pytorch中的卷积和池化计算方式详解
TensorFlow里面的padding只有两个选项也就是valid和same
pytorch里面的padding么有这两个选项,它是数字0,1,2,3等等,默认是0
所以输出的h和w的计算方式也是稍微有一点点不同的:tf中的输出大小是和原来的大小成倍数关系,不能任意的输出大小;而nn输出大小可以通过padding进行改变
nn里面的卷积操作或者是池化操作的H和W部分都是一样的计算公式:H和W的计算

class torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size, stride=None, padding=0, dilation=1, return_indices=False, ceil_mode=False): """ Parameters: kernel_size – the size of the window to take a max over stride – the stride of the window. 默认值是kernel_size padding – implicit zero padding to be added on both side,默认值是0 dilation – a parameter that controls the stride of elements in the window,默认值是1 return_indices – if True, will return the max indices along with the outputs. Useful when Unpooling later ceil_mode – when True, will use ceil instead of floor to compute the output shape,向上取整和向下取整,默认是向下取整 """
不一样的地方在于:第一点,步长stride默认值,上面默认和设定的kernel_size一样,下面默认是1;第二点,输出通道的不一样,上面的输出通道和输入通道是一样的也就是没有改变特征图的数目,下面改变特征图的数目为out_channels
class torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True):
pass
"""
Parameters:
in_channels (int) – Number of channels in the input image
out_channels (int) – Number of channels produced by the convolution
kernel_size (int or tuple) – Size of the convolving kernel
stride (int or tuple, optional) – Stride of the convolution. Default: 1,默认是1
padding (int or tuple, optional) – Zero-padding added to both sides of the input. Default: 0
dilation (int or tuple, optional) – Spacing between kernel elements. Default: 1
groups (int, optional) – Number of blocked connections from input channels to output channels. Default: 1
bias (bool, optional) – If True, adds a learnable bias to the output. Default: True
"""
第三点不一样是卷积有一个参数groups,将特征图分开给不同的卷积进行操作然后再整合到一起,xception就是利用这一个。
""" At groups=1, all inputs are convolved to all outputs. At groups=2, the operation becomes equivalent to having two conv layers side by side, each seeing half the input channels, and producing half the output channels, and both subsequently concatenated. At groups= in_channels, each input channel is convolved with its own set of filters (of size ⌊out_channelsin_channels⌋ ). """
pytorch AvgPool2d函数
class torch.nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size, stride=None, padding=0,
ceil_mode=False, count_include_pad=True):
pass
"""
kernel_size: the size of the window
stride: the stride of the window. Default value is :attr:`kernel_size`
padding: implicit zero padding to be added on both sides
ceil_mode: when True, will use `ceil` instead of `floor` to compute the output shape
count_include_pad: when True, will include the zero-padding in the averaging calculation
"""
shape的计算公式,在(h,w)位置处的输出值的计算。
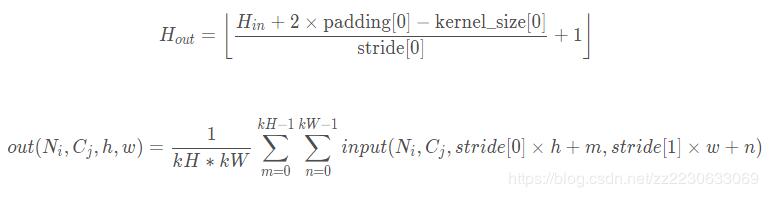
pytorch中的F.avg_pool1d()平均池化操作作用于一维,input 的维度是三维比如[2,2,7]。F.avg_pool1d()中核size是3,步长是2表示每三个数取平均,每隔两个数取一次.比如[1,3,3,4,5,6,7]安照3个数取均值,两步取一次,那么结果就是[ 2.3333 ,4 ,6 ],也就是核是一维的,也只作用于一个维度。按照池化操作计算公式input size为[2,2,7],kernel size为3,步长为2,则输出维度计算(7-3)/2+1=3所以输出维度是[2,2,3],这与输出结果是一致的。
pytorch中的F.avg_pool2d(),input 是维度是4维如[2,2,4,4],表示这里批量数是2也就是两张图像,这里通道数量是2,图像是size 是4*4的.核size是(2,2),步长是(2,2)表示被核覆盖的数取平均,横向纵向的步长都是2.那么核是二维的,所以取均值时也是覆盖二维取的。输出中第一个1.5的计算是:(1+2+1+2)/4=1.5.表示第一张图像左上角的四个像素点的均值。按照池化操作计算公式input size为[2,2,4,4],kernel size为2*2,步长为2,则输出维度计算(4-2)/2+1=2所以输出维度是[2,2,2,2],这与输出结果是一致的。
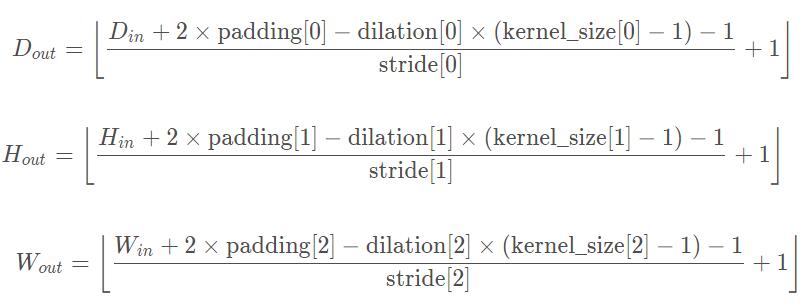
Conv3d函数
class torch.nn.Conv3d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1,
padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True):
pass
"""
in_channels (int): Number of channels in the input image
out_channels (int): Number of channels produced by the convolution
kernel_size (int or tuple): Size of the convolving kernel
stride (int or tuple, optional): Stride of the convolution. Default: 1
padding (int or tuple, optional): Zero-padding added to all three sides of the input. Default: 0
dilation (int or tuple, optional): Spacing between kernel elements. Default: 1
groups (int, optional): Number of blocked connections from input channels to output channels. Default: 1
bias (bool, optional): If ``True``, adds a learnable bias to the output. Default: ``True``
Shape:
- Input: :math:`(N, C_{in}, D_{in}, H_{in}, W_{in})`
- Output: :math:`(N, C_{out}, D_{out}, H_{out}, W_{out})`
"""
C_out = out_channels
以上这篇pytorch中的卷积和池化计算方式详解就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

