对numpy中轴与维度的理解
NumPy's main object is the homogeneous multidimensional array. It is a table of elements (usually numbers), all of the same type, indexed by a tuple of positive integers. In NumPy dimensions are called axes. The number of axes is rank.
For example, the coordinates of a point in 3D space [1, 2, 1] is an array of rank 1, because it has one axis. That axis has a length of 3. In the example pictured below, the array has rank 2 (it is 2-dimensional). The first dimension (axis) has a length of 2, the second dimension has a length of 3.
[[ 1., 0., 0.], [ 0., 1., 2.]]
ndarray.ndim
数组轴的个数,在python的世界中,轴的个数被称作秩
>> X = np.reshape(np.arange(24), (2, 3, 4))
# 也即 2 行 3 列的 4 个平面(plane)
>> X
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]],
[[12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23]]])
shape函数是numpy.core.fromnumeric中的函数,它的功能是读取矩阵的长度,比如shape[0]就是读取矩阵第一维度的长度。
shape(x)
(2,3,4)
shape(x)[0]
2
或者
x.shape[0]
2
再来分别看每一个平面的构成:
>> X[:, :, 0]
array([[ 0, 4, 8],
[12, 16, 20]])
>> X[:, :, 1]
array([[ 1, 5, 9],
[13, 17, 21]])
>> X[:, :, 2]
array([[ 2, 6, 10],
[14, 18, 22]])
>> X[:, :, 3]
array([[ 3, 7, 11],
[15, 19, 23]])
也即在对 np.arange(24)(0, 1, 2, 3, ..., 23) 进行重新的排列时,在多维数组的多个轴的方向上,先分配最后一个轴(对于二维数组,即先分配行的方向,对于三维数组即先分配平面的方向)
reshpae,是数组对象中的方法,用于改变数组的形状。
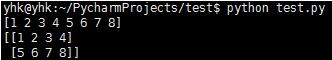
二维数组
#!/usr/bin/env python # coding=utf-8 import numpy as np a=np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]) print a d=a.reshape((2,4)) print d
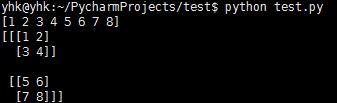
三维数组
#!/usr/bin/env python # coding=utf-8 import numpy as np a=np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]) print a f=a.reshape((2, 2, 2)) print f
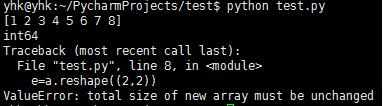
形状变化的原则是数组元素不能发生改变,比如这样写就是错误的,因为数组元素发生了变化。
#!/usr/bin/env python # coding=utf-8 import numpy as np a=np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]) print a print a.dtype e=a.reshape((2,2)) print e
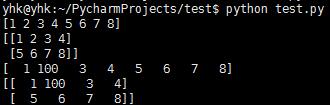
注意:通过reshape生成的新数组和原始数组公用一个内存,也就是说,假如更改一个数组的元素,另一个数组也将发生改变。
#!/usr/bin/env python # coding=utf-8 import numpy as np a=np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]) print a e=a.reshape((2, 4)) print e a[1]=100 print a print e
Python中reshape函数参数-1的意思
a=np.arange(0, 60, 10) >>>a array([0,10,20,30,40,50]) >>>a.reshape(-1,1) array([[0], [10], [20], [30], [40], [50]])
如果写成a.reshape(1,1)就会报错
ValueError:cannot reshape array of size 6 into shape (1,1)
>>> a = np.array([[1,2,3], [4,5,6]])
>>> np.reshape(a, (3,-1)) # the unspecified value is inferred to be 2
array([[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[5, 6]])
-1表示我懒得计算该填什么数字,由python通过a和其他的值3推测出来。
# 下面是两张2*3大小的照片(不知道有几张照片用-1代替),如何把所有二维照片给摊平成一维
>>> image = np.array([[[1,2,3], [4,5,6]], [[1,1,1], [1,1,1]]])
>>> image.shape
(2, 2, 3)
>>> image.reshape((-1, 6))
array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]])
以上这篇对numpy中轴与维度的理解就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

