Java自定义Spring配置标签
引言:
在Sping中,一般使用<bean>这样的元素来配置一个bean,Spring在创建容器的时候会扫描这些配置,根据配置创建对象存放于容器中,然后我们再从容器中取出,或者在配置其他bean的时候作为属性注入。使用bean配置的一个限制是我们必须遵循配置文件的XML Schema定义,这在大多数情况下不会出现问题。但是在一些情况下,我们希望实现更为灵活的bean配置。Spring为此提供了 Custom tag Support,也称为Extensible XML Authoring。通过这个拓展点,我们可以灵活定制自己需要的配置格式。
例如,如果我们使用了责任链设计应用程序,那么我们可能希望用下面的方式来配置责任链:
<chain id="orderChain" class="foo.bar">
<handler> handler1</handler>
<hadnler> handler2</handler>
</chain>
档Spring创建容器时,扫描到这样的元素的时候,会根据我们事先的定义实例化一个责任链对象,并填充属性。因此,这种特殊的<chain>标签可以作为<bean>标签以外的另一种形式。借助Spring的Custome Tag,我们完全可以实现这样的bean配置。在产品级的应用框架中,可以实现更为复杂的定制标签元素。作为一个入门级别的介绍,我们定义一个用于配置日期格式化的一个类SimpleDateFormat。当然,使用传统的<bean>完全够用,我们这里只是作为例子。
一个HelloWorld例子:
定制标签的第一步是要定义标签元素的XML结构,也就是采用XSD来元素我们要定制的元素的结构时怎样的。
我们定义如下一个简单的XSD:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xsd:schema xmlns="http://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
targetNamespace="http://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns"
elementFormDefault="qualified"
attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<xsd:import namespace="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"/>
<xsd:element name="dateformat">
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:complexContent>
<xsd:extension base="beans:identifiedType">
<xsd:attribute name="lenient" type="xsd:boolean"/>
<xsd:attribute name="pattern" type="xsd:string" use="required"/>
</xsd:extension>
</xsd:complexContent>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
</xsd:schema>
在这个XSD定义中,有一个标签叫dateformat,这就是我们用来替换bean标签的自定义标签。注意到我们导入了Spring本身的beans命名空间,并且在beans:identifiedType基础之上定义dateformat标签。也就是我们这个标签可以像<bean>标签一样拥有id属性。同时我们增加了两个属性lenient和pattern。这有点继承的味道。
定义完XSD之后,我们要告诉Spring遇到这样的标记(命名空间+元素名称)时,如何创建对象。Spring中,完成这个任务的是NamespaceHandler。因此我们需要提供一个NamespaceHandler实现来处理自定义的<dateformat>标签元素。
一个简单的实现如下:
package extensiblexml.customtag;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.NamespaceHandlerSupport;
public class MyNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("dateformat",
new SimpleDateFormatBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}
我们在初始化方法中注册了一个Bean定义的解析器,这个解析器就是用来解析定制的配置标签的。
其实现如下:
package extensiblexml.customtag;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
public class SimpleDateFormatBeanDefinitionParser extends AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser {
protected Class<SimpleDateFormat> getBeanClass(Element element) {
return SimpleDateFormat.class;
}
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
protected void doParse(Element element, BeanDefinitionBuilder bean) {
// this will never be null since the schema explicitly requires that a value be supplied
String pattern = element.getAttribute("pattern");
bean.addConstructorArg(pattern);
// this however is an optional property
String lenient = element.getAttribute("lenient");
if (StringUtils.hasText(lenient)) {
bean.addPropertyValue("lenient", Boolean.valueOf(lenient));
}
}
}
这个解析器的doParse中,实现了解析的具体逻辑,借助Spring提供的支持类,我们可以很轻松地完成解析。以上三个文件放在同一个目录下,即把XSD文件跟Java代码放在同一目录。编码完毕之后,还需要做一些配置工作。我们必须告诉Spring我们准备使用自定义的标签元素,告诉Spring如何解析元素,否则Spring没那么聪明。这里需要2个配置文件,在与代码根路径同一级别下,床垫一个叫META-INF的文件。并在里面创建名为spring.handlers和spring.schemas,用于告诉Spring自定义标签的文档结构以及解析它的类。两个文件内容分别如下:
spring.handlers:
http\://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns=extensiblexml.customtag.MyNamespaceHandler
等号的左边是XSD定义中的targetNamespace属性,右边是NamespaceHandler的全称限定名。
spring.schemas:
http\://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns/myns.xsd=extensiblexml/customtag/myns.xsd
然后像往常一样配置bean,作为简单的测试,我们定义一个bean:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:myns="http://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns http://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns/myns.xsd" > <myns:dateformat id="defaultDateFormat" pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm" lenient="true" /> </beans>
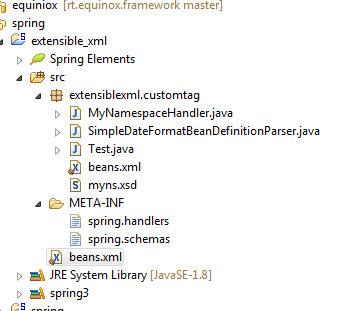
在Eclipse中,整个项目结构如下图:
最后我们写个测试类测试一下能否工作:
package extensiblexml.customtag;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"beans.xml");
SimpleDateFormat format = (SimpleDateFormat) context
.getBean("defaultDateFormat");
System.out.println(format.format(new Date()));
}
}
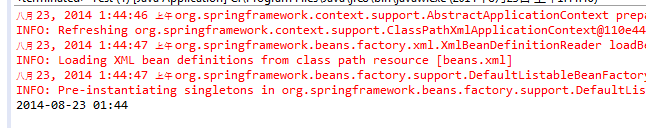
一切正常,输出如下:
更实用的例子
第一个例子主要是为了举例,在实际中用处不大,我们接着来看一个更复杂的自定义标签。我们自定义一个<fileList>标签,当Spring扫描到这个标签的时候,创建一个指定目录下的File类的集合。另外,可以使用<fileFilter>对该目录的文件进行过滤。
如下:
<core-commons:fileList id="xmlList" directory="src/extensiblexml/example">
<core-commons:fileFilter>
<bean class="org.apache.commons.io.filefilter.RegexFileFilter">
<constructor-arg value=".*.java" />
</bean>
</core-commons:fileFilter>
</core-commons:fileList>
上面的bean定义中,我们从“src/extensible/example”目录中筛选出java源码文件。
使用下面的测试迭代输出文件名:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<File> fileList = (List<File>) context.getBean("xmlList");
for (File file : fileList) {
System.out.println(file.getName());
}
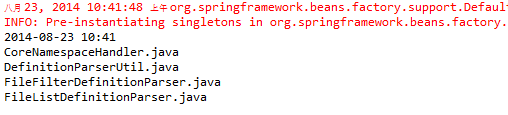
输出结果如下:
根据第一个例子中的步骤,各部分配置及代码如下:
core-commons-1.0.xsd:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xsd:schema xmlns="http://www.example.com/schema/core-commons-1.0"
targetNamespace="http://www.example.com/schema/core-commons-1.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
elementFormDefault="qualified"
attributeFormDefault="unqualified"
version="1.0">
<xsd:import namespace="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"/>
<xsd:element name="fileList">
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:complexContent>
<xsd:extension base="beans:identifiedType">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element ref="fileFilter" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xsd:element ref="fileList" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xsd:sequence>
<xsd:attribute name="directory" type="xsd:string"/>
<xsd:attribute name="scope" type="xsd:string"/>
</xsd:extension>
</xsd:complexContent>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
<xsd:element name="fileFilter">
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:complexContent>
<xsd:extension base="beans:identifiedType">
<xsd:group ref="limitedType"/>
<xsd:attribute name="scope" type="xsd:string"/>
</xsd:extension>
</xsd:complexContent>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
<xsd:group name="limitedType">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:choice minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xsd:element ref="beans:bean"/>
<xsd:element ref="beans:ref"/>
<xsd:element ref="beans:idref"/>
<xsd:element ref="beans:value"/>
<xsd:any minOccurs="0"/>
</xsd:choice>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:group>
</xsd:schema>
CoreNamespaceHandler.java:
package extensiblexml.example;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.NamespaceHandlerSupport;
public class CoreNamespaceHandler
extends NamespaceHandlerSupport
{
@Override
public void init() {
this.registerBeanDefinitionParser("fileList", new FileListDefinitionParser());
this.registerBeanDefinitionParser("fileFilter", new FileFilterDefinitionParser());
}
}
FileListDefinitionParser.java:
public class FileListDefinitionParser
extends AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser
{
/**
* The bean that is created for this tag element
*
* @param element The tag element
* @return A FileListFactoryBean
*/
@Override
protected Class<?> getBeanClass(Element element) {
return FileListFactoryBean.class;
}
/**
* Called when the fileList tag is to be parsed
*
* @param element The tag element
* @param ctx The context in which the parsing is occuring
* @param builder The bean definitions build to use
*/
@Override
protected void doParse(Element element, ParserContext ctx, BeanDefinitionBuilder builder) {
// Set the directory property
builder.addPropertyValue("directory", element.getAttribute("directory"));
// Set the scope
builder.setScope(element.getAttribute("scope"));
// We want any parsing to occur as a child of this tag so we need to make
// a new one that has this as it's owner/parent
ParserContext nestedCtx = new ParserContext(ctx.getReaderContext(), ctx.getDelegate(), builder.getBeanDefinition());
// Support for filters
Element exclusionElem = DomUtils.getChildElementByTagName(element, "fileFilter");
if (exclusionElem != null) {
// Just make a new Parser for each one and let the parser do the work
FileFilterDefinitionParser ff = new FileFilterDefinitionParser();
builder.addPropertyValue("filters", ff.parse(exclusionElem, nestedCtx));
}
// Support for nested fileList
List<Element> fileLists = DomUtils.getChildElementsByTagName(element, "fileList");
// Any objects that created will be placed in a ManagedList
// so Spring does the bulk of the resolution work for us
ManagedList<Object> nestedFiles = new ManagedList<Object>();
if (fileLists.size() > 0) {
// Just make a new Parser for each one and let them do the work
FileListDefinitionParser fldp = new FileListDefinitionParser();
for (Element fileListElem : fileLists) {
nestedFiles.add(fldp.parse(fileListElem, nestedCtx));
}
}
// Support for other tags that return File (value will be converted to file)
try {
// Go through any other tags we may find. This does not mean we support
// any tag, we support only what parseLimitedList will process
NodeList nl = element.getChildNodes();
for (int i=0; i<nl.getLength(); i++) {
// Parse each child tag we find in the correct scope but we
// won't support custom tags at this point as it coudl destablize things
DefinitionParserUtil.parseLimitedList(nestedFiles, nl.item(i), ctx,
builder.getBeanDefinition(), element.getAttribute("scope"), false);
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
// Set the nestedFiles in the properties so it is set on the FactoryBean
builder.addPropertyValue("nestedFiles", nestedFiles);
}
public static class FileListFactoryBean
implements FactoryBean<Collection<File>>
{
String directory;
private Collection<FileFilter> filters;
private Collection<File> nestedFiles;
@Override
public Collection<File> getObject() throws Exception {
// These can be an array list because the directory will have unique's and the nested is already only unique's
Collection<File> files = new ArrayList<File>();
Collection<File> results = new ArrayList<File>(0);
if (directory != null) {
// get all the files in the directory
File dir = new File(directory);
File[] dirFiles = dir.listFiles();
if (dirFiles != null) {
files = Arrays.asList(dirFiles);
}
}
// If there are any files that were created from the nested tags,
// add those to the list of files
if (nestedFiles != null) {
files.addAll(nestedFiles);
}
// If there are filters we need to go through each filter
// and see if the files in the list pass the filters.
// If the files does not pass any one of the filters then it
// will not be included in the list
if (filters != null) {
boolean add;
for (File f : files) {
add = true;
for (FileFilter ff : filters) {
if (!ff.accept(f)) {
add = false;
break;
}
}
if (add) results.add(f);
}
return results;
}
return files;
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return Collection.class;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return false;
}
public void setDirectory(String dir) {
this.directory = dir;
}
public void setFilters(Collection<FileFilter> filters) {
this.filters = filters;
}
/**
* What we actually get from the processing of the nested tags
* is a collection of files within a collection so we flatten it and
* only keep the uniques
*/
public void setNestedFiles(Collection<Collection<File>> nestedFiles) {
this.nestedFiles = new HashSet<File>(); // keep the list unique
for (Collection<File> nested : nestedFiles) {
this.nestedFiles.addAll(nested);
}
}
}
}
FileFilterDefinitionParser.java
public class FileFilterDefinitionParser
extends AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser
{
/**
* The bean that is created for this tag element
*
* @param element The tag element
* @return A FileFilterFactoryBean
*/
@Override
protected Class<?> getBeanClass(Element element) {
return FileFilterFactoryBean.class;
}
/**
* Called when the fileFilter tag is to be parsed
*
* @param element The tag element
* @param ctx The context in which the parsing is occuring
* @param builder The bean definitions build to use
*/
@Override
protected void doParse(Element element, ParserContext ctx, BeanDefinitionBuilder builder) {
// Set the scope
builder.setScope(element.getAttribute("scope"));
try {
// All of the filters will eventually end up in this list
// We use a 'ManagedList' and not a regular list because anything
// placed in a ManagedList object will support all of Springs
// functionalities and scopes for us, we dont' have to code anything
// in terms of reference lookups, EL, etc
ManagedList<Object> filters = new ManagedList<Object>();
// For each child node of the fileFilter tag, parse it and place it
// in the filtes list
NodeList nl = element.getChildNodes();
for (int i=0; i<nl.getLength(); i++) {
DefinitionParserUtil.parseLimitedList(filters, nl.item(i), ctx, builder.getBeanDefinition(), element.getAttribute("scope"));
}
// Add the filtes to the list of properties (this is applied
// to the factory beans setFilters below)
builder.addPropertyValue("filters", filters);
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static class FileFilterFactoryBean
implements FactoryBean<Collection<FileFilter>>
{
private final List<FileFilter> filters = new ArrayList<FileFilter>();
@Override
public Collection<FileFilter> getObject() throws Exception {
return filters;
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return Collection.class;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return false;
}
/**
* Go through the list of filters and convert the String ones
* (the ones that were set with <value> and make them NameFileFilters
*/
public void setFilters(Collection<Object> filterList) {
for (Object o : filterList) {
if (o instanceof String) {
filters.add(new NameFileFilter(o.toString()));
}
else if (o instanceof FileFilter) {
filters.add((FileFilter)o);
}
}
}
}
}
DefinitionParserUtil.java:
package extensiblexml.example;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinitionHolder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionReaderUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ManagedList;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.BeanDefinitionParserDelegate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.ParserContext;
import org.springframework.expression.Expression;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
public class DefinitionParserUtil {
/**
* Parses the children of the passed in ParentNode for the following tags:
* <br/>
* value
* ref
* idref
* bean
* property
* *custom*
* <p/>
*
* The value tag works with Spring EL even in a Spring Batch scope="step"
*
* @param objects The list of resultings objects from the parsing (passed in for recursion purposes)
* @param parentNode The node who's children should be parsed
* @param ctx The ParserContext to use
* @param parentBean The BeanDefinition of the bean who is the parent of the parsed bean
* (i.e. the Bean that is the parentNode)
* @param scope The scope to execute in. Checked if 'step' to provide Spring EL
* support in a Spring Batch env
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void parseLimitedList(ManagedList<Object> objects, Node node,
ParserContext ctx, BeanDefinition parentBean, String scope)
throws Exception
{
parseLimitedList(objects, node, ctx, parentBean, scope, true);
}
/**
* Parses the children of the passed in ParentNode for the following tags:
* <br/>
* value
* ref
* idref
* bean
* property
* *custom*
* <p/>
*
* The value tag works with Spring EL even in a Spring Batch scope="step"
*
* @param objects The list of resultings objects from the parsing (passed in for recursion purposes)
* @param parentNode The node who's children should be parsed
* @param ctx The ParserContext to use
* @param parentBean The BeanDefinition of the bean who is the parent of the parsed bean
* (i.e. the Bean that is the parentNode)
* @param scope The scope to execute in. Checked if 'step' to provide Spring EL
* support in a Spring Batch env
* @param supportCustomTags Should we support custom tags within our tags?
* @throws Exception
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static void parseLimitedList(ManagedList<Object> objects, Node node,
ParserContext ctx, BeanDefinition parentBean, String scope, boolean supportCustomTags)
throws Exception
{
// Only worry about element nodes
if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
Element elem = (Element)node;
String tagName = node.getLocalName();
if (tagName.equals("value")) {
String val = node.getTextContent();
// to get around an issue with Spring Batch not parsing Spring EL
// we will do it for them
if (scope.equals("step")
&& (val.startsWith("#{") && val.endsWith("}"))
&& (!val.startsWith("#{jobParameters"))
)
{
// Set up a new EL parser
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
// Parse the value
Expression exp = parser.parseExpression(val.substring(2, val.length()-1));
// Place the results in the list of created objects
objects.add(exp.getValue());
}
else {
// Otherwise, just treat it as a normal value tag
objects.add(val);
}
}
// Either of these is a just a lookup of an existing bean
else if (tagName.equals("ref") || tagName.equals("idref")) {
objects.add(ctx.getRegistry().getBeanDefinition(node.getTextContent()));
}
// We need to create the bean
else if (tagName.equals("bean")) {
// There is no quick little util I could find to create a bean
// on the fly programmatically in Spring and still support all
// Spring functionality so basically I mimic what Spring actually
// does but on a smaller scale. Everything Spring allows is
// still supported
// Create a factory to make the bean
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
// Set up a parser for the bean
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate pd = new BeanDefinitionParserDelegate(ctx.getReaderContext());
// Parse the bean get its information, now in a DefintionHolder
BeanDefinitionHolder bh = pd.parseBeanDefinitionElement(elem, parentBean);
// Register the bean will all the other beans Spring is aware of
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bh, beanFactory);
// Get the bean from the factory. This will allows Spring
// to do all its work (EL processing, scope, etc) and give us
// the actual bean itself
Object bean = beanFactory.getBean(bh.getBeanName());
objects.add(bean);
}
/*
* This is handled a bit differently in that it actually sets the property
* on the parent bean for us based on the property
*/
else if (tagName.equals("property")) {
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate pd = new BeanDefinitionParserDelegate(ctx.getReaderContext());
// This method actually set eh property on the parentBean for us so
// we don't have to add anything to the objects object
pd.parsePropertyElement(elem, parentBean);
}
else if (supportCustomTags) {
// handle custom tag
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate pd = new BeanDefinitionParserDelegate(ctx.getReaderContext());
BeanDefinition bd = pd.parseCustomElement(elem, parentBean);
objects.add(bd);
}
}
}
}
spring.schemas
http\://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns/myns.xsd=extensiblexml/customtag/myns.xsd
http\://www.example.com/schema/core-commons-1.0.xsd=extensiblexml/example/core-commons-1.0.xsd
spring.handlers
http\://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns=extensiblexml.customtag.MyNamespaceHandler
http\://www.example.com/schema/core-commons-1.0=extensiblexml.example.CoreNamespaceHandler
小结:
要自定义Spring的配置标签,需要一下几个步骤:
- 使用XSD定义XML配置中标签元素的结构(myns.XSD)
- 提供该XSD命名空间的处理类,它可以处理多个标签定义(MyNamespaceHandler.java)
- 为每个标签元素的定义提供解析类。(SimpleDateFormatBeanDefinitionParser.java)
- 两个特殊文件通知Spring使用自定义标签元素(spring.handlers 和spring.schemas)
到此这篇关于Java自定义Spring配置标签的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java Spring配置标签内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

