vue封装组件js版基本步骤
目录
- 什么是组件化:
- Vue组件化思想
- 一.注册组件的基本步骤
- 1.创建组件构造器c-input
- 2.注册组件
- 3.父组件使用
- 二.丰富组件
- 三.父子组件间的通讯
- 1.父---->子通信 [props Down]
- 2. 子----> 父传值 [Events Up]
- 3. 子<----> 父 双向传值
- 四.slot插槽
- 什么是插槽?
- 怎么用插槽?
- 具名插槽
- 作用域插槽
什么是组件化:
组件化就是将一个页面拆分成一个个小的功能模块,每个功能模块完成属于自己这部分独立的功能,使得整个页面的管理和维护变得非常容易。
Vue组件化思想
- 组件化是Vue中的重要思想,当我们对vue的基本知识有了一定的基础就要开始封装组件了
它提供了一种抽象,让我们可以开发出一个个独立可复用的小组件来构造我们的应用。组件树。
- 组件化思想的应用
1.在项目中充分利用组件化的思想
2.尽可能的将也页面拆分成一个个小的可复用的组件
3.好处:代码更加方便组织和管理,扩展性也更强
一.注册组件的基本步骤
下面我们用一个封装一个Element Ui 的输入框组件为例,贯彻全文
组件的使用分成三个步骤
1.创建组件构造器c-input
组件的模板 template
注意:只能有一个根元素,否则警告报错
1 template 可以是字面量字符串,缺点是没有高亮,内置在 JavaScript 中,写起来麻烦
2 template 可以写在 script 标签中,虽然解决了高亮的问题,但是也麻烦
3 以上方式都不好,我们最终的解决方案是使用 Vue 的 .vue 单文件组件来写。(webpack)
但是要想使用这种方式必须结合一些构建工具
<template>
<el-input >
</el-input>
</template>
2.注册组件
注册组件 分为 局部注册 与 全局注册,下一章再讲
......使用代码.........
import cInput from "组件地址/c-ipunt.vue";
export default {
components: {cInput},
.......
3.父组件使用
<template>
<c-ipunt/>
</template>
<script>
import cInput from "组件地址/c-ipunt.vue";
export default {
components: {cInput},
.......
</script>
二.丰富组件
组件是独立的作用域,就像我们 Node 中的 JavaScript 模块一样,独立的
组件其实就是一个特殊的 Vue 实例,可以有自己的 data、methods、computed、watch 等等选项
组件的 data 必须是函数
函数中返回一个对象作为组件的 data
<template>
<el-input >
</el-input>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'c-input',
model: {
prop: 'value',
event: 'input',
},
props: {
},
data() {
return {
}
},
watch: {
},
methods: {
},
mounted() {
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
三.父子组件间的通讯
1.父---->子通信 [props Down]
父组件通过 props 向下传递数据给子组件
所以子组件要定义接收的参数
我们可以看到Element Ui 的输入框组件,有这些属性我们可以重新定义封装
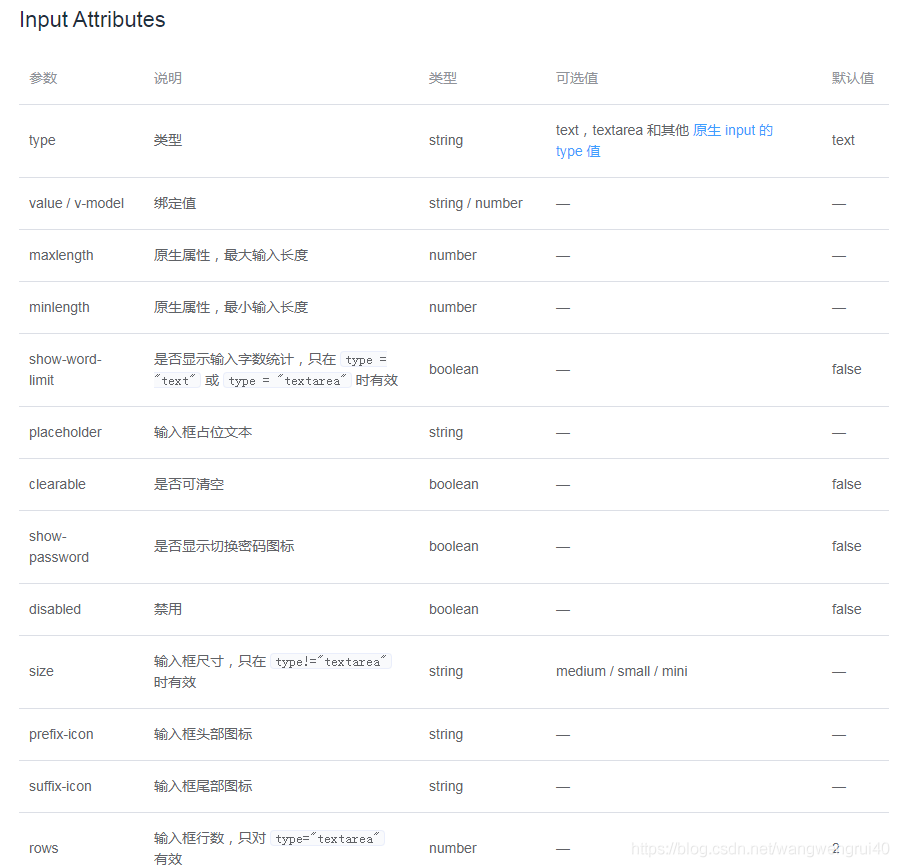
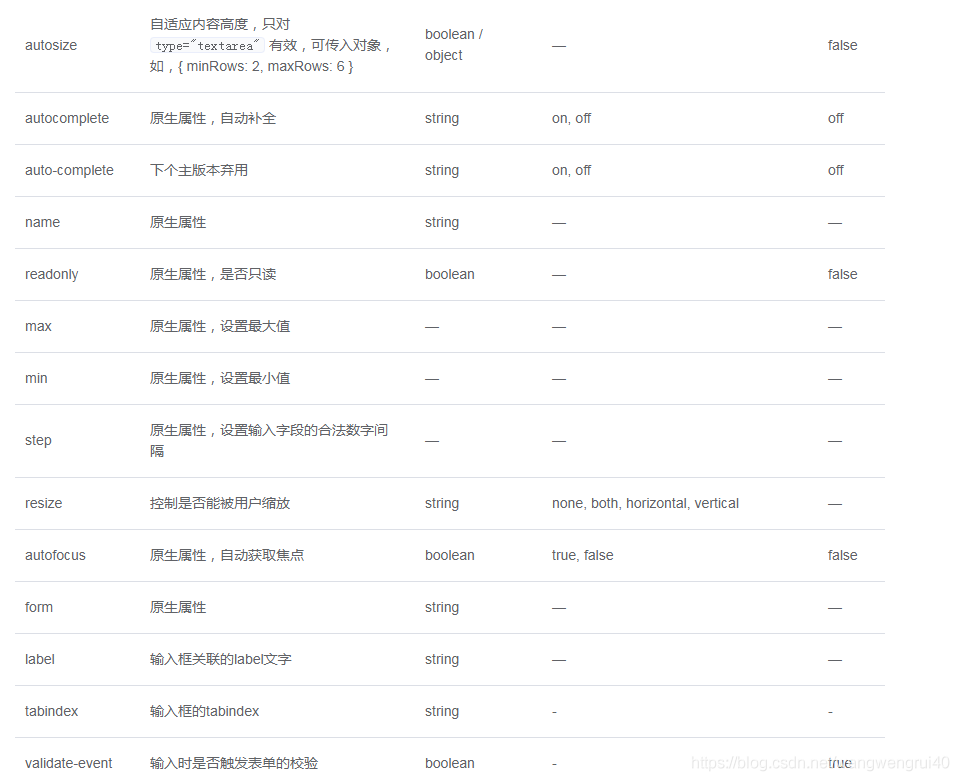
<template>
<el-input :disabled="disabled" ref="input" :placeholder="placeholder"
:type="type" :auto-complete="autocomplete">
</el-input>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'c-input',
model: {
prop: 'value',
event: 'input',
},
props: {
labelwidth: {
type: String,
default: undefined,
},
autosize: {
default() {
return { minRows: 2, maxRows: 4 }//如果不使用这个属性的默认值
},
},
inputCss: {
type: String,
default: '',
},
label: {
type: String,
default: '',
},
value: {
default: undefined,
},
prop: {
type: String,
default: null,
},
placeholder: {
type: String,
default: undefined,
},
required: {
type: Boolean,
default: false,
},
width: {
type: String,
},
type: {
type: String,
default: undefined,
},
autocomplete: {
type: String,
default: 'on',
},
disabled: {
type: Boolean,
default: false,
},
span: {
type: Number,
},
},
data() {
return {
}
},
watch: {
},
methods: {
},
mounted() {
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
父组件使用
<template>
<c-input label="用户名" :span="12" />
</template>
<script>
import cInput from "组件地址/c-ipunt.vue";
export default {
components: {cInput},
.......
</script>
2. 子----> 父传值 [Events Up]
子组件通过 events 给父组件发送消息,实际上就是子组件把自己的数据发送到父组件。
在 element ui 的 el-input中是有@input.native="updateValue($event.target.value)" 获取现在输入值 @keyup.enter.native="handleEnter" 回车 @focus="focus" 得到焦点 等事件的

<template>
<el-input :disabled="disabled" ref="input" :placeholder="placeholder"
:type="type" :auto-complete="autocomplete" @input.native="updateValue($event.target.value)" @keyup.enter.native="handleEnter" @focus="focus">
</el-input>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'c-input',
model: {
prop: 'value',
event: 'input',
},
props: {
labelwidth: {
type: String,
default: undefined,
},
autosize: {
default() {
return { minRows: 2, maxRows: 4 }//如果不使用这个属性的默认值
},
},
inputCss: {
type: String,
default: '',
},
label: {
type: String,
default: '',
},
value: {
default: undefined,
},
prop: {
type: String,
default: null,
},
placeholder: {
type: String,
default: undefined,
},
required: {
type: Boolean,
default: false,
},
width: {
type: String,
},
type: {
type: String,
default: undefined,
},
autocomplete: {
type: String,
default: 'on',
},
disabled: {
type: Boolean,
default: false,
},
span: {
type: Number,
},
},
data() {
return {
}
},
watch: {
},
methods: {
updateValue(val) {
this.$emit('input', val)
},
handleEnter() {
this.$emit('keyup-enter')
},
focus() {
this.$emit('focus')
},
},
mounted() {
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
父组件使用
<template>
<c-input label="用户名" :span="12" @keyup-enter="mykeyupEnter" @focus="myfocus"/>
</template>
<script>
import cInput from "组件地址/c-ipunt.vue";
export default {
components: {cInput},
.......
methods: {
mykeyupEnter(){
console.log("我是父组件的输入框回车")},
myfocus(){
console.log("我是父组件的输入框得到焦点")
}
},
......
</script>
3. 子<----> 父 双向传值
我们知道Vue的核心特性之一是双向绑定,
v-model是一个指令用来实现双向绑定,限制在<input>、<select>、<textarea>、components中使用,修饰符.lazy(取代input监听change事件)、.number(输入字符串转为有效的数字)、.trim(输入首尾空格过滤)。那么我们封装的组件怎么进行双向绑定呢。
- 首先 props添加一个value,接收父组件的数据变化。
- 再添加一个value的监听,监听父组件的数据变化。
- 而子组件数据变化的时候会出发这个事件@input.native="",所以这个时间触发this.$emit('input',val),向父组件传递 子组件的数据变化
<template>
<el-input :disabled="disabled" ref="input" :placeholder="placeholder"
:type="type" :auto-complete="autocomplete" @input.native="updateValue($event.target.value)" @keyup.enter.native="handleEnter" @focus="focus" v-model="modelValue">
</el-input>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'c-input',
model: {
prop: 'value',
event: 'input',
},
props: {
labelwidth: {
type: String,
default: undefined,
},
autosize: {
default() {
return { minRows: 2, maxRows: 4 }//如果不使用这个属性的默认值
},
},
inputCss: {
type: String,
default: '',
},
label: {
type: String,
default: '',
},
value: {
default: undefined,
},
prop: {
type: String,
default: null,
},
placeholder: {
type: String,
default: undefined,
},
required: {
type: Boolean,
default: false,
},
width: {
type: String,
},
type: {
type: String,
default: undefined,
},
autocomplete: {
type: String,
default: 'on',
},
disabled: {
type: Boolean,
default: false,
},
span: {
type: Number,
},
},
data() {
return {
modelValue: undefined,
}
},
watch: {
value: {
handler(newValue) {
this.modelValue = newValue
},
immediate: true,
},
},
methods: {
updateValue(val) {
this.$emit('input', val)
},
handleEnter() {
this.$emit('keyup-enter')
},
focus() {
this.$emit('focus')
},
},
mounted() {
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
使用
<template>
<c-input label="用户名" :span="12" @keyup-enter="mykeyupEnter" @focus="myfocus" v-model="myName"/>
</template>
<script>
import cInput from "组件地址/c-ipunt.vue";
export default {
components: {cInput},
data() {
return {
myName: undefined,
}},
.......
methods: {
mykeyupEnter(){
console.log("我是父组件的输入框回车")},
myfocus(){
console.log("我是父组件的输入框得到焦点")
}
},
......
</script>
四.slot插槽
什么是插槽?
插槽(Slot)是Vue提出来的一个概念,正如名字一样,插槽用于决定将所携带的内容,插入到指定的某个位置,从而使模板分块,具有模块化的特质和更大的重用性。
插槽显不显示、怎样显示是由父组件来控制的,而插槽在哪里显示就由子组件来进行控制
怎么用插槽?
默认插槽
父组件
<template>
<div>
我是父组件
<slotOne1>
<p style="color:red">我是父组件插槽内容</p>
</slotOne1>
</div>
</template>
在父组件引用的子组件中写入想要显示的内容(可以使用标签,也可以不用)
子组件(slotOne1)
<template>
<div class="slotOne1">
<div>我是slotOne1组件</div>
<slot></slot>
</div>
</template>
在子组件中写入slot,slot所在的位置就是父组件要显示的内容

具名插槽
子组件
<template>
<div class="slottwo">
<div>slottwo</div>
<slot name="header"></slot>
<slot></slot>
<slot name="footer"></slot>
</div>
</template>
在子组件中定义了三个slot标签,其中有两个分别添加了name属性header和footer
父组件
<template>
<div>
我是父组件
<slot-two>
<p>啦啦啦,啦啦啦,我是卖报的小行家</p>
<template slot="header">
<p>我是name为header的slot</p>
</template>
<p slot="footer">我是name为footer的slot</p>
</slot-two>
</div>
</template>
在父组件中使用template并写入对应的slot值来指定该内容在子组件中现实的位置(当然也不用必须写到template),没有对应值的其他内容会被放到子组件中没有添加name属性的slot中

作用域插槽
子组件
<template>
<div>
我是作用域插槽的子组件
<slot :data="user"></slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'slotthree',
data () {
return {
user: [
{name: 'Jack', sex: 'boy'},
{name: 'Jone', sex: 'girl'},
{name: 'Tom', sex: 'boy'}
]
}
}
}
</script>
在子组件的slot标签上绑定需要的值
父组件
<template>
<div>
我是作用域插槽
<slot-three>
<template slot-scope="user">
<div v-for="(item, index) in user.data" :key="index">
{{item}}
</div>
</template>
</slot-three>
</div>
</template>
在父组件上使用slot-scope属性,user.data就是子组件传过来的值

以上就是vue封装组件js版基本步骤的详细内容,更多关于js封装vue组件的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!

