Pytorch损失函数nn.NLLLoss2d()用法说明
最近做显著星检测用到了NLL损失函数
对于NLL函数,需要自己计算log和softmax的概率值,然后从才能作为输入
输入 [batch_size, channel , h, w]
目标 [batch_size, h, w]
输入的目标矩阵,每个像素必须是类型.举个例子。第一个像素是0,代表着类别属于输入的第1个通道;第二个像素是0,代表着类别属于输入的第0个通道,以此类推。
x = Variable(torch.Tensor([[[1, 2, 1],
[2, 2, 1],
[0, 1, 1]],
[[0, 1, 3],
[2, 3, 1],
[0, 0, 1]]]))
x = x.view([1, 2, 3, 3])
print("x输入", x)
这里输入x,并改成[batch_size, channel , h, w]的格式。
soft = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
log_soft = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
然后使用softmax函数计算每个类别的概率,这里dim=1表示从在1维度
上计算,也就是channel维度。logsoftmax是计算完softmax后在计算log值

手动计算举个栗子:第一个元素

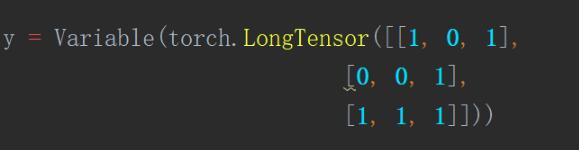
y = Variable(torch.LongTensor([[1, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 1]]))
y = y.view([1, 3, 3])
输入label y,改变成[batch_size, h, w]格式
loss = nn.NLLLoss2d() out = loss(x, y) print(out)
输入函数,得到loss=0.7947
来手动计算
第一个label=1,则 loss=-1.3133
第二个label=0, 则loss=-0.3133
. … … loss= -(-1.3133-0.3133-0.1269-0.6931-1.3133-0.6931-0.6931-1.3133-0.6931)/9 =0.7947222222222223
是一致的
注意:这个函数会对每个像素做平均,每个batch也会做平均,这里有9个像素,1个batch_size。
补充知识:PyTorch:NLLLoss2d
我就废话不多说了,大家还是直接看代码吧~
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch import autograd
import torch.nn.functional as F
inputs_tensor = torch.FloatTensor([
[[2, 4],
[1, 2]],
[[5, 3],
[3, 0]],
[[5, 3],
[5, 2]],
[[4, 2],
[3, 2]],
])
inputs_tensor = torch.unsqueeze(inputs_tensor,0)
# inputs_tensor = torch.unsqueeze(inputs_tensor,1)
print '--input size(nBatch x nClasses x height x width): ', inputs_tensor.shape
targets_tensor = torch.LongTensor([
[0, 2],
[2, 3]
])
targets_tensor = torch.unsqueeze(targets_tensor,0)
print '--target size(nBatch x height x width): ', targets_tensor.shape
inputs_variable = autograd.Variable(inputs_tensor, requires_grad=True)
inputs_variable = F.log_softmax(inputs_variable)
targets_variable = autograd.Variable(targets_tensor)
loss = nn.NLLLoss2d()
output = loss(inputs_variable, targets_variable)
print '--NLLLoss2d: {}'.format(output)
以上这篇Pytorch损失函数nn.NLLLoss2d()用法说明就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。
赞 (0)

