mybatis3使用@Select等注解实现增删改查操作
1.需要的jar包
2.目录树
3.具体代码
一.需要的jar包
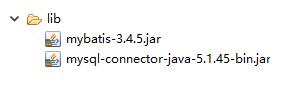
第一个:mybatis的jar包
第二个:mysql数据的驱动
二.目录树
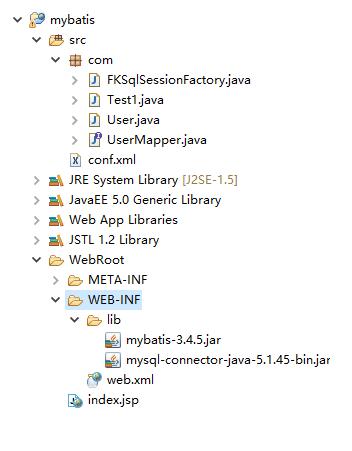
三.具体代码
使用框架,配置文件先行!
conf.xml:(配置 登录数据库,映射文件)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <environments default="mysql"> <environment id="mysql"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="zhujunwen"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <!-- 配置映射--> <mappers> <!-- 若映射文件mapper 是xml,则<mapper recourse...>,若映射文件为java文件,则<mapper class.....> --> <mapper class="com.UserMapper"/> </mappers> </configuration>
映射文件:
UserMapper.java:(用于映射SQL语句)
package com;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Delete;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Update;
public interface UserMapper {
/*
这个一个接口,但不需要实现它,用于 函数与SQL语句 的映射
* */
@Insert("insert into tb_user(name,sex) values(#{name},#{sex})")
public void insertT(User user);
@Delete("delete from tb_user where id=#{id}")
public void deleteById(int id);
@Update("update tb_user set name=#{name},sex=#{sex} where id=#{id}")
public void updateT(User user);
@Select("select * from tb_user where id=#{id}")
public User getUser(int id);
@Select("select * from tb_user")
public List<User> getAllUsers();
}
持久类:
User.java:(持久类中的成员变量要与数据表中的字段名字一致)
package com;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String sex;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", sex=" + sex + "]";
}
}
必要变量的快速获取:(获取Session)
FKSqlSessionFactory.java:
package com;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
public class FKSqlSessionFactory {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null;
static{
InputStream input;
try {
input = Resources.getResourceAsStream("conf.xml");
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(input);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(){
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}
public static SqlSessionFactory getSqlSessionFactory(){
return sqlSessionFactory;
}
}
测试文件(只是演示对数据库的插入)
package com;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SqlSessionFactory factory= FKSqlSessionFactory.getSqlSessionFactory();
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);//获取映射器实例
User user = new User();
user.setName("zhujunwen");
user.setSex("m");
mapper.insertT(user); //调用映射器中的insertT()方法进行数据库插入
session.commit();
session.close();
}
}
效果:
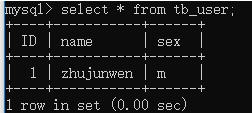
已有数据插入到数据表
数据表的样式:
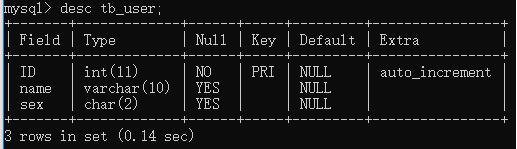
补充知识:mybatis 一次select操作执行流程分析
1.测试代码
package com.testmybatis;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.testmybatis.dao.TestMapper;
import com.testmybatis.model.Test;
public class testlanjie {
private static Logger log=Logger.getLogger(testlanjie.class);
public static void main(String args[]){
List<Test> tests=null;
try {
String resource = "com/testmybatis/mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
TestMapper mapper=session.getMapper(TestMapper.class);
tests=mapper.test();
session.commit();
} finally {
session.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(tests!=null)
log.info(JSON.toJSONString(tests));
}
}
2.流程分析
第一步构造SqlSessionFactory
String resource = "com/testmybatis/mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder下的build函数
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) {
return build(inputStream, null, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
先用配置文件的文件流对象构造一个XMLConfigBuilder对象,在调用parse函数得到Configuration对象
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
Properties settings = settingsAsPropertiess(root.evalNode("settings"));
//issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
其中mybatis主要的配置都在这里完成,存放在configuration中,本次分析会用到的两个函数是environmentsElement和mapperElement,一个是构造datasource,一个是构造存放所有MapperProxyFactory的MapperRegistry,相应的源代码如下
private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
if (environment == null) {
environment = context.getStringAttribute("default");
}
for (XNode child : context.getChildren()) {
String id = child.getStringAttribute("id");
if (isSpecifiedEnvironment(id)) {
TransactionFactory txFactory = transactionManagerElement(child.evalNode("transactionManager"));
DataSourceFactory dsFactory = dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource"));
DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource();
Environment.Builder environmentBuilder = new Environment.Builder(id)
.transactionFactory(txFactory)
.dataSource(dataSource);
configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build());
}
}
}
}
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
其中MapperRegistry对象中存放所有MapperProxyFactory对象的容器是一个hashmap
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>>();
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
在构造factory的最后返回了一个DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象,并将创建好的Configuration对象当作参数传给了该对象,成为了他的成员变量。
第二步得到SqlSession对象
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
跟踪获取session的过程
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
最终得到的DefaultSqlSession中包含两个重要对象,一个是从configuration里来的Enviroment,另外一个是包含TransactionFactroy对象的Executor对象。
其中获得Executor对象的函数如下
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
这其中应用的包装模式(将SimpleExecutor对象包装成CachingExecutor)和责任链模式(给CachingExecutro对象装配上plugin)
第三步 根据传入的接口信息生成动态代理
TestMapper mapper=session.getMapper(TestMapper.class);
继续跟踪代码
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this);
}
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
大致流程就是先从configuration中找mapperRegistry,再从mapperRegistry中找当初存放mapperfactory的hashmap,再从这个hashmap中找到相应的mapperfactory,最后mapperfactory构造了一个mapperproxy对象,并调用了java的Proxy类,构造了一个动态代理对象的实例。
看一下MapperProxy的代码
/**
* Copyright 2009-2015 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.ibatis.binding;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ExceptionUtil;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
* @author Eduardo Macarron
*/
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
}
该class实现了InvocationHandler接口,我们知道java中的动态代理模式需要代理class来实现InvocationHandler接口,
而最后动态得到的实例调用函数实际上调用的是代理对象的invoke的函数,所以我们第四步的入口就在这个class里
第四步 调用接口函数test,执行sql语句
由代理对象中的inove函数知道,函数最后执行的其实是MapperMethod类的execute函数。
一路跟踪代码到SimpleExecutor下的doQuery函数中
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
此处生成了一个StatementHandler对象和一个Statement对象
先看看Statement的生成过程
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
先生成Connection对象 ,用的也是代理模式
protected Connection getConnection(Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = transaction.getConnection();
if (statementLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
return ConnectionLogger.newInstance(connection, statementLog, queryStack);
} else {
return connection;
}
}
public static Connection newInstance(Connection conn, Log statementLog, int queryStack) {
InvocationHandler handler = new ConnectionLogger(conn, statementLog, queryStack);
ClassLoader cl = Connection.class.getClassLoader();
return (Connection) Proxy.newProxyInstance(cl, new Class[]{Connection.class}, handler);
}
然后生成preparestatement
@Override
public Statement prepare(Connection connection, Integer transactionTimeout) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().sql(boundSql.getSql());
Statement statement = null;
try {
statement = instantiateStatement(connection);
setStatementTimeout(statement, transactionTimeout);
setFetchSize(statement);
return statement;
} catch (SQLException e) {
closeStatement(statement);
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
closeStatement(statement);
throw new ExecutorException("Error preparing statement. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
@Override
protected Statement instantiateStatement(Connection connection) throws SQLException {
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
if (mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator() instanceof Jdbc3KeyGenerator) {
String[] keyColumnNames = mappedStatement.getKeyColumns();
if (keyColumnNames == null) {
return connection.prepareStatement(sql, PreparedStatement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
} else {
return connection.prepareStatement(sql, keyColumnNames);
}
} else if (mappedStatement.getResultSetType() != null) {
return connection.prepareStatement(sql, mappedStatement.getResultSetType().getValue(), ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY);
} else {
return connection.prepareStatement(sql);
}
}
最后调用了connec tion的prepareStatement函数,而因为connection其实是一个代理对象,他实际调用的函数是
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] params)
throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, params);
}
if ("prepareStatement".equals(method.getName())) {
if (isDebugEnabled()) {
debug(" Preparing: " + removeBreakingWhitespace((String) params[0]), true);
}
PreparedStatement stmt = (PreparedStatement) method.invoke(connection, params);
//实际调用创建prepareedstatement对象的地方
stmt = PreparedStatementLogger.newInstance(stmt, statementLog, queryStack);
return stmt;
} else if ("prepareCall".equals(method.getName())) {
if (isDebugEnabled()) {
debug(" Preparing: " + removeBreakingWhitespace((String) params[0]), true);
}
PreparedStatement stmt = (PreparedStatement) method.invoke(connection, params);
stmt = PreparedStatementLogger.newInstance(stmt, statementLog, queryStack);
return stmt;
} else if ("createStatement".equals(method.getName())) {
Statement stmt = (Statement) method.invoke(connection, params);
stmt = StatementLogger.newInstance(stmt, statementLog, queryStack);
return stmt;
} else {
return method.invoke(connection, params);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
public static PreparedStatement newInstance(PreparedStatement stmt, Log statementLog, int queryStack) {
InvocationHandler handler = new PreparedStatementLogger(stmt, statementLog, queryStack);
ClassLoader cl = PreparedStatement.class.getClassLoader();
return (PreparedStatement) Proxy.newProxyInstance(cl, new Class[]{PreparedStatement.class, CallableStatement.class}, handler);
}
发现原来这个pareparedStatement对象还是个代理对象
继续跟踪代码
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
ps.execute();
return resultSetHandler.<E> handleResultSets(ps);
}
调用了之前生成的preparedStatement对象的execute函数,其实也就是代理对象的inovke函数
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] params) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, params);
}
if (EXECUTE_METHODS.contains(method.getName())) {
if (isDebugEnabled()) {
debug("Parameters: " + getParameterValueString(), true);
}
clearColumnInfo();
if ("executeQuery".equals(method.getName())) {
ResultSet rs = (ResultSet) method.invoke(statement, params);
return rs == null ? null : ResultSetLogger.newInstance(rs, statementLog, queryStack);
} else {
return method.invoke(statement, params);
}
} else if (SET_METHODS.contains(method.getName())) {
if ("setNull".equals(method.getName())) {
setColumn(params[0], null);
} else {
setColumn(params[0], params[1]);
}
return method.invoke(statement, params);
} else if ("getResultSet".equals(method.getName())) {
ResultSet rs = (ResultSet) method.invoke(statement, params);
return rs == null ? null : ResultSetLogger.newInstance(rs, statementLog, queryStack);
} else if ("getUpdateCount".equals(method.getName())) {
int updateCount = (Integer) method.invoke(statement, params);
if (updateCount != -1) {
debug(" Updates: " + updateCount, false);
}
return updateCount;
} else {
return method.invoke(statement, params);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
此时sql语句执行完成,之后是获取结果集
第五步 获取结果集
@Override
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(mappedStatement.getId());
final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<Object>();
int resultSetCount = 0;
ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt);
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);
while (rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
ResultMap resultMap = resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null);
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
String[] resultSets = mappedStatement.getResultSets();
if (resultSets != null) {
while (rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) {
ResultMapping parentMapping = nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]);
if (parentMapping != null) {
String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId();
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, null, parentMapping);
}
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
}
return collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}
此处调用stmt.getResultSet(),然后他又进了代理对象的invoke函数
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] params) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, params);
}
if (EXECUTE_METHODS.contains(method.getName())) {
if (isDebugEnabled()) {
debug("Parameters: " + getParameterValueString(), true);
}
clearColumnInfo();
if ("executeQuery".equals(method.getName())) {
ResultSet rs = (ResultSet) method.invoke(statement, params);
return rs == null ? null : ResultSetLogger.newInstance(rs, statementLog, queryStack);
} else {
return method.invoke(statement, params);
}
} else if (SET_METHODS.contains(method.getName())) {
if ("setNull".equals(method.getName())) {
setColumn(params[0], null);
} else {
setColumn(params[0], params[1]);
}
return method.invoke(statement, params);
} else if ("getResultSet".equals(method.getName())) {
ResultSet rs = (ResultSet) method.invoke(statement, params);
return rs == null ? null : ResultSetLogger.newInstance(rs, statementLog, queryStack);
} else if ("getUpdateCount".equals(method.getName())) {
int updateCount = (Integer) method.invoke(statement, params);
if (updateCount != -1) {
debug(" Updates: " + updateCount, false);
}
return updateCount;
} else {
return method.invoke(statement, params);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
public static ResultSet newInstance(ResultSet rs, Log statementLog, int queryStack) {
InvocationHandler handler = new ResultSetLogger(rs, statementLog, queryStack);
ClassLoader cl = ResultSet.class.getClassLoader();
return (ResultSet) Proxy.newProxyInstance(cl, new Class[]{ResultSet.class}, handler);
}
可以看到这还是一个代理模式,创建了一个用来获取结果集的对象ResultSetLogger,看一下他的invoke函数
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] params) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, params);
}
Object o = method.invoke(rs, params);
if ("next".equals(method.getName())) {
if (((Boolean) o)) {
rows++;
if (isTraceEnabled()) {
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
final int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
if (first) {
first = false;
printColumnHeaders(rsmd, columnCount);
}
printColumnValues(columnCount);
}
} else {
debug(" Total: " + rows, false);
}
}
clearColumnInfo();
return o;
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
从ResultSetLogger对象遍历出结果集还要经过一步处理得到最终需要返回类型的结果集
第六步 封装结果集
private void handleResultSet(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, List<Object> multipleResults, ResultMapping parentMapping) throws SQLException {
try {
if (parentMapping != null) {
handleRowValues(rsw, resultMap, null, RowBounds.DEFAULT, parentMapping);
} else {
if (resultHandler == null) {
DefaultResultHandler defaultResultHandler = new DefaultResultHandler(objectFactory);
handleRowValues(rsw, resultMap, defaultResultHandler, rowBounds, null);
multipleResults.add(defaultResultHandler.getResultList());
} else {
handleRowValues(rsw, resultMap, resultHandler, rowBounds, null);
}
}
} finally {
// issue #228 (close resultsets)
closeResultSet(rsw.getResultSet());
}
}
public void handleRowValues(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, ResultHandler<?> resultHandler, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultMapping parentMapping) throws SQLException {
if (resultMap.hasNestedResultMaps()) {
ensureNoRowBounds();
checkResultHandler();
handleRowValuesForNestedResultMap(rsw, resultMap, resultHandler, rowBounds, parentMapping);
} else {
handleRowValuesForSimpleResultMap(rsw, resultMap, resultHandler, rowBounds, parentMapping);
}
}
private void handleRowValuesForSimpleResultMap(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, ResultHandler<?> resultHandler, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultMapping parentMapping)
throws SQLException {
DefaultResultContext<Object> resultContext = new DefaultResultContext<Object>();
skipRows(rsw.getResultSet(), rowBounds);
while (shouldProcessMoreRows(resultContext, rowBounds) && rsw.getResultSet().next()) {
ResultMap discriminatedResultMap = resolveDiscriminatedResultMap(rsw.getResultSet(), resultMap, null);
Object rowValue = getRowValue(rsw, discriminatedResultMap);
storeObject(resultHandler, resultContext, rowValue, parentMapping, rsw.getResultSet());
}
}
private Object getRowValue(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap) throws SQLException {
final ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader = new ResultLoaderMap();
Object resultObject = createResultObject(rsw, resultMap, lazyLoader, null);
if (resultObject != null && !hasTypeHandlerForResultObject(rsw, resultMap.getType())) {
final MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(resultObject);
boolean foundValues = !resultMap.getConstructorResultMappings().isEmpty();
if (shouldApplyAutomaticMappings(resultMap, false)) {
foundValues = applyAutomaticMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, null) || foundValues;
}
foundValues = applyPropertyMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, lazyLoader, null) || foundValues;
foundValues = lazyLoader.size() > 0 || foundValues;
resultObject = foundValues ? resultObject : null;
return resultObject;
}
return resultObject;
}
这一步最核心的代码就是上面这个函数,可以看到他是由configuration生成一个MetaObject,在通过applyAutomaticMappings函数,将数据库结果中相应字段的值填充到MetaObject中,代码如下
private boolean applyAutomaticMappings(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, MetaObject metaObject, String columnPrefix) throws SQLException {
List<UnMappedColumnAutoMapping> autoMapping = createAutomaticMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, columnPrefix);
boolean foundValues = false;
if (autoMapping.size() > 0) {
for (UnMappedColumnAutoMapping mapping : autoMapping) {
final Object value = mapping.typeHandler.getResult(rsw.getResultSet(), mapping.column);
if (value != null) {
foundValues = true;
}
if (value != null || (configuration.isCallSettersOnNulls() && !mapping.primitive)) {
// gcode issue #377, call setter on nulls (value is not 'found')
metaObject.setValue(mapping.property, value);
}
}
}
return foundValues;
}
最后将得到的封装好的对象放入一个list中返回结果,关闭数据库连接,一次完整的sql语句执行流程至此完结 。
以上这篇mybatis3使用@Select等注解实现增删改查操作就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

