ASP.Net Core中使用枚举类而不是枚举的方法
前言:
我相信大家在编写代码时经常会遇到各种状态值,而且为了避免硬编码和代码中出现魔法数,通常我们都会定义一个枚举,来表示各种状态值,直到我看到Java中这样使用枚举,我再想C# 中可不可以这样写,今天就分享一下我的感悟。
一、通常我们是这样使用枚举的
(1)switch中使用枚举
public enum EmployeeType
{
Manager,
Servant,
AssistantToTheRegionalManager
}
public class Employee
{
public EmployeeType Type { get; set; }
public decimal Bonus { get; set; }
}
static void ProcessBonus(Employee employee)
{
switch (employee.Type)
{
case EmployeeType.Manager:
employee.Bonus = 1000m;
break;
case EmployeeType.Servant:
employee.Bonus = 0.01m;
break;
case EmployeeType.AssistantToTheRegionalManager:
employee.Bonus = 1.0m;
break;
default:
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException();
}
}
在没有进某唐时我也是这样的写的,代码很烂,违法了开闭原则,扩展性极差。在代码规范中是不允许出现这样的写法的。对于上面的写法可以使用设计模式来重构。后面会继续更新设计模式的文章。
(2)类型转换
EnumTricks.IsVolumeHigh((Volume)27); EnumTricks.High((int)Medium);
二、枚举的不好之处
关于枚举的MSDN文档说了什么:
“The enum keyword is used to declare an enumeration, a distinct type that consists of a set of named constants called the enumerator list. Every enumeration type has an underlying type, which can be any integral type except char. The default underlying type of the enumeration elements is int. By default, the first enumerator has the value 0, and the value of each successive enumerator is increased by 1.
(1)没有类型安全
枚举是简单的值类型,可以提供对无效值的保护,并且不会出现任何行为。他们是有用的,因为他们是魔法数字的改进,但就是这样。如果要约束类型可能的值,枚举不一定能帮助您,因为仍然可以提供无效类型。例如,此枚举有三个值,默认情况下将具有int类型。值范围为1到3。
public enum Volume
{
Low = 1,
Medium,
High
}
public static class EnumTricks
{
public static bool IsVolumeHigh(Volume volume)
{
var result = false;
switch (volume)
{
case Volume.Low:
Console.WriteLine("Volume is low.");
break;
case Volume.Medium:
Console.WriteLine("Volume is medium.");
break;
case Volume.High:
Console.WriteLine("Volume is high.");
result = true;
break;
}
return result;
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
EnumTricks.IsVolumeHigh((Volume)27);
Console.ReadKey();
}
public static class EnumTricks
{
public static bool IsVolumeHigh(Volume volume)
{
var result = false;
switch (volume)
{
case Volume.Low:
Console.WriteLine("Volume is low.");
break;
case Volume.Medium:
Console.WriteLine("Volume is medium.");
break;
case Volume.High:
Console.WriteLine("Volume is high.");
result = true;
break;
}
return result;
}
public static int EnumToInt(Volume volume)
{
return (int)volume;
}
public static Volume IntToEnum(int intValue)
{
return (Volume)intValue;
}
public static Volume StringToEnum(string stringValue)
{
return (Volume)Enum.Parse(typeof(Volume), stringValue);
}
public static int StringToInt(string stringValue)
{
var volume = StringToEnum(stringValue);
return EnumToInt(volume);
}
public static string EnumToString(Volume volume)
{
return volume.ToString();
}
}
这应该失败,至少在运行时。它没有。这真的很奇怪......在编译期间或运行期间都不会检测到错误的调用。你会觉得自己处于一个虚假的安全状态。如果,我们把传进去的枚举转换为string时,来看看这两种情况有什么不同:
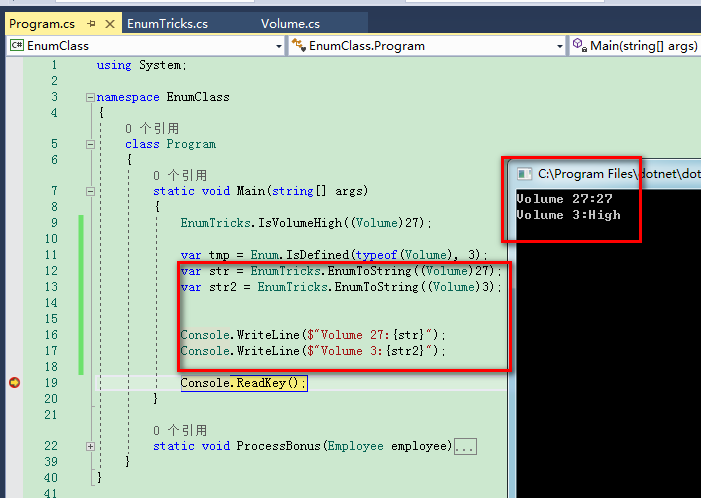
我不知道大家平时在使用枚举的时候,是否有意识检查传入的是否是有效的值。可以使用Enum.IsDefined()来检查int值是否是一个有效的值
解决方案:如果int值在枚举值的定义范围内,则使用Enum.IsDefined()查找。如果在范围内,则返回True,否则返回False。
(2)转化
您是否尝试过将enum转换为int,int转换为enum,string转换为enum,将字符串转换为enum的int值?如下代码:
public static class EnumTricks
{
public static bool IsVolumeHigh(Volume volume)
{
var result = false;
switch (volume)
{
case Volume.Low:
Console.WriteLine("Volume is low.");
break;
case Volume.Medium:
Console.WriteLine("Volume is medium.");
break;
case Volume.High:
Console.WriteLine("Volume is high.");
result = true;
break;
}
return result;
}
public static int EnumToInt(Volume volume)
{
return (int)volume;
}
public static Volume IntToEnum(int intValue)
{
return (Volume)intValue;
}
public static Volume StringToEnum(string stringValue)
{
return (Volume)Enum.Parse(typeof(Volume), stringValue);
}
public static int StringToInt(string stringValue)
{
var volume = StringToEnum(stringValue);
return EnumToInt(volume);
}
}
是不是我们日常的代码中也有这样的类型转换代码,不是说不好,只是类型转换也是有性能损失的,如果能换中方式可以同样实现而且还避免以上问题岂不是更好,这样我们的代码也更好维护和扩展,下面我们通过使用枚举类的方式来解决这个问题。
三、使用枚举类而不是枚举类型
public class Enumeration: IComparable
{
private readonly int _value;
private readonly string _displayName;
protected Enumeration()
{
}
protected Enumeration(int value, string displayName)
{
_value = value;
_displayName = displayName;
}
public int Value
{
get { return _value; }
}
public string DisplayName
{
get { return _displayName; }
}
public override string ToString()
{
return DisplayName;
}
public static IEnumerable<T> GetAll<T>() where T : Enumeration, new()
{
var type = typeof(T);
var fields = type.GetFields(BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.Static | BindingFlags.DeclaredOnly);
foreach (var info in fields)
{
var instance = new T();
var locatedValue = info.GetValue(instance) as T;
if (locatedValue != null)
{
yield return locatedValue;
}
}
}
public override bool Equals(object obj)
{
var otherValue = obj as Enumeration;
if (otherValue == null)
{
return false;
}
var typeMatches = GetType().Equals(obj.GetType());
var valueMatches = _value.Equals(otherValue.Value);
return typeMatches && valueMatches;
}
public override int GetHashCode()
{
return _value.GetHashCode();
}
public static int AbsoluteDifference(Enumeration firstValue, Enumeration secondValue)
{
var absoluteDifference = Math.Abs(firstValue.Value - secondValue.Value);
return absoluteDifference;
}
public static T FromValue<T>(int value) where T : Enumeration, new()
{
var matchingItem = parse<T, int>(value, "value", item => item.Value == value);
return matchingItem;
}
public static T FromDisplayName<T>(string displayName) where T : Enumeration, new()
{
var matchingItem = parse<T, string>(displayName, "display name", item => item.DisplayName == displayName);
return matchingItem;
}
private static T parse<T, K>(K value, string description, Func<T, bool> predicate) where T : Enumeration, new()
{
var matchingItem = GetAll<T>().FirstOrDefault(predicate);
if (matchingItem == null)
{
var message = string.Format("'{0}' is not a valid {1} in {2}", value, description, typeof(T));
throw new ApplicationException(message);
}
return matchingItem;
}
public int CompareTo(object other)
{
return Value.CompareTo(((Enumeration)other).Value);
}
}
public class Volume: Enumeration
{
private Volume() { throw new Exception(""); }
private Volume(int value, string displayName): base(value, displayName) { }
public static readonly Volume Low = new Volume(1, nameof(Low).ToLowerInvariant());
public static readonly Volume Medium = new Volume(2, nameof(Medium).ToLowerInvariant());
public static readonly Volume High = new Volume(3, nameof(High).ToLowerInvariant());
public static IEnumerable<Volume> List() =>
new[] { Low, Medium, High };
public static Volume From(int value)
{
var state = List().SingleOrDefault(s => s.Value == value);
if (state == null)
{
throw new Exception($"Possible values for Volume: {String.Join(",", List().Select(s => s.Value))}");
}
return state;
}
public static Volume FromName(string name)
{
var state = List()
.SingleOrDefault(s => String.Equals(s.DisplayName, name, StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase));
if (state == null)
{
throw new Exception($"Possible values for Volume: {String.Join(",", List().Select(s => s.DisplayName))}");
}
return state;
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//EnumTricks.IsVolumeHigh((Volume)27);
//var tmp = Enum.IsDefined(typeof(Volume), 3);
//var str = EnumTricks.EnumToString((Volume)27);
//var str2 = EnumTricks.EnumToString((Volume)3);
//Console.WriteLine($"Volume 27:{str}");
//Console.WriteLine($"Volume 3:{str2}");
Console.WriteLine("------------------------------------------------------------");
Console.WriteLine(Volume.High.Value);
Console.WriteLine(Volume.High.DisplayName);
var volume = Volume.From(2);
var volume2 = Volume.FromName("high");
var none = Volume.From(27);
Console.ReadKey();
}
四、应用
代码如下:
Error文件下:
public interface ICommonError
{
int GetErrCode();
string GetErrMsg();
ICommonError SetErrMsg(string errMsg);
}
public class Enumeration : IComparable
{
private readonly int _value;
private readonly string _displayName;
protected Enumeration()
{
}
protected Enumeration(int value, string displayName)
{
_value = value;
_displayName = displayName;
}
public int Value
{
get { return _value; }
}
public string DisplayName
{
get { return _displayName; }
}
public override string ToString()
{
return DisplayName;
}
public static IEnumerable<T> GetAll<T>() where T : Enumeration, new()
{
var type = typeof(T);
var fields = type.GetFields(BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.Static | BindingFlags.DeclaredOnly);
foreach (var info in fields)
{
var instance = new T();
var locatedValue = info.GetValue(instance) as T;
if (locatedValue != null)
{
yield return locatedValue;
}
}
}
public override bool Equals(object obj)
{
var otherValue = obj as Enumeration;
if (otherValue == null)
{
return false;
}
var typeMatches = GetType().Equals(obj.GetType());
var valueMatches = _value.Equals(otherValue.Value);
return typeMatches && valueMatches;
}
public override int GetHashCode()
{
return _value.GetHashCode();
}
public static int AbsoluteDifference(Enumeration firstValue, Enumeration secondValue)
{
var absoluteDifference = Math.Abs(firstValue.Value - secondValue.Value);
return absoluteDifference;
}
public static T FromValue<T>(int value) where T : Enumeration, new()
{
var matchingItem = parse<T, int>(value, "value", item => item.Value == value);
return matchingItem;
}
public static T FromDisplayName<T>(string displayName) where T : Enumeration, new()
{
var matchingItem = parse<T, string>(displayName, "display name", item => item.DisplayName == displayName);
return matchingItem;
}
private static T parse<T, K>(K value, string description, Func<T, bool> predicate) where T : Enumeration, new()
{
var matchingItem = GetAll<T>().FirstOrDefault(predicate);
if (matchingItem == null)
{
var message = string.Format("'{0}' is not a valid {1} in {2}", value, description, typeof(T));
throw new ApplicationException(message);
}
return matchingItem;
}
public int CompareTo(object other)
{
return Value.CompareTo(((Enumeration)other).Value);
}
}
public class EmBusinessError : Enumeration, ICommonError
{
private int errCode;
private String errMsg;
public static readonly EmBusinessError parameterValidationError = new EmBusinessError(10001, "参数不合法");
private EmBusinessError() { throw new Exception("私有构造函数不能调用"); }
private EmBusinessError(int value, string displayName) : base(value, displayName) {
this.errCode = value;
this.errMsg = displayName;
}
public int GetErrCode()
{
return this.errCode;
}
public string GetErrMsg()
{
return this.errMsg;
}
public void SetErrCode(int errCode)
{
this.errCode = errCode;
}
public ICommonError SetErrMsg(string errMsg)
{
this.errMsg = errMsg;
return this;
}
}
//包装器业务异常类实现
public class BusinessException : Exception, ICommonError
{
private ICommonError commonError;
//直接接收EmBusinessError的传参用于构造业务异常
public BusinessException(ICommonError commonError):base()
{
this.commonError = commonError;
}
public BusinessException(ICommonError commonError, string errMsg):base()
{
this.commonError = commonError;
this.commonError.SetErrMsg(errMsg);
}
public int GetErrCode()
{
return this.commonError.GetErrCode();
}
public string GetErrMsg()
{
return this.commonError.GetErrMsg();
}
public ICommonError SetErrMsg(string errMsg)
{
this.commonError.SetErrMsg(errMsg);
return this;
}
public ICommonError GetCommonError()
{
return commonError;
}
}
异常中间件:
public class ExceptionHandlerMiddleWare
{
private readonly RequestDelegate next;
/// <summary>
///
/// </summary>
/// <param name="next"></param>
public ExceptionHandlerMiddleWare(RequestDelegate next)
{
this.next = next;
}
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
try
{
await next(context);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
await HandleExceptionAsync(context, ex);
}
}
private static async Task HandleExceptionAsync(HttpContext context, Exception exception)
{
if (exception == null) return;
await WriteExceptionAsync(context, exception).ConfigureAwait(false);
}
private static async Task WriteExceptionAsync(HttpContext context, Exception exception)
{
var response = context.Response;
response.ContentType = "application/json;charset=utf-8";
var result = new CommonReturnType();
if (exception is BusinessException)
{
var businessException = (BusinessException)exception;
var errModel = new { errCode= businessException.GetErrCode(), errMsg= businessException.GetErrMsg() };
result = CommonReturnType.Create(errModel, "fail");
}
await response.WriteAsync(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(new { data = result.GetData(), status = result.GetStatus() }) ).ConfigureAwait(false);
}
}
Response文件夹:
public class CommonReturnType
{
//表明对应请求的返回处理结果 "success" 或 "fail"
private string status;
//若status=success,则data内返回前端需要的json数据
//若status=fail,则data内使用通用的错误码格式
private object data;
//定义一个通用的创建方法
public static CommonReturnType Create(object result)
{
return CommonReturnType.Create(result, "success");
}
public static CommonReturnType Create(object result, string status)
{
CommonReturnType type = new CommonReturnType();
type.SetStatus(status);
type.SetData(result);
return type;
}
public string GetStatus()
{
return status;
}
public void SetStatus(string status)
{
this.status = status;
}
public object GetData()
{
return data;
}
public void SetData(object data)
{
this.data = data;
}
}
最后推荐一个类库,这是我在Nuget上发现的枚举类库,地址:https://github.com/ardalis/SmartEnum
好了,先分享到这里,希望对你有帮助和启发。
参考资料:
(2)https://ardalis.com/enum-alternatives-in-c
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,谢谢大家对我们的支持。

