TensorFlow2基本操作之 张量排序 填充与复制 查找与替换
目录
- 张量排序
- tf.sort
- tf.argsort
- tf.math.top_k
- 填充与复制
- tf.pad
- tf.tile
- 查找与替换
- tf.where (第一种)
- tf.where (第二种)
- tf.scatter_nd
张量排序

tf.sort
tf.sort函数可以帮我们对张量进行排序.
格式:
tf.sort(
values, axis=-1, direction='ASCENDING', name=None
)
参数:
- values: 要进行排序的张量
- axis: 操作维度
- direction: 正序或者倒序
- name: 数据名称
例子:
# 创建张量0~9, 并打乱顺序 a = tf.random.shuffle(tf.range(10)) print(a) # 从小到大 b = tf.sort(a) # direction="ASCENDING" print(b) # 从大到小 c = tf.sort(a, direction="DESCENDING") print(c)
输出结果:
tf.Tensor([6 3 7 5 4 0 2 9 8 1], shape=(10,), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor([0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9], shape=(10,), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor([9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0], shape=(10,), dtype=int32)
tf.argsort
tf.argsort返回张量的索引排序, 沿给的轴排序.
格式:
tf.argsort(
values, axis=-1, direction='ASCENDING', stable=False, name=None
)
参数:
- 要进行排序的张量
- axis: 操作维度
- direction: 正序或者倒序
- stable: 如果为 True, 则原始张量中的相等元素将不会按返回的顺序重新排序
- name: 数据名称
例子:
# 创建张量0~9, 并打乱顺序 a = tf.random.shuffle(tf.range(10)) print(a) # 从小到大 b = tf.argsort (a) print(b) # 从大到小 c = tf.argsort (a, direction="DESCENDING") print(c)
输出结果:
tf.Tensor([9 4 3 1 2 6 0 5 7 8], shape=(10,), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor([6 3 4 2 1 7 5 8 9 0], shape=(10,), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor([0 9 8 5 7 1 2 4 3 6], shape=(10,), dtype=int32)
tf.math.top_k
tf.math.top_k可以帮助我们查找最后一个维度的 k 个最大条目的值和索引.
格式:
tf.math.top_k(
input, k=1, sorted=True, name=None
)
参数:
- input: 传入张量
- k=1: 前 k 位
- sorted: 是否排序
- name: 数据名称
例子:
# 创建张量0~9, 并打乱顺序, 形状为 3*3 a = tf.reshape(tf.random.shuffle(tf.range(9)), [3, 3]) print(a) # 取top2 b = tf.math.top_k(a, 2) print(b)
输出结果:
tf.Tensor(
[[2 1 4]
[5 7 0]
[8 6 3]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=int32)
TopKV2(values=<tf.Tensor: shape=(3, 2), dtype=int32, numpy=
array([[4, 2],
[7, 5],
[8, 6]])>, indices=<tf.Tensor: shape=(3, 2), dtype=int32, numpy=
array([[2, 0],
[1, 0],
[0, 1]])>)
填充与复制
tf.pad
tf.pad可以帮我们对一个 tensor 四周进行填充.

格式:
tf.pad(
tensor, paddings, mode='CONSTANT', constant_values=0, name=None
)
参数:
- tensor: 传入的张量
- paddings: 要扩展的维度
- mode: 模式, 默认为 “CONSTANT”
- constant_value: 在 “CONSTANT” 模式下, 要使用的标量填充值 (必须与张量类型相同)
- name: 数据名称
例子:
# pad a = tf.reshape(tf.range(9), [3, 3]) print(a) # 上下左右填充一圈0 b = tf.pad(a, [[1, 1], [1, 1]]) print(b)
输出结果:
tf.Tensor(
[[0 1 2]
[3 4 5]
[6 7 8]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(
[[0 0 0 0 0]
[0 0 1 2 0]
[0 3 4 5 0]
[0 6 7 8 0]
[0 0 0 0 0]], shape=(5, 5), dtype=int32)
tf.tile
tf.tile可以帮助我们实现 tensor 的复制.
格式:
tf.tile(
input, multiples, name=None
)
参数:
- input: 传入的张量
- multiples: 复制的次数
- name: 数据名称
例子:
# tile a = tf.reshape(tf.range(9), [3, 3]) print(a) b = tf.tile(a, [2, 2]) print(b)
输出结果:
tf.Tensor(
[[0 1 2]
[3 4 5]
[6 7 8]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(
[[0 1 2 0 1 2]
[3 4 5 3 4 5]
[6 7 8 6 7 8]
[0 1 2 0 1 2]
[3 4 5 3 4 5]
[6 7 8 6 7 8]], shape=(6, 6), dtype=int32)
查找与替换

tf.where (第一种)
返回元素为 True 的位置.
格式:
tf.where(
condition, name=None
)
参数:
- condition: 判断条件
- name: 数据名称
例子:
# 第一种用法(单参数) mask = tf.constant([[True, True, True], [False, True, True], [True, False, False]]) print(mask) indices = tf.where(mask) print(indices)
输出结果:
tf.Tensor(
[[ True True True]
[False True True]
[ True False False]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=bool)
tf.Tensor(
[[0 0]
[0 1]
[0 2]
[1 1]
[1 2]
[2 0]], shape=(6, 2), dtype=int64)
tf.where (第二种)
类似三元运算符的用法.
格式:
tf.where(
condition, x=None, y=None, name=None
)
参数:
- condition: 判断条件
- x: 如果条件为 True 赋值
- y: 如果条件为 False 赋值
- name: 数据名称
例子:
# 第二种用法(三个参数) zeros = tf.zeros([3, 3]) print(zeros) ones = tf.ones([3, 3]) print(ones) mask = tf.constant([[True, True, True], [False, True, True], [True, False, False]]) print(mask) result = tf.where(mask, zeros, ones) print(result)
输出结果:
tf.Tensor(
[[0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0.]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor(
[[1. 1. 1.]
[1. 1. 1.]
[1. 1. 1.]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor(
[[ True True True]
[False True True]
[ True False False]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=bool)
tf.Tensor(
[[0. 0. 0.]
[1. 0. 0.]
[0. 1. 1.]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=float32)
tf.scatter_nd
使用索引更新张量.
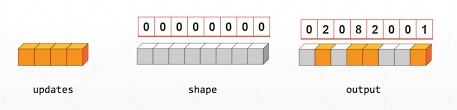
格式:
tf.scatter_nd(
indices, updates, shape, name=None
)
参数:
- indices: 索引
- updates: 更新的值
- shape: 形状
- name: 数据名称
例子:
# scatter_nd indices = tf.constant([[4], [3], [1], [7]]) print(indices) updates = tf.constant([9, 10, 11, 12]) print(updates) shape = tf.constant([8]) print(shape) result = tf.scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape) print(result)
输出结果:
tf.Tensor(
[[4]
[3]
[1]
[7]], shape=(4, 1), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor([ 9 10 11 12], shape=(4,), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor([8], shape=(1,), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor([ 0 11 0 10 9 0 0 12], shape=(8,), dtype=int32)
到此这篇关于TensorFlow2基本操作之 张量排序 填充与复制 查找与替换的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关TensorFlow2基本操作内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

