浅谈C#中Action和Func回调的常用方式
目录
- 一、简介
- 二、Action
- 例1
- 例2
- 三、Func
- 例1
- 例2
- 结束
一、简介
Action和Func泛型委托实际上就是一个.NET Framework预定义的委托,3.5引入的特性。基本涵盖了所有常用的委托,所以一般不用用户重新声明。Action系列泛型委托,是没有返回参数的委托,最多可以有16参数,也可以没有参数。
Func系列的委托是有返回值的委托,最多可以有16个参数;元组是C# 4.0引入的一个新特性,编写的时候需要基于.NET Framework 4.0或者更高版本。元组使用泛型来简化一个类的定义.提供用于创造元组对象的静态方法。最多可以提供创建新的 8 元组,即八元组。
二、Action
委托其实就是把方法当作参数来调用,Action就是其中之一,Action 作为参数不能有返回值,参数可以是任意类型,也可以不传递参数。
例1
调用某个类中的Action
using System;
namespace Test1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Test1 test1 = new Test1();
test1.myAction();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public class Test1
{
public Action myAction = null;
private void sayHi()
{
Console.WriteLine("fuck you!");
}
public Test1()
{
myAction = sayHi;
}
}
}
运行:

这种方式用的比较少,Action常用的方式通常是用来作为和回调
例2
执行一系列的操作后,再执行回调,也是比较推荐的使用方式。
using System;
namespace Test1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Test1 test1 = new Test1();
test1.Calculation(1, 2, ReceiveResult);
Console.ReadKey();
}
private static void ReceiveResult(int res)
{
Console.WriteLine("结算的结果是:" + res);
}
}
public class Test1
{
public void Calculation(int x, int y, Action<int> call)
{
if (call != null)
{
call(x + y);
}
}
}
}
运行:

将方法换成 Lambda 表达式,效果一样的,关于Lambda的使用方法,可以参考:点击跳转
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Test1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Test1 test1 = new Test1();
test1.Calculation(1, 2, (int res) =>
{
Console.WriteLine("结算的结果是:" + res);
});
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public class Test1
{
public void Calculation(int x, int y, Action<int> call)
{
if (call != null)
{
call(x + y);
}
}
}
}
三、Func
上面使用Action的案例中,执行回调后,都没有返回值,这是因为Action并不能接收返回值,如果想执行回调,又有返回值怎么办呢,Func就是用来解决这个问题的。
Func 必须有一个返回值,否则会报错,如下图:
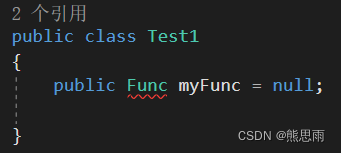
返回值通常是在参数的最后一个,参考例1,Func<int, float, string> MyFunc = null 这个委托中,string 就是返回值,传递参数的时候,也只能传递两个参数,如果再多写一个参数就会报错,如下图:

例1
基本的用法,func赋值,执行委托,并接收返回值
using System;
namespace Test1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Test1 test1 = new Test1();
string userName = test1.MyFunc(15, 180.2f);
Console.WriteLine(userName);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public class Test1
{
public Func<int, float, string> MyFunc = null;
private string GetUserName(int age, float height)
{
if (age == 15 && height == 180.2f)
{
return "张三";
}
return null;
}
public Test1()
{
MyFunc = GetUserName;
}
}
}
运行:

例2
把func作为方法的参数传递,并执行回调
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Test1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Test1 test1 = new Test1();
Func<string> func = () =>
{
string name = "张三";
string feel = "精力非常旺盛";
string msg = name + feel;
return msg;
};
test1.Calculation(10, 12, func);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public class Test1
{
public void Calculation(int x,int y, Func<string> sayFunc)
{
if(sayFunc != null)
{
int age = x + y;
string msg = string.Format("年龄是:{0},对年龄的感受:{1}", age, sayFunc());
Console.WriteLine(msg);
}
}
}
}
运行:

上面代码只是作为一个参考,读者可以根据自己的需求做一个改进。
结束
到此这篇关于浅谈C#中Action和Func回调的常用方式的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C# Action和Func回调内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

