C#多线程之线程池ThreadPool用法
目录
- 一、ThreadPool
- 1、QueueUserWorkItem()
- 2、GetMaxThreads()
- 3、GetMinThreads()
- 4、SetMaxThreads()和SetMinThreads()
- 二、线程等待
- 三、线程重用
一、ThreadPool
ThreadPool是.Net Framework 2.0版本中出现的。
ThreadPool出现的背景:Thread功能繁多,而且对线程数量没有管控,对于线程的开辟和销毁要消耗大量的资源。每次new一个THread都要重新开辟内存。
如果某个线程的创建和销毁的代价比较高,同时这个对象还可以反复使用的,就需要一个池子(容器),保存多个这样的对象,需要用的时候从池子里面获取,用完之后不用销毁,在放到池子里面。这样不但能节省内存资源,提高性能,而且还能管控线程的总数量,防止滥用。这时就需要使用ThreadPool了。
我们来看看ThreadPool中常用的一些方法。
1、QueueUserWorkItem()
QueueUserWorkItem()方法用来启动一个多线程。我们先看看方法的定义:
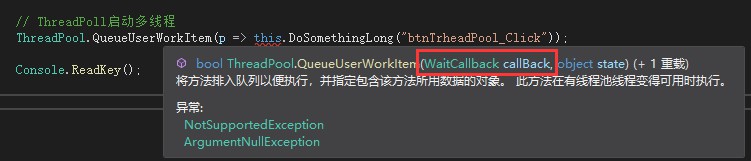
QueueUserWorkItem()方法有一个WaitCallback类型的参数,在看看WaitCallback的定义:

可以看到WaitCallback就是有一个object类型参数的委托,所以ThreadPool启动多线程使用下面的代码:
using System;
using System.Threading;
namespace ThreadPoolDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine($"start ThreadId: {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")}");
// ThreadPoll启动多线程
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(p => DoSomethingLong("启动多线程"));
Console.WriteLine($"end ThreadId: {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")}");
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void DoSomethingLong(string para)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{para} ThreadId: {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")}");
}
}
}
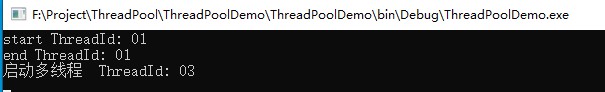
运行结果:
2、GetMaxThreads()
GetMaxThreads()用来获取线程池中最多可以有多少个辅助线程和最多有多少个异步线程。
ThreadPool.GetMaxThreads(out int workerThreads, out int completionPortThreads);
Console.WriteLine($"GetMaxThreads workerThreads={workerThreads} completionPortThreads={completionPortThreads}");
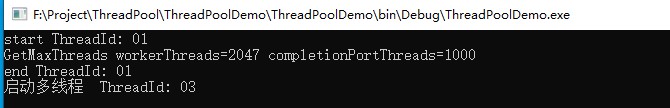
程序运行结果:
3、GetMinThreads()
GetMinThreads()用来获取线程池中最少可以有多少个辅助线程和最少有多少个异步线程。
ThreadPool.GetMinThreads(out int minworkerThreads, out int mincompletionPortThreads);
Console.WriteLine($"GetMinThreads workerThreads={minworkerThreads} completionPortThreads={mincompletionPortThreads}");
程序运行结果:

4、SetMaxThreads()和SetMinThreads()
SetMaxThreads()和SetMinThreads()分别用来设置线程池中最多线程数和最少线程数。
using System;
using System.Threading;
namespace ThreadPoolDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine($"start ThreadId: {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")}");
// ThreadPoll启动多线程
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(p => DoSomethingLong("启动多线程"));
// 获取最大线程
ThreadPool.GetMaxThreads(out int workerThreads, out int completionPortThreads);
Console.WriteLine($"GetMaxThreads workerThreads={workerThreads} completionPortThreads={completionPortThreads}");
// 获取最小线程
ThreadPool.GetMinThreads(out int minworkerThreads, out int mincompletionPortThreads);
Console.WriteLine($"GetMinThreads workerThreads={minworkerThreads} completionPortThreads={mincompletionPortThreads}");
// 设置线程池线程
SetThreadPool();
// 输出设置后的线程池线程个数
Console.WriteLine("输出修改后的最多线程数和最少线程数");
ThreadPool.GetMaxThreads(out int maxworkerThreads, out int maxcompletionPortThreads);
Console.WriteLine($"GetMaxThreads workerThreads={maxworkerThreads} completionPortThreads={maxcompletionPortThreads}");
ThreadPool.GetMinThreads(out int workerEditThreads, out int completionPortEditThreads);
Console.WriteLine($"GetMinThreads workerThreads={workerEditThreads} completionPortThreads={completionPortEditThreads}");
Console.WriteLine($"end ThreadId: {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")}");
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void DoSomethingLong(string para)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{para} ThreadId: {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")}");
}
/// <summary>
/// 设置线程池线程个数
/// </summary>
static void SetThreadPool()
{
Console.WriteLine("************设置最多线程数和最少线程数****************");
// 设置最大线程
ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(16, 16);
// 设置最小线程
ThreadPool.SetMinThreads(8, 8);
}
}
}
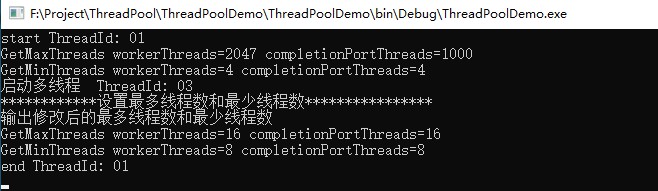
程序运行结果:
二、线程等待
先来看下面一个小例子:
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(p => DoSomethingLong("启动多线程"));
Console.WriteLine("等着QueueUserWorkItem完成后才执行");
我们想让异步多线程执行完以后再输出“等着QueueUserWorkItem完成后才执行” 这句话,上面的代码运行效果如下:
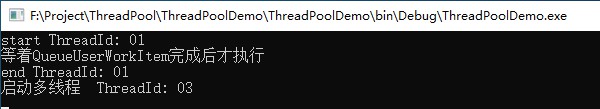
从截图中可以看出,效果并不是我们想要的,Thread中提供了暂停、恢复等API,但是ThreadPool中没有这些API,在ThreadPool中要实现线程等待,需要使用到ManualResetEvent类。
ManualResetEvent类的定义如下:
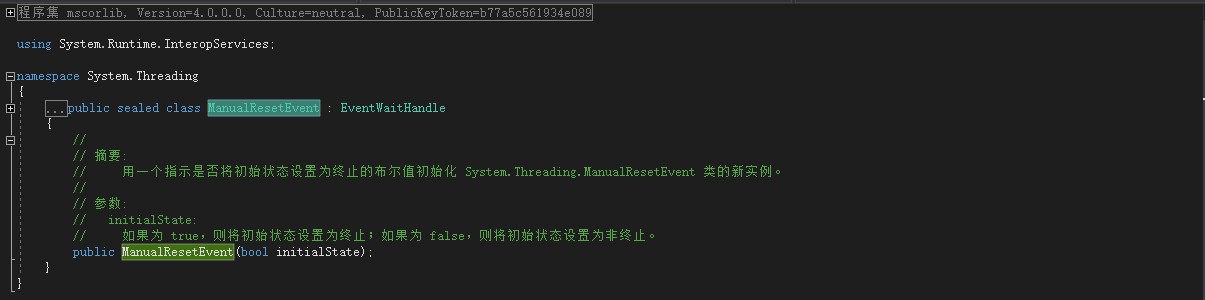
ManualResetEvent需要一个bool类型的参数来表示暂停和停止。上面的代码修改如下:
// 参数设置为false
ManualResetEvent manualResetEvent = new ManualResetEvent(false);
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(p =>
{
DoSomethingLong("启动多线程");
// 设置为true
manualResetEvent.Set();
});
//
manualResetEvent.WaitOne();
Console.WriteLine("等着QueueUserWorkItem完成后才执行");
结果:

ManualResetEvent类的参数值执行顺序如下:
(1)、false--WaitOne等待--Set--true--WaitOne直接过去
(2)、true--WaitOne直接过去--ReSet--false--WaitOne等待
注意:一般情况下,不要阻塞线程池中的线程,因为这样会导致一些无法预见的错误。来看下面的一个例子:
static void SetWait()
{
// 设置最大线程
ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(16, 16);
// 设置最小线程
ThreadPool.SetMinThreads(8, 8);
ManualResetEvent manualResetEvent = new ManualResetEvent(false);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
int k = i;
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(p =>
{
Console.WriteLine(k);
if (k < 18)
{
manualResetEvent.WaitOne();
}
else
{
// 设为true
manualResetEvent.Set();
}
});
}
if (manualResetEvent.WaitOne())
{
Console.WriteLine("没有死锁、、、");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("发生死锁、、、");
}
}
启动20个线程,如果k小于18就阻塞当前的线程,结果:
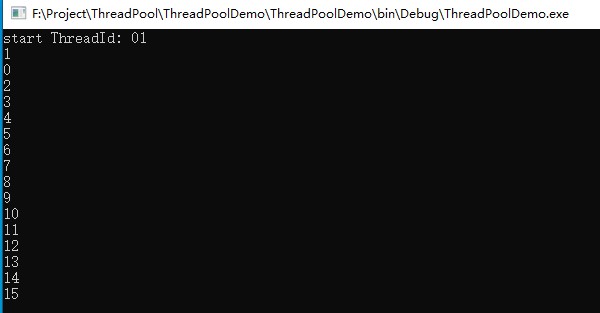
从截图中看出,只执行了16个线程,后面的线程没有执行,这是为什么呢?因为我们在上面设置了线程池中最多可以有16个线程,当16个线程都阻塞的时候,会造成死锁,所以后面的线程不会再执行了。
三、线程重用
ThreadPool可以很好的实现线程的重用,这样就可以减少内存的消耗,看下面的代码:
/// <summary>
/// 测试ThreadPool线程重用
/// </summary>
static void ThreadPoolTest()
{
// 线程重用
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t =>DoSomethingLong("ThreadPool"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t =>DoSomethingLong("ThreadPool"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t =>DoSomethingLong("ThreadPool"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t =>DoSomethingLong("ThreadPool"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t =>DoSomethingLong("ThreadPool"));
Thread.Sleep(10 * 1000);
Console.WriteLine("前面的计算都完成了。。。。。。。。");
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t =>DoSomethingLong("ThreadPool"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t =>DoSomethingLong("ThreadPool"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t =>DoSomethingLong("ThreadPool"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t =>DoSomethingLong("ThreadPool"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t =>DoSomethingLong("ThreadPool"));
}
然后在Main方法里面调用该方法,输出结果如下图所示:

我们在代码里面总共创建了10个线程,而结果里面只有4个线程ID,这就说明ThreadPool可以实现线程的重用。下面我们在看看Thread是否可以实现线程的重用,代码如下:
/// <summary>
/// 测试Thread线程重用
/// </summary>
static void ThreadTest()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
new Thread(() => DoSomethingLong("Threads")).Start();
}
Thread.Sleep(10 * 1000);
Console.WriteLine("前面的计算都完成了。。。。。。。。");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
new Thread(() => DoSomethingLong("btnThreads")).Start();
}
}
然后在Main方法里面调用,输入结果如下图所示:
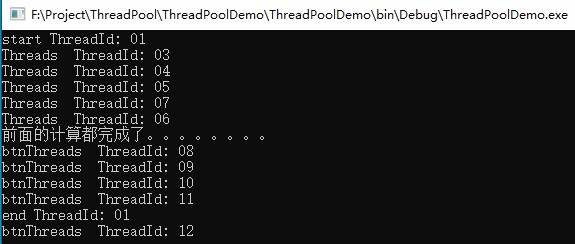
我们同样在代码里面创建了10个线程,结果输出了10个线程的ID,这就说明Thread不能实现线程的重用。同样也说明THread的效率没有ThreadPool高。
程序完整代码:
using System;
using System.Threading;
namespace ThreadPoolDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine($"start ThreadId: {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")}");
//// ThreadPoll启动多线程
//ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(p => DoSomethingLong("启动多线程"));
//// 获取最大线程
//ThreadPool.GetMaxThreads(out int workerThreads, out int completionPortThreads);
//Console.WriteLine($"GetMaxThreads workerThreads={workerThreads} completionPortThreads={completionPortThreads}");
//// 获取最小线程
//ThreadPool.GetMinThreads(out int minworkerThreads, out int mincompletionPortThreads);
//Console.WriteLine($"GetMinThreads workerThreads={minworkerThreads} completionPortThreads={mincompletionPortThreads}");
//// 设置线程池线程
//SetThreadPool();
//// 输出设置后的线程池线程个数
//Console.WriteLine("输出修改后的最多线程数和最少线程数");
//ThreadPool.GetMaxThreads(out int maxworkerThreads, out int maxcompletionPortThreads);
//Console.WriteLine($"GetMaxThreads workerThreads={maxworkerThreads} completionPortThreads={maxcompletionPortThreads}");
//ThreadPool.GetMinThreads(out int workerEditThreads, out int completionPortEditThreads);
//Console.WriteLine($"GetMinThreads workerThreads={workerEditThreads} completionPortThreads={completionPortEditThreads}");
//Console.WriteLine($"end ThreadId: {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")}");
//// 参数设置为false
//ManualResetEvent manualResetEvent = new ManualResetEvent(false);
//ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(p =>
//{
// DoSomethingLong("启动多线程");
// // 设置为true
// manualResetEvent.Set();
//});
////
//manualResetEvent.WaitOne();
//Console.WriteLine("等着QueueUserWorkItem完成后才执行");
// SetWait();
// ThreadPool实现线程的重用
// ThreadPoolTest();
// Thread
ThreadTest();
Console.WriteLine($"end ThreadId: {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")}");
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void DoSomethingLong(string para)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{para} ThreadId: {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")}");
}
/// <summary>
/// 设置线程池线程个数
/// </summary>
static void SetThreadPool()
{
Console.WriteLine("************设置最多线程数和最少线程数****************");
// 设置最大线程
ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(16, 16);
// 设置最小线程
ThreadPool.SetMinThreads(8, 8);
}
static void SetWait()
{
// 设置最大线程
ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(16, 16);
// 设置最小线程
ThreadPool.SetMinThreads(8, 8);
ManualResetEvent manualResetEvent = new ManualResetEvent(false);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
int k = i;
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(p =>
{
Console.WriteLine(k);
if (k < 18)
{
manualResetEvent.WaitOne();
}
else
{
// 设为true
manualResetEvent.Set();
}
});
}
if (manualResetEvent.WaitOne())
{
Console.WriteLine("没有死锁、、、");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("发生死锁、、、");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 测试ThreadPool线程重用
/// </summary>
static void ThreadPoolTest()
{
// 线程重用
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t => DoSomethingLong("ThreadPool"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t => DoSomethingLong("ThreadPool"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t => DoSomethingLong("ThreadPool"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t => DoSomethingLong("ThreadPool"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t => DoSomethingLong("ThreadPool"));
Thread.Sleep(10 * 1000);
Console.WriteLine("前面的计算都完成了。。。。。。。。");
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t => DoSomethingLong("ThreadPool"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t => DoSomethingLong("ThreadPool"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t => DoSomethingLong("ThreadPool"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t => DoSomethingLong("ThreadPool"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t => DoSomethingLong("ThreadPool"));
}
/// <summary>
/// 测试Thread线程重用
/// </summary>
static void ThreadTest()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
new Thread(() => DoSomethingLong("Threads")).Start();
}
Thread.Sleep(10 * 1000);
Console.WriteLine("前面的计算都完成了。。。。。。。。");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
new Thread(() => DoSomethingLong("btnThreads")).Start();
}
}
}
}
到此这篇关于C#多线程之线程池ThreadPool用法的文章就介绍到这了。希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。

