startsWithIgnoreCase("c2.")) {
return CreateCCodec();
} else if (name.startsWithIgnoreCase("omx.")) {
// at this time only ACodec specifies a mime type.
return new ACodec;
} else if (name.startsWithIgnoreCase("android.filter.")) {
return new MediaFilter;
} else {
return NULL;
}
}
如果走CCodec里面调用MediaCodec.cpp文件中:
static CodecBase *CreateCCodec() {
return new CCodec;
}
这时候就走到的CCodec这个类中,它的构造函数:
// CCodec
CCodec::CCodec()
: mChannel(new CCodecBufferChannel(std::make_shared<CCodecCallbackImpl>(this))),
mConfig(new CCodecConfig) {
}
这里的 mChannel 和 mConfig 都是new出来的。
class CCodecBufferChannel : public BufferChannelBase;
上面的 mBufferChannel = mCodec->getBufferChannel(); 就是把CCodec的mChannel返回到MediaCodec中。
std::shared_ptr<BufferChannelBase> CCodec::getBufferChannel() {
return mChannel;
}
也就是说MediaCodec调用BufferChannelBase类型的mBufferChannel 实际上是调用CCodec里面的 mChannel
mBufferChannel设置一个new 的BufferCallback()对象的。
mCodec->setCallback(
std::unique_ptr<CodecBase::CodecCallback>(
new CodecCallback(new AMessage(kWhatCodecNotify, this))));
实际上设置的是CodecBase里面的CodecCallback mCallback
struct CodecBase : public AHandler{
void setCallback(std::unique_ptr<CodecCallback> &&callback) {
mCallback = std::move(callback);
}
protected:
std::unique_ptr<CodecCallback> mCallback;
}
之后设置了BufferCallBack。
mBufferChannel->setCallback(
std::unique_ptr<CodecBase::BufferCallback>(
new BufferCallback(new AMessage(kWhatCodecNotify, this))));
实际上设置的是BufferChannelBase::BufferCallback mCallback的指针。
class BufferChannelBase {
public:
void setCallback(std::unique_ptr<CodecBase::BufferCallback> &&callback) {
mCallback = std::move(callback);
}
protected:
std::unique_ptr<CodecBase::BufferCallback> mCallback;
};
之后Init发送kWhatInit消息,处理之后就调用了CCodec->initiateAllocateComponent()。接下来我们需要看CCodec里面的调用逻辑了。
2、CCodec调用流程
CCodec的源码路径如下:
frameworks/av/media/codec2
首先看下mConfig和mChannel的定义和初始化,具体如下:
//CCodec.h
class CCodec : public CodecBase {
Mutexed<std::unique_ptr<CCodecConfig>> mConfig;
std::shared_ptr<CCodecBufferChannel> mChannel;
}
//CCodec.cpp
CCodec::CCodec()
: mChannel(new CCodecBufferChannel(std::make_shared<CCodecCallbackImpl>(this))),
mConfig(new CCodecConfig){}
构造函数初始化的时候,就创建new CCodecCallbackImpl对象出来,CCodecCallbackImpl是继承CCodecCallBack的 就做一个适配封装处理。CCodecCallbackImpl 是CCodec的友元类。
上面调用了CCodec->initiateAllocateComponent(),其实CCodec::initiateAllocateComponent 也就是发送kWhatAllocate消息。一切都交给CCodec::onMessageReceived 进行处理。在接受 onMessageReceived 中的case语句中,kWhatAllocate 调用CCodec::allocate
接着使用client = Codec2Client::CreateFromService(“default”);创建一个服务,根据传入的setAsPreferredCodec2ComponentStore 设置SetPreferredCodec2ComponentStore 默认是false.但是默认是false,这里没有传入。
这里的client = Codec2Client::CreateFromService(“default”);创建成功后调用SetPreferredCodec2ComponentStore,将vendor下支持的Codec2的server设置进来。之后将重置的mClientListener、获得的componentName名字、Codec2Client::Component的组件comp及Codec2Client::CreateFromService(“default”)返回的client,一起作为参数,再重新调用CreateComponentByName创建组件。
之后给CCodecBufferChannel mChannel设置组件,用于绑定组件的回调。
class CCodecBufferChannel : public BufferChannelBase;
接着CCodec::allocate中调用CCodecConfig::initialize、CCodecConfig::queryConfiguration、CodecCallback::onComponentAllocated函数。
具体的代码调用逻辑,如下所示:
//Codec2Client::Component : public Codec2Client::Configurable
status_t CCodecConfig::initialize(
const std::shared_ptr<C2ParamReflector> &client,
const std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client::Configurable> &configurable);
//具体CCodec::allocate的调用逻辑如下(删除不必要语句):
void CCodec::allocate(const sp<MediaCodecInfo> &codecInfo) {
if (codecInfo == nullptr) {
mCallback->onError(UNKNOWN_ERROR, ACTION_CODE_FATAL);
return;
}
ALOGD("allocate(%s)", codecInfo->getCodecName());
mClientListener.reset(new ClientListener(this));
AString componentName = codecInfo->getCodecName();
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client> client;
// set up preferred component store to access vendor store parameters
client = Codec2Client::CreateFromService("default");
if (client) {
ALOGI("setting up '%s' as default (vendor) store", client->getServiceName().c_str());
SetPreferredCodec2ComponentStore(std::make_shared<Codec2ClientInterfaceWrapper>(client));
}
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client::Component> comp;
c2_status_t status = Codec2Client::CreateComponentByName(
componentName.c_str(),
mClientListener,
&comp,
&client);
ALOGI("Created component [%s]", componentName.c_str());
mChannel->setComponent(comp);
Mutexed<std::unique_ptr<Config>>::Locked configLocked(mConfig);
const std::unique_ptr<Config> &config = *configLocked;
status_t err = config->initialize(mClient->getParamReflector(), comp);
config->queryConfiguration(comp);
mCallback->onComponentAllocated(componentName.c_str());
}
小结:
1、MediaCodec创建CCodec的对象,并用赋值给mCodec。
2、设置mCodec的CodecCallback 和 mBufferChannel的BufferCallback。
3、调用mCodec的initiateAllocateComponent,并且根据传入的codecInfo创建Service服务,并获得平台硬件编解码支持的服务。
4、根据componentName创建解码组件,并且调用数据回调类CCodecBufferChannel::setComponent设置组件。
5、调用initialize、queryConfiguration、onComponentAllocated等函数初始化。
3、整体时序图
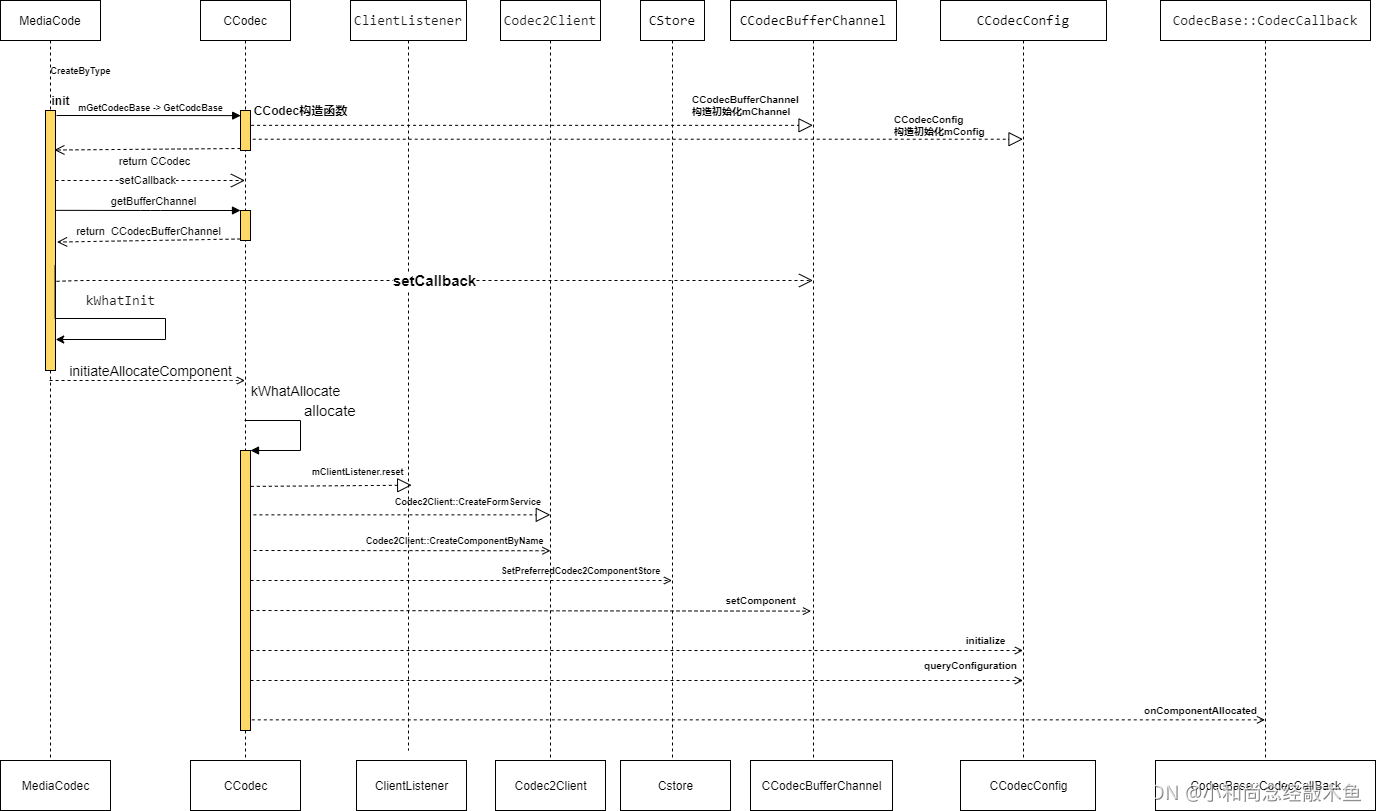
站在巨人的肩膀上!
参考连接:
1、一文搞懂Codec2框架解析
最后,如果错误,希望读者不吝赐教,共同进步!
到此这篇关于Android中初始化Codec2的具体流程的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Android Codec2内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

