Spring Cache和EhCache实现缓存管理方式
目录
- 1、认识 Spring Cache
- 2、认识 EhCache
- 3、创建SpringBoot与MyBatis的整合项目
- 3.1 创建数据表
- 3.2 创建项目
- 4、配置EhCache缓存管理器
- 4.1 创建 ehcache.xml 配置文件
- 4.2 配置缓存管理器
- 4.3 开启缓存功能
- 5、使用EhCache实现缓存管理
- 5.1 创建实体类(Entity层)
- 5.2 数据库映射层(Mapper层)
- 5.3 业务逻辑层(Service层)
- 5.4 控制器方法(Controller层)
- 5.5 显示页面(View层)
1、认识 Spring Cache
Spring Cache是Spring提供的一整套缓存解决方案。它本身并不提供缓存实现,而是提供统一的接口和代码规范、配置、注解等,以便整合各种Cache方案,使用户不用关心Cache的细节。
Spring支持“透明”地向应用程序添加缓存,将缓存应用于方法,在方法执行前检查缓存中是否有可用的数据。这样可以减少方法执行的次数,同时提高响应的速度。缓存的应用方式“透明”,不会对调用者造成任何干扰。只要通过注解@EnableCaching启用了缓存支持,Spring Boot就会自动处理好缓存的基础配置。
Spring Cache作用在方法上。当调用一个缓存方法时,会把该方法参数和返回结果作为一个“键值对”(key / value)存放在缓存中,下次用同样的参数来调用该方法时将不再执行该方法,而是直接从缓存中获取结果进行返回。所以在使用Spring Cache时,要保证在缓存的方法和方法参数相同时返回相同的结果。
Spring Boot提供的声明式缓存(cache)注解,如下表:
| 注解 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| @EnableCaching | 开启缓存。 |
| @Cacheable | 可以作用在类和方法上,以键值对的方式缓存类或方法的返回值。 |
| @CachePut | 方法被调用,然后结果被缓存。 |
| @CacheEvict | 清空缓存。 |
| @Caching | 用来组合多个注解标签。 |
2、认识 EhCache
Spring Boot支持多种不同的缓存产品。在默认情况下使用的是简单缓存,不建议在正式环境中使用。我们可以配置一些更加强大的缓存,比如Ehcache。
Ehcache是一种广泛使用的开源Java分布式缓存,它具有内存和磁盘存储、缓存加载器、缓存扩展、缓存异常处理、GZIP缓存、Servlet 过滤器,以及支持 REST 和 SOAP API 等特点。
3、创建SpringBoot与MyBatis的整合项目
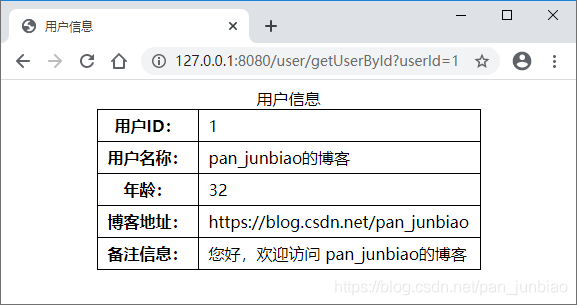
【实例】创建SpringBoot与MyBatis的整合项目,实现用户信息的查询、新增、修改、删除功能。并使用 Spring Cache 和 EhCache 实现缓存管理,执行结果如下图:
3.1 创建数据表
在MySQL数据库中创建用户信息表(tb_user),并添加数据。
-- 判断数据表是否存在,存在则删除
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS tb_user;
-- 创建“用户信息”数据表
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS tb_user
(
user_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY COMMENT '用户编号',
user_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户姓名',
age INT DEFAULT(0) NOT NULL COMMENT '年龄',
blog_url VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL COMMENT '博客地址',
blog_remark VARCHAR(50) COMMENT '博客信息'
) COMMENT = '用户信息表';
-- 添加数据
INSERT INTO tb_user(user_name,age,blog_url,blog_remark) VALUES('pan_junbiao的博客',32,'https://blog.csdn.net/pan_junbiao','您好,欢迎访问 pan_junbiao的博客');
3.2 创建项目
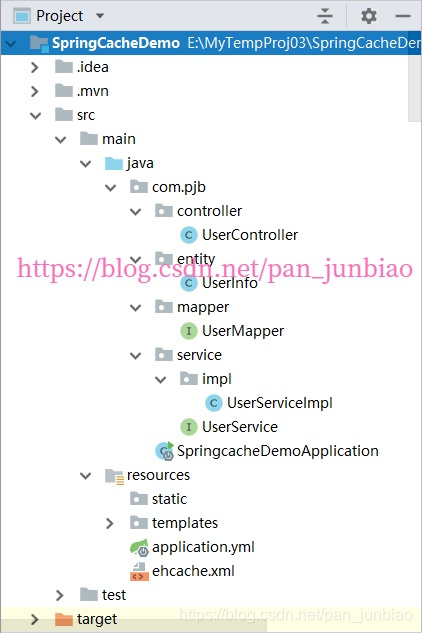
(1)创建SpringBoot项目,项目结构如下图:
(2)添加pom.xml配置信息
在pom.xml配置文件中添加MyBatis、 MySQL的JDBC数据库驱动、Spring Boot 缓存支持启动器、Ehcache 缓存等。
<!-- MyBatis与SpringBoot整合依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL的JDBC数据库驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.20</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入Thymeleaf模板引擎 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Boot缓存支持启动器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
<version>2.3.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Ehcache缓存管理器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
</dependency>
(3)配置相关信息
将默认的application.properties文件的后缀修改为“.yml”,即配置文件名称为:application.yml,并配置以下信息:
#Spring配置
spring:
#缓存管理器
cache:
type: ehcache
ehcache:
config: classpath:ehcache.xml #缓存加载配置文件
#使用Thymeleaf模板引擎
thymeleaf:
mode: HTML5
encoding: UTF-8
cache: false #使用Thymeleaf模板引擎,关闭缓存
servlet:
content-type: text/html
#DataSource数据源
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_admin?useSSL=false&
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
#MyBatis配置
mybatis:
type-aliases-package: com.pjb.entity #别名定义
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl #指定 MyBatis 所用日志的具体实现,未指定时将自动查找
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true #开启自动驼峰命名规则(camel case)映射
lazy-loading-enabled: true #开启延时加载开关
aggressive-lazy-loading: false #将积极加载改为消极加载(即按需加载),默认值就是false
#lazy-load-trigger-methods: "" #阻挡不相干的操作触发,实现懒加载
cache-enabled: true #打开全局缓存开关(二级环境),默认值就是true
4、配置EhCache缓存管理器
4.1 创建 ehcache.xml 配置文件
在 resources (资源目录)下,创建 ehcache.xml 配置文件,配置信息如下:
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="../config/ehcache.xsd">
<!-- 这个是磁盘存储路径,当内存缓存满了的时候,就会往这里面放,
java.io.tmdir是操作系统缓存的临时目录,不同操作系统缓存目录不一样 -->
<diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/>
<!--defaultCache:echcache的默认缓存策略 -->
<defaultCache
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="120"
timeToLiveSeconds="120"
maxElementsOnDisk="10000000"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU">
<persistence strategy="localTempSwap"/>
</defaultCache>
<cache name="userCache"
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="120"
timeToLiveSeconds="120"
maxElementsOnDisk="10000000"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU">
<persistence strategy="localTempSwap"/>
</cache>
</ehcache>
配置属性说明:
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| <diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/> | 这个是磁盘存储路径,当内存缓存满了的时候,就会往这里面放,java.io.tmdir是操作系统缓存的临时目录,不同操作系统缓存目录不一样。 |
| maxElementsInMemory | 内存缓存中最多可以存放的元素数量,若放入Cache中的元素超过这个数值,则有以下两种情况: (1)若 overflowToDisk=true,则会将Cache中多出的元素放入磁盘文件中。 (2)若 overflowToDisk=false,则根据memoryStoreEvictionPolicy策略替换Cache中原有的元素。 |
| overflowToDisk | 内存不足时,是否启用磁盘缓存。 |
| eternal | 缓存中对象是否永久有效。 |
| timeToIdleSeconds | 缓存数据在失效前的允许闲置时间(单位:秒),仅当 eternal=false 时使用,默认值是0表示可闲置时间无穷大,若超过这个时间没有访问此Cache中的某个元素,那么此元素将被从Cache中清除。 |
| timeToLiveSeconds | 缓存数据的总的存活时间(单位:秒),仅当 eternal=false 时使用,从创建开始计时,失效结束。 |
| maxElementsOnDisk | 磁盘缓存中最多可以存放的元素数量,0表示无穷大。 |
| diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds | 磁盘缓存的清理线程运行间隔,默认是120秒。 |
| memoryStoreEvictionPolicy | 内存存储与释放策略,即达到 maxElementsInMemory 限制时,Ehcache会根据指定策略清理内存,共有三种策略,分别为LRU(最近最少使用)、LFU(最常用的)、FIFO(先进先出)。 |
| defaultCache | 默认缓存方式。 |
| cache | 自定义的缓存方式,自行设置 name。 |
4.2 配置缓存管理器
在 application.yml 配置文件中配置目标缓存管理器,支持 Ehcache、Generic、Redis、Jcache等。这里配置使用Ehcache。
#Spring配置
spring:
#缓存管理器
cache:
type: ehcache
ehcache:
config: classpath:ehcache.xml #缓存加载配置文件
4.3 开启缓存功能
在SpringBoot项目启动入口类中添加注解@EnableCaching,开启缓存功能。
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class SpringcacheDemoApplication
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SpringApplication.run(SpringcacheDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
5、使用EhCache实现缓存管理
5.1 创建实体类(Entity层)
在com.pjb.entity包中,创建UserInfo类(用户信息实体类)。
package com.pjb.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* 用户信息实体类
* @author pan_junbiao
**/
public class UserInfo implements Serializable
{
private int userId; //用户编号
private String userName; //用户姓名
private int age; //年龄
private String blogUrl; //博客地址
private String blogRemark; //博客信息
//省略getter与setter方法...
}
注意:实体类必须实现 Serializable 接口,否则无法实现缓存功能。
5.2 数据库映射层(Mapper层)
在com.pjb.mapper包中,创建UserMapper接口(用户信息Mapper动态代理接口)。
package com.pjb.mapper;
import com.pjb.entity.UserInfo;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
/**
* 用户信息Mapper动态代理接口
* @author pan_junbiao
**/
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface UserMapper
{
/**
* 根据用户ID,获取用户信息
*/
@Select("SELECT * FROM tb_user WHERE user_id = #{userId}")
public UserInfo getUserById(int userId);
/**
* 新增用户,并获取自增主键
*/
@Insert("INSERT INTO tb_user(user_name,age,blog_url,blog_remark) VALUES(#{userName},#{age},#{blogUrl},#{blogRemark});")
@Options(useGeneratedKeys = true, keyColumn = "user_id", keyProperty = "userId")
public int insertUser(UserInfo userInfo);
/**
* 修改用户
*/
@Update("UPDATE tb_user SET user_name = #{userName} ,age = #{age} ,blog_url = #{blogUrl} ,blog_remark = #{blogRemark} WHERE user_id = #{userId}")
public int updateUser(UserInfo userInfo);
/**
* 删除用户
*/
@Delete("DELETE FROM tb_user WHERE user_id = #{userId}")
public int deleteUser(int userId);
}
5.3 业务逻辑层(Service层)
在com.pjb.service包下,创建UserService接口(用户信息业务逻辑接口)。
package com.pjb.service;
import com.pjb.entity.UserInfo;
/**
* 用户信息业务逻辑接口
* @author pan_junbiao
**/
public interface UserService
{
/**
* 根据用户ID,获取用户信息
*/
public UserInfo getUserById(int userId);
/**
* 新增用户,并获取自增主键
*/
public UserInfo insertUser(UserInfo userInfo);
/**
* 修改用户
*/
public UserInfo updateUser(UserInfo userInfo);
/**
* 删除用户
*/
public int deleteUser(int userId);
}
在com.pjb.service.impl包下,创建UserServiceImpl类(用户信息业务逻辑类)。
package com.pjb.service.impl;
import com.pjb.entity.UserInfo;
import com.pjb.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.pjb.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheConfig;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* 用户信息业务逻辑类
* @author pan_junbiao
**/
//注意:必须对应配置文件ehcache.xml中cache节点的name属性值
//@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "userCache")
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService
{
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
//注意:必须对应配置文件ehcache.xml中cache节点的name属性值
private static final String CACHE_NAME = "userCache";
/**
* 根据用户ID,获取用户信息
*/
@Override
@Cacheable(value = CACHE_NAME, key = "#userId")
public UserInfo getUserById(int userId)
{
return userMapper.getUserById(userId);
}
/**
* 新增用户,并获取自增主键
*/
@Override
@CachePut(value = CACHE_NAME, key = "#userInfo.userId")
public UserInfo insertUser(UserInfo userInfo)
{
userMapper.insertUser(userInfo);
return userInfo;
}
/**
* 修改用户
*/
@Override
@CachePut(value = CACHE_NAME, key = "#userInfo.userId")
public UserInfo updateUser(UserInfo userInfo)
{
userMapper.updateUser(userInfo);
return userInfo;
}
/**
* 删除用户
*/
@Override
@CacheEvict(value = CACHE_NAME, key = "#userId")
public int deleteUser(int userId)
{
return userMapper.deleteUser(userId);
}
}
从上述代码可以看出,查询用户的方法使用了 @Cacheable 注解来开启缓存。添加和修改方法使用了 @CachePut 注解,它是先处理方法,然后把结果进行缓存的。要想删除数据,则需要使用 @CacheEvict 注解来清空缓存。
@CacheConfig注解:如果所有的 @Cacheable() 里面都有一个 value=“xxx” 的属性,这显然如果方法多了,写起来也是挺累的,如果可以一次性声明完 那就省事了,所以有了 @CacheConfig 这个配置,@CacheConfig is a class-level annotation that allows to share the cache names,如果你在方法写别的名字,那么依然以方法的名字为准。
5.4 控制器方法(Controller层)
在com.pjb.controller包中,创建UserController类(用户控制器),实现用户数据的查询、新增、修改、删除,并实现数据的返回。
package com.pjb.controller;
import com.pjb.entity.UserInfo;
import com.pjb.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
/**
* 用户信息控制器
* @author pan_junbiao
**/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController
{
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
/**
* 获取用户信息
*/
@RequestMapping("getUserById")
public ModelAndView getUserById(int userId)
{
//根据用户ID,获取用户信息
UserInfo userInfo = userService.getUserById(userId);
if(userInfo==null)
{
userInfo = new UserInfo();
}
//返回结果
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("userInfo",userInfo);
modelAndView.setViewName("/user-info.html");
return modelAndView;
}
/**
* 新增用户
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("insertUser")
public boolean insertUser()
{
//创建新用户
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUserName("pan_junbiao的博客");
userInfo.setAge(32);
userInfo.setBlogUrl("https://blog.csdn.net/pan_junbiao");
userInfo.setBlogRemark("您好,欢迎访问 pan_junbiao的博客");
//执行新增方法
userService.insertUser(userInfo);
//返回结果
return userInfo.getUserId() > 0 ? true : false;
}
/**
* 修改用户
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("updateUser")
public boolean updateUser(int userId)
{
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUserId(userId);
userInfo.setUserName("pan_junbiao的博客_02");
userInfo.setAge(35);
userInfo.setBlogUrl("https://blog.csdn.net/pan_junbiao");
userInfo.setBlogRemark("您好,欢迎访问 pan_junbiao的博客");
//执行修改方法
userService.updateUser(userInfo);
//返回结果
return true;
}
/**
* 删除用户
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("deleteUser")
public boolean deleteUser(int userId)
{
//执行新增方法
int result = userService.deleteUser(userId);
//返回结果
return result > 0 ? true : false;
}
}
5.5 显示页面(View层)
在 resources/templates 目录下,创建 user-info.html 用户信息显示页面。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>用户信息</title>
<meta name="author" content="pan_junbiao的博客">
<style>
table { border-collapse: collapse; margin-bottom: 10px}
table,table tr th, table tr td { border:1px solid #000000; padding: 5px 10px;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div align="center">
<table>
<caption>用户信息</caption>
<tr>
<th>用户ID:</th>
<td th:text="${userInfo.userId}"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>用户名称:</th>
<td th:text="${userInfo.userName}"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>年龄:</th>
<td th:text="${userInfo.age}"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>博客地址:</th>
<td th:text="${userInfo.blogUrl}"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>备注信息:</th>
<td th:text="${userInfo.blogRemark}"></td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</body>
</html>
至此,项目已经编写完成,执行结果如下图:
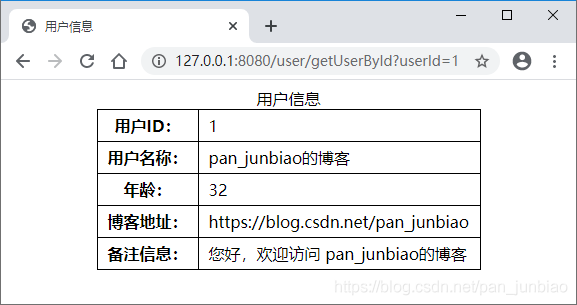
接着运行项目的其他方法,然后多次访问查询方法的URL,体验缓存效果。主要观察数据库是否进行了操作,如果数据库没有操作数据而正常返回数据,则代表缓存成功。
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

