Keras搭建自编码器操作
简介:
传统机器学习任务任务很大程度上依赖于好的特征工程,但是特征工程往往耗时耗力,在视频、语音和视频中提取到有效特征就更难了,工程师必须在这些领域有非常深入的理解,并且需要使用专业算法提取这些数据的特征。深度学习则可以解决人工难以提取有效特征的问题,大大缓解机器学习模型对特征工程的依赖。
深度学习在早期一度被认为是一种无监督的特征学习过程,模仿人脑对特征逐层抽象的过程。这其中两点很重要:一是无监督学习;二是逐层训练。例如在图像识别问题中,假定我们有许多汽车图片,要如何利用计算机进行识别任务呢?如果从像素级开始进行训练分类器,那么绝大多数算法很难工作。如果我们提取高阶特征,比如汽车的车轮、汽车的车窗、车身等。那么就可以使用这些高阶特征非常准确的对图像进行分类。不过高阶特征都是由底层特征组成,这便是深度学习训练过程中所做的特征学习。
早年有学者发现,可以使用少量的基本特征进行组合拼装得到更高层抽象的特征,这其实就是我们常说的特征的稀疏表达。对图像任务来说,一张原始图片可以由较少的图片碎片组合得到。对语音识别任务来讲,绝大多数的声音也可以由一些基本的结构线性组合得到。对人脸识别任务来说,根据不同的器官,如:鼻子、嘴、眉毛、眼睛瞪,这些器官可以向上拼出不同样式的人脸,最后模型通过在图片中匹配这些不同样式的人脸来进行识别。在深度神经网络中,对每一层神经网络来说前一层的输出都是未加工的像素,而这一层则是对像素进行加工组织成更高阶的特征的过程(即前面提到过的图片碎片进行线性组合加工的过程)。
根据上述基本概念的描述,特征是可以不断抽象转为高一层特征的,那我们如何找到这些基本结构,然后如何抽象?这里引出无监督的自编码器来提取特征。自编码器--顾名思义,可以使用自身高阶特征编码自己。它的输入和输出是一致的。因此,它的基本思想是使用稀疏一些高阶特征重新组合来重构自己。自编码器的刚开始提出是Hinton在Science上发表文章,用来解决数据降维问题。此外,Hinton还提出了基于深度信念网络的无监督逐层训练的贪心算法,为训练很深的网络提供了一个可行的方案。深度信念网络的提出是使用逐层训练的方式提取特征,使得在有监督学习任务之前,使得网络权重初始化到一个比较好的位置。其思想与自编码器的非常相似。在此基础上,国内外学者又提出了自编码器的各种版本,如:稀疏自编码器、去噪自编码器等。
本文使用Keras深度学习开发库,在MNIST数据集上实现了简单自编码器、深度稀疏自编码器和卷积自编码器。
自编码器用途:
目前自编码器的应用主要有两个方面,第一是数据去噪,第二是为进行可视化而降维。配合适当的维度和稀疏约束,自编码器可以学习到比PCA等技术更有意思的数据投影。此外,在数据共有特征建模方面,也有叫广泛的应用。
1、简单自编码器
简单自编码器
from keras.layers import Input, Dense
from keras.models import Model
from keras.datasets import mnist
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
(x_train, _), (x_test, _) = mnist.load_data()
x_train = x_train.astype('float32') / 255.
x_test = x_test.astype('float32') / 255.
x_train = x_train.reshape((len(x_train), np.prod(x_train.shape[1:])))
x_test = x_test.reshape((len(x_test), np.prod(x_test.shape[1:])))
print(x_train.shape)
print(x_test.shape)
encoding_dim = 32
input_img = Input(shape=(784,))
encoded = Dense(encoding_dim, activation='relu')(input_img)
decoded = Dense(784, activation='sigmoid')(encoded)
autoencoder = Model(inputs=input_img, outputs=decoded)
encoder = Model(inputs=input_img, outputs=encoded)
encoded_input = Input(shape=(encoding_dim,))
decoder_layer = autoencoder.layers[-1]
decoder = Model(inputs=encoded_input, outputs=decoder_layer(encoded_input))
autoencoder.compile(optimizer='adadelta', loss='binary_crossentropy')
autoencoder.fit(x_train, x_train, epochs=50, batch_size=256,
shuffle=True, validation_data=(x_test, x_test))
encoded_imgs = encoder.predict(x_test)
decoded_imgs = decoder.predict(encoded_imgs)
n = 10 # how many digits we will display
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 4))
for i in range(n):
ax = plt.subplot(2, n, i + 1)
plt.imshow(x_test[i].reshape(28, 28))
plt.gray()
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
ax = plt.subplot(2, n, i + 1 + n)
plt.imshow(decoded_imgs[i].reshape(28, 28))
plt.gray()
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.show()
测试效果:

2、深度自编码器、稀疏自编码器
为解决自编码重构损失大的问题,使用多层网络搭建自编码器。对隐层单元施加稀疏性约束的话,会得到更为紧凑的表达,只有一小部分神经元会被激活。在Keras中,我们可以通过添加一个activity_regularizer达到对某层激活值进行约束的目的
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(1337) # for reproducibility
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.models import Model #泛型模型
from keras.layers import Dense, Input
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# X shape (60,000 28x28), y shape (10,000, )
(x_train, _), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
# 数据预处理
x_train = x_train.astype('float32') / 255. # minmax_normalized
x_test = x_test.astype('float32') / 255. # minmax_normalized
x_train = x_train.reshape((x_train.shape[0], -1))
x_test = x_test.reshape((x_test.shape[0], -1))
print(x_train.shape)
print(x_test.shape)
# 压缩特征维度至2维
encoding_dim = 2
# this is our input placeholder
input_img = Input(shape=(784,))
# 编码层
encoded = Dense(128, activation='relu')(input_img)
encoded = Dense(64, activation='relu')(encoded)
encoded = Dense(10, activation='relu')(encoded)
encoder_output = Dense(encoding_dim)(encoded)
# 解码层
decoded = Dense(10, activation='relu')(encoder_output)
decoded = Dense(64, activation='relu')(decoded)
decoded = Dense(128, activation='relu')(decoded)
decoded = Dense(784, activation='tanh')(decoded)
# 构建自编码模型
autoencoder = Model(inputs=input_img, outputs=decoded)
# 构建编码模型
encoder = Model(inputs=input_img, outputs=encoder_output)
# compile autoencoder
autoencoder.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='mse')
autoencoder.summary()
encoder.summary()
# training
autoencoder.fit(x_train, x_train, epochs=10, batch_size=256, shuffle=True)
# plotting
encoded_imgs = encoder.predict(x_test)
plt.scatter(encoded_imgs[:, 0], encoded_imgs[:, 1], c=y_test,s=3)
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
decoded_imgs = autoencoder.predict(x_test)
# use Matplotlib (don't ask)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
n = 10 # how many digits we will display
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 4))
for i in range(n):
# display original
ax = plt.subplot(2, n, i + 1)
plt.imshow(x_test[i].reshape(28, 28))
plt.gray()
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
# display reconstruction
ax = plt.subplot(2, n, i + 1 + n)
plt.imshow(decoded_imgs[i].reshape(28, 28))
plt.gray()
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.show()
运行结果:
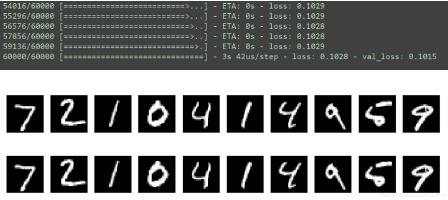
3、卷积自编码器
卷积自编码器的编码器部分由卷积层和MaxPooling层构成,MaxPooling负责空域下采样。而解码器由卷积层和上采样层构成。
from keras.layers import Input, Dense, Convolution2D, MaxPooling2D, UpSampling2D
from keras.models import Model
from keras.datasets import mnist
import numpy as np
(x_train, _), (x_test, _) = mnist.load_data()
x_train = x_train.astype('float32') / 255.
x_test = x_test.astype('float32') / 255.
print('---> x_train shape: ', x_train.shape)
x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (len(x_train), 28, 28, 1))
x_test = np.reshape(x_test, (len(x_test), 28, 28, 1))
print('---> xtrain shape: ', x_train.shape)
print('---> x_test shape: ', x_test.shape)
input_img = Input(shape=(28, 28, 1))
x = Convolution2D(16, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(input_img)
x = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), padding='same')(x)
x = Convolution2D(8, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)
x = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), padding='same')(x)
x = Convolution2D(8, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)
encoded = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), padding='same')(x)
x = Convolution2D(8, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(encoded)
x = UpSampling2D((2, 2))(x)
x = Convolution2D(8, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)
x = UpSampling2D((2, 2))(x)
x = Convolution2D(16, (3, 3), activation='relu')(x)
x = UpSampling2D((2, 2))(x)
decoded = Convolution2D(1, (3, 3), activation='sigmoid', padding='same')(x)
autoencoder = Model(inputs=input_img, outputs=decoded)
autoencoder.compile(optimizer='adadelta', loss='binary_crossentropy')
# 打开一个终端并启动TensorBoard,终端中输入 tensorboard --logdir=/autoencoder
autoencoder.fit(x_train, x_train, epochs=10, batch_size=256,
shuffle=True, validation_data=(x_test, x_test))
decoded_imgs = autoencoder.predict(x_test)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
decoded_imgs = autoencoder.predict(x_test)
n = 10
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 4))
for i in range(1, n+1):
# display original
ax = plt.subplot(2, n, i)
plt.imshow(x_test[i].reshape(28, 28))
plt.gray()
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
# display reconstruction
ax = plt.subplot(2, n, i + n)
plt.imshow(decoded_imgs[i].reshape(28, 28))
plt.gray()
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.show()
训练结果展示:

以上这篇Keras搭建自编码器操作就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

