java8从list集合中取出某一属性的值的集合案例
我就废话不多说了,大家还是直接看代码吧~
List<Order> list = new ArrayList<User>();
Order o1 = new Order("1","MCS-2019-1123");
list.add(o1 );
Order o2= new Order("2","MCS-2019-1124");
list.add(o2);
Order o3= new Order("3","MCS-2019-1125");
list.add(o3);
List<String> orderNoList=list.stream().map(Order::getOrderNo).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("输出单号集合:"+orderNoList);
List<String> idList=list.stream().map(Order::getId()).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(idList)
结果
输出第一个:
["MCS-2019-1123", "MCS-2019-1124", "MCS-2019-1125"]
[1, 2, 3]
order类:
public class Order{
String id;
String orderNo;
public Order(String id, String orderNo) {
this.id = id;
this.orderNo= orderNo;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String order) {
this.id= id;
}
public String getOrderNo() {
return orderNo;
}
public void setOrderNo(String message) {
this.orderNo= orderNo;
}
}
补充知识:java8快速对list集合的筛选计算取值总结
在我们日常开发过程中,有很多场景需要对list集合进行取值筛选,以下是我对常用的一些知识点进行总结
首先,创建一个需要用到的对象,例如学生对象,有相关字段:姓名,年龄,性别
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
public Student( String name, int age,String sex) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
}
其次,对这些字段属性进行赋值
Student s1 = new Student("小金",20,"女");
Student s2 = new Student("小宋",21,"女");
Student s3 = new Student("小张",25,"男");
Student s4 = new Student("小王",27,"男");
Student s5 = new Student("小王",30,"未知");
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(s1);
list.add(s2);
list.add(s3);
list.add(s4);
list.add(s5);
1、遍历-foreach
使用stream流进行foreach遍历
list.stream().forEach(student->{
//处理逻辑,打印出所有学生的姓名
System.out.println(student.getName());
});
运行结果:

2、筛选list
filter函数的()里,应该放逻辑,判断条件,将符合条件的放到resultList中
代码如下,筛选集合中所有性别为女的学生
List<Student> resultList = list.stream().filter(student -> Objects.equals(student.getSex(),"女")).collect(Collectors.toList());
resultList.stream().forEach(student->{
System.out.println(student.getName());
});
运行结果:

3、list去重
根据性别去重
List<Student> unique = list.stream().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(
Collectors.toCollection(() -> new TreeSet<>(Comparator.comparing(Student::getSex))), ArrayList::new));
unique.stream().forEach(student->{
System.out.println(student.getName());
});
运行结果:

4、取出list集合对象中某一个属性
取出每个对象中的姓名组成一个新的集合
List<String> listStr = list.stream().map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());
去重
List<String> listNew = listStr .stream().map(Student::getName).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
运行结果:

5、list与map互转,并根据某一属性进行分组
list转map (下方studentMap运行会报错,因为作为key值,name不能重复,所以正式开发中应该使用唯一性id作为key值)
Map<String, Student> studentMap = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Student::getName, student -> student));
list转数组
String[] listStrs = list.stream()
.filter(e -> Objects.equals(e.getSex(), "男"))
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(Student::getName))
.map(Student::getName).toArray(String[]::new);
list转map并且分组
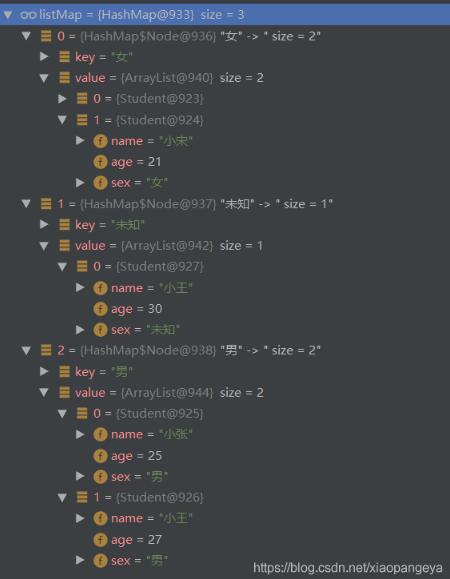
Map<String, List<Student>> listMap = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getSex));
运行结果:
根据对象某些属性,进行分组
Map<List, List> studentsMap= list.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(f -> Arrays.asList(f.getAge),f.getSex())));
map转list
List<Student> collect = studentMap.values().stream().collect(Collectors.toList());
6、过滤属性为空的字段
Student s6 = new Student("",30,"男");
list.add(s6);
List<String> stringList = list.stream().map(s -> s.getName()).filter(s -> !s.isEmpty()).collect(Collectors.toList());
7、根据某一属性进行计算
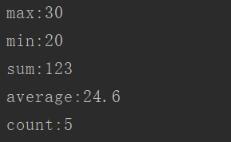
根据年龄求最大值、最小值、平均值、总和、个数
IntSummaryStatistics resultNum = list.stream().mapToInt((item)->item.getAge()).summaryStatistics();
System.out.println("max:"+resultNum.getMax());
System.out.println("min:"+resultNum.getMin());
System.out.println("sum:"+resultNum.getSum());
System.out.println("average:"+resultNum.getAverage());
System.out.println("count:"+resultNum.getCount());
运行结果:
注意:
1、求和有三种类型,mapToInt,mapToLong,mapToDouble
2、如果是Bigdecimal数值类型,则计算方法如下,(新建对象)
Frult frult1 = new Frult("西瓜",new BigDecimal(1));
Frult frult2 = new Frult("梨子",new BigDecimal(2));
List<Frult> frultList = new ArrayList<>();
frultList.add(frult1);
frultList.add(frult2);
BigDecimal totalPrice = frultList.stream().map(Frult::getPrice).reduce(BigDecimal.ZERO, BigDecimal::add);
//或者用mapToInt()进行强转(int->Bigdecimal)
结语:本人目前用到这么多,希望各位有更好的或者其它的用法给予建议与评论,有错误也希望能得到指正!也希望大家多多支持我们。

