Pandas统计计数value_counts()的使用
value_counts()方法返回一个序列Series,该序列包含每个值的数量(对于数据框中的任何列,value_counts()方法会返回该列每个项的计数)
value_counts()是Series拥有的方法,一般在DataFrame中使用时,需要指定对哪一列进行使用
语法
value_counts(values,
sort=True,
ascending=False,
normalize=False,
bins=None,
dropna=True)
参数说明
- sort: 是否要进行排序(默认进行排序,取值为True)
- ascending: 默认降序排序(取值为False),升序排序取值为True
- normalize: 是否要对计算结果进行标准化,并且显示标准化后的结果,默认是False
- bins: 可以自定义分组区间,默认是否
- dropna: 是否包括对NaN进行计数,默认不包括
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame({'City': ['北京', '广州', '深圳', '上海', '大连', '成都', '深圳', '厦门', '北京', '北京', '上海', '珠海'],
'Revenue': [10000, 10000, 5000, 5000, 40000, 50000, 8000, 5000, 5000, 5000, 10000, 12000],
'Age': [50, 43, 34, 40, 25, 25, 45, 32, 25, 25, 34, np.nan]})
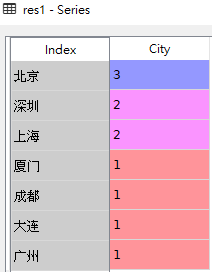
# 1.查看'City'这一列的计数结果(对给定列里面的每个值进行计数并进行降序排序,缺失值nan也会被排除)
# value_counts()并不是未带任何参数,而是所有参数都是默认的
res1 = df['City'].value_counts()
# 2.查看'Revenue'这一列的计数结果(采用升序的方式)
res2 = df['Revenue'].value_counts(ascending=True)
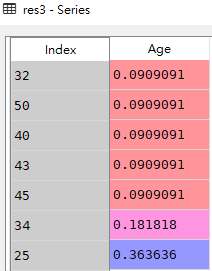
# 3.查看'Age'这一列的计数占比(使用标准化normalize=True)
res3 = df['Age'].value_counts(ascending=True,normalize=True)
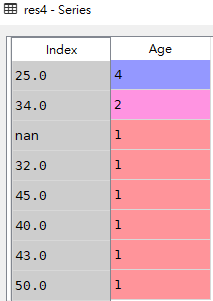
# 4.查看'Age'这一列的计数结果(展示NaN值的计数)
res4 = df['Age'].value_counts(dropna=False)
# 5.查看'Age'这一列的计数结果(不展示NaN值的计数)
# res5 = df['Age'].value_counts()
res5 = df['Age'].value_counts(dropna=True)
df

res1
res2

res3
res4
res5

到此这篇关于Pandas统计计数value_counts()的使用的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Pandas统计计数value_counts()内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!
赞 (0)

