SpringBoot结合Redis实现接口幂等性的示例代码
目录
- 介绍
- 实现过程
- 引入 maven 依赖
- spring 配置文件写入
- 引入 Redis
- 自定义注解
- token 的创建和实现
- 拦截器的配置
- 测试用例
介绍
幂等性的概念是,任意多次执行所产生的影响都与一次执行产生的影响相同,按照这个含义,最终的解释是对数据库的影响只能是一次性的,不能重复处理。手段如下
- 数据库建立唯一索引
- token机制
- 悲观锁或者是乐观锁
- 先查询后判断
小小主要带你们介绍Redis实现自动幂等性。其原理如下图所示。
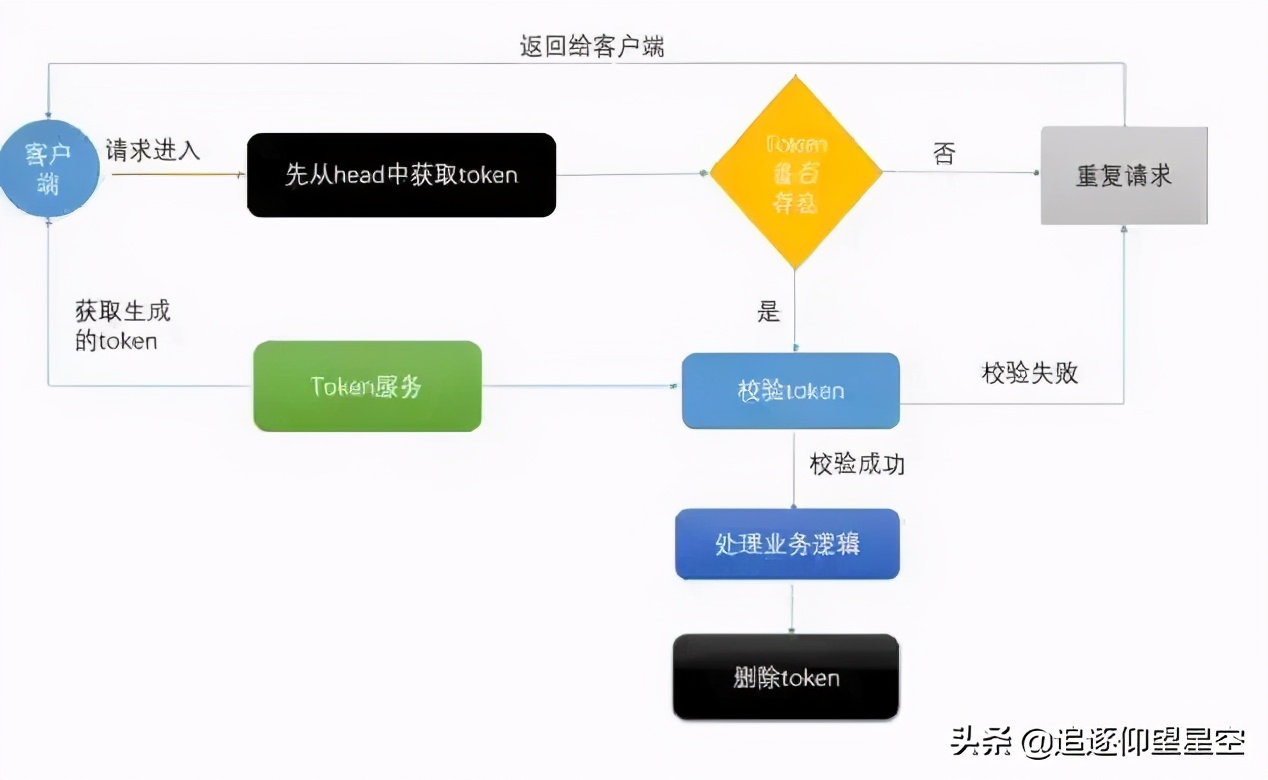
实现过程
引入 maven 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
spring 配置文件写入
server.port=8080 core.datasource.druid.enabled=true core.datasource.druid.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.225:3306/?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8 core.datasource.druid.username=root core.datasource.druid.password= core.redis.enabled=true spring.redis.host=192.168.1.225 #本机的redis地址 spring.redis.port=16379 spring.redis.database=3 spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=10 spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle=10 spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait=5s spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle=10
引入 Redis
引入 Spring boot 中的redis相关的stater,后面需要用到 Spring Boot 封装好的 RedisTemplate
package cn.smallmartial.demo.utils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @Author smallmartial
* @Date 2020/4/16
* @Email smallmarital@qq.com
*/
@Component
public class RedisUtil {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
/**
* 写入缓存
*
* @param key
* @param value
* @return
*/
public boolean set(final String key, Object value) {
boolean result = false;
try {
ValueOperations<Serializable, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
operations.set(key, value);
result = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
/**
* 写入缓存设置时间
*
* @param key
* @param value
* @param expireTime
* @return
*/
public boolean setEx(final String key, Object value, long expireTime) {
boolean result = false;
try {
ValueOperations<Serializable, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
operations.set(key, value);
redisTemplate.expire(key, expireTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
result = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
/**
* 读取缓存
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public Object get(final String key) {
Object result = null;
ValueOperations<Serializable, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
result = operations.get(key);
return result;
}
/**
* 删除对应的value
*
* @param key
*/
public boolean remove(final String key) {
if (exists(key)) {
Boolean delete = redisTemplate.delete(key);
return delete;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 判断key是否存在
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public boolean exists(final String key) {
boolean result = false;
ValueOperations<Serializable, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
if (Objects.nonNull(operations.get(key))) {
result = true;
}
return result;
}
}
自定义注解
自定义一个注解,定义此注解的目的是把它添加到需要实现幂等的方法上,只要某个方法注解了其,都会自动实现幂等操作。其代码如下
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface AutoIdempotent {
}
token 的创建和实现
token 服务接口,我们新建一个接口,创建token服务,里面主要是有两个方法,一个用来创建 token,一个用来验证token
public interface TokenService {
/**
* 创建token
* @return
*/
public String createToken();
/**
* 检验token
* @param request
* @return
*/
public boolean checkToken(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;
}
token 的实现类,token中引用了服务的实现类,token引用了 redis 服务,创建token采用随机算法工具类生成随机 uuid 字符串,然后放入 redis 中,如果放入成功,返回token,校验方法就是从 header 中获取 token 的值,如果不存在,直接跑出异常,这个异常信息可以被直接拦截到,返回给前端。
package cn.smallmartial.demo.service.impl;
import cn.smallmartial.demo.bean.RedisKeyPrefix;
import cn.smallmartial.demo.bean.ResponseCode;
import cn.smallmartial.demo.exception.ApiResult;
import cn.smallmartial.demo.exception.BusinessException;
import cn.smallmartial.demo.service.TokenService;
import cn.smallmartial.demo.utils.RedisUtil;
import io.netty.util.internal.StringUtil;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.UUID;
/**
* @Author smallmartial
* @Date 2020/4/16
* @Email smallmarital@qq.com
*/
@Service
public class TokenServiceImpl implements TokenService {
@Autowired
private RedisUtil redisService;
/**
* 创建token
*
* @return
*/
@Override
public String createToken() {
String str = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", "");
StringBuilder token = new StringBuilder();
try {
token.append(RedisKeyPrefix.TOKEN_PREFIX).append(str);
redisService.setEx(token.toString(), token.toString(), 10000L);
boolean empty = StringUtils.isEmpty(token.toString());
if (!empty) {
return token.toString();
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 检验token
*
* @param request
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean checkToken(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
String token = request.getHeader(RedisKeyPrefix.TOKEN_NAME);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(token)) {// header中不存在token
token = request.getParameter(RedisKeyPrefix.TOKEN_NAME);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(token)) {// parameter中也不存在token
throw new BusinessException(ApiResult.BADARGUMENT);
}
}
if (!redisService.exists(token)) {
throw new BusinessException(ApiResult.REPETITIVE_OPERATION);
}
boolean remove = redisService.remove(token);
if (!remove) {
throw new BusinessException(ApiResult.REPETITIVE_OPERATION);
}
return true;
}
}
拦截器的配置
用于拦截前端的 token,判断前端的 token 是否有效
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
@Bean
public AuthInterceptor authInterceptor() {
return new AuthInterceptor();
}
/**
* 拦截器配置
*
* @param registry
*/
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(authInterceptor());
// .addPathPatterns("/ksb/**")
// .excludePathPatterns("/ksb/auth/**", "/api/common/**", "/error", "/api/*");
super.addInterceptors(registry);
}
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/**").addResourceLocations(
"classpath:/static/");
registry.addResourceHandler("swagger-ui.html").addResourceLocations(
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/");
registry.addResourceHandler("/webjars/**").addResourceLocations(
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/");
super.addResourceHandlers(registry);
}
}
拦截处理器:主要用于拦截扫描到 Autoldempotent 到注解方法,然后调用 tokenService 的 checkToken 方法校验 token 是否正确,如果捕捉到异常就把异常信息渲染成 json 返回给前端。这部分代码主要和自定义注解部分挂钩。其主要代码如下所示
@Slf4j
public class AuthInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter {
@Autowired
private TokenService tokenService;
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
if (!(handler instanceof HandlerMethod)) {
return true;
}
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler;
Method method = handlerMethod.getMethod();
//被ApiIdempotment标记的扫描
AutoIdempotent methodAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(AutoIdempotent.class);
if (methodAnnotation != null) {
try {
return tokenService.checkToken(request);// 幂等性校验, 校验通过则放行, 校验失败则抛出异常, 并通过统一异常处理返回友好提示
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new BusinessException(ApiResult.REPETITIVE_OPERATION);
}
}
return true;
}
}
测试用例
这里进行相关的测试用例 模拟业务请求类,通过相关的路径获得相关的token,然后调用 testidempotence 方法,这个方法注解了 @Autoldempotent,拦截器会拦截所有的请求,当判断到处理的方法上面有该注解的时候,就会调用 TokenService 中的 checkToken() 方法,如果有异常会跑出,代码如下所示
/**
* @Author smallmartial
* @Date 2020/4/16
* @Email smallmarital@qq.com
*/
@RestController
public class BusinessController {
@Autowired
private TokenService tokenService;
@GetMapping("/get/token")
public Object getToken(){
String token = tokenService.createToken();
return ResponseUtil.ok(token) ;
}
@AutoIdempotent
@GetMapping("/test/Idempotence")
public Object testIdempotence() {
String token = "接口幂等性测试";
return ResponseUtil.ok(token) ;
}
}
用浏览器进行访问
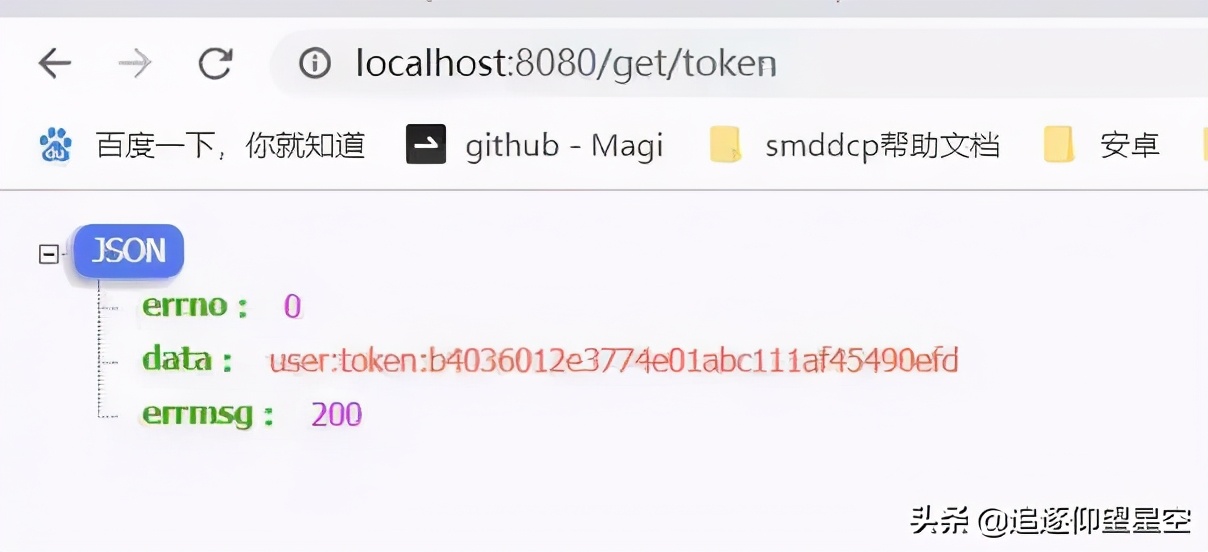
用获取到的token第一次访问
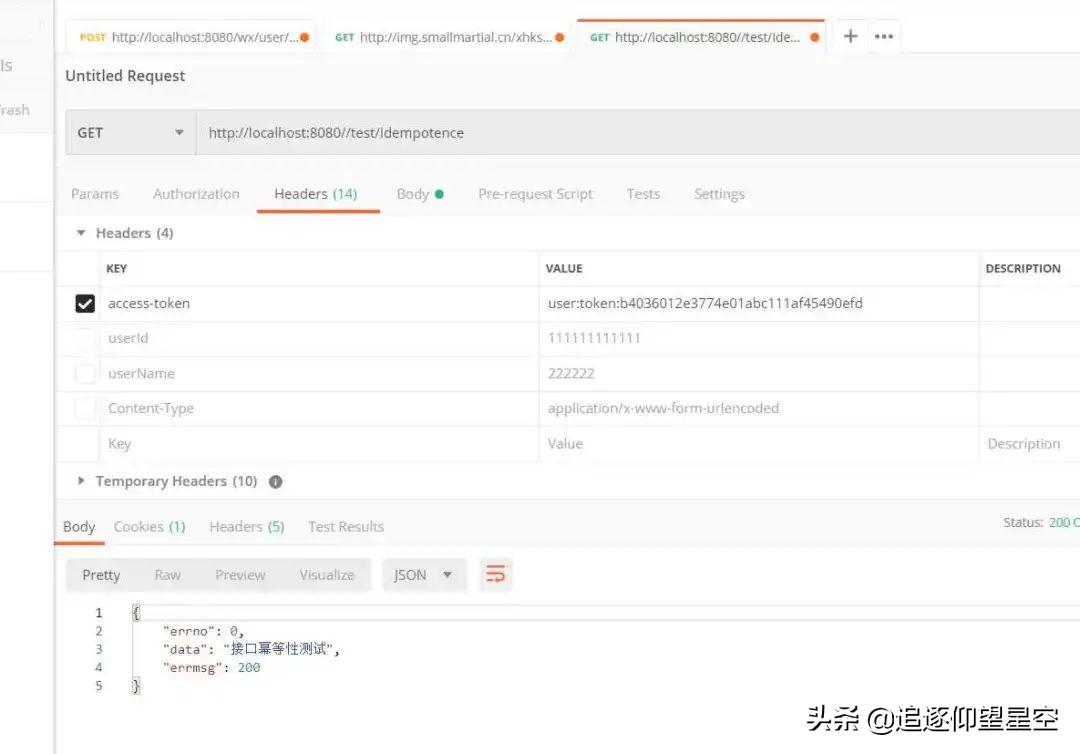
用获取到的token再次访问
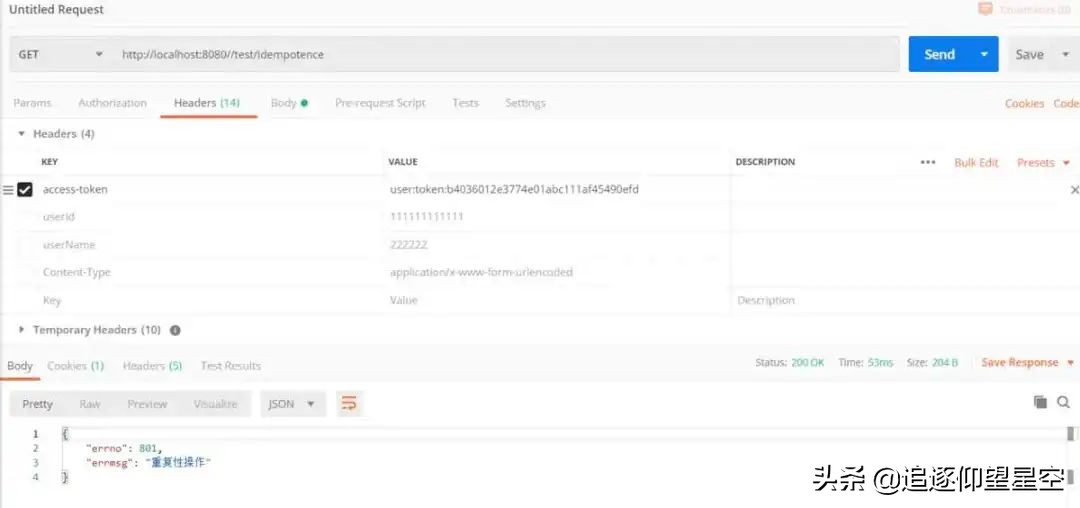
可以看到,第二次访问失败,即,幂等性验证通过。
到此这篇关于SpringBoot结合Redis实现接口幂等性的示例代码的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot Redis接口幂等性内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

