Spring Cache框架应用介绍
目录
- 介绍
- 常用注解
- 实际测试
介绍
Spring Cache是一个框架,实现了基于注解的缓存功能,只需要简单地加一个注解,就能实现缓存功能。
Spring Cache提供了一层抽象,底层可以切换不同的cache实现。具体就是通过CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术。
CacheManager是Spring提供的各种缓存技术抽象接口。
针对不同的缓存技术需要实现不同的CacheManager:
| CacheManager | 描述 |
|---|---|
| EhCacheCacheManager | 使用EhCache作为缓存技术 |
| GuavaCacheManager | 使用Google的GuavaCache作为缓存技术 |
| RedisCacheManager | 使用Redis作为缓存技术 |
常用注解
| 注解 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| @EnableCaching | 开启缓存注解功能 |
| @Cacheable | 在方法执行前spring先查看缓存中是否有数据,如果有数据,则直接返回缓存数据;若没有数据,调用方法并将方法返回值放到缓存中 |
| @CachePut | 将方法的返回值放到缓存中 |
| @CacheEvict | 将一条或多条数据从缓存中删除 |
在Spring Boot项目中,使用缓存技术只需在项目中导入相关缓存技术的依赖包,并在启动类上使用@EnableCaching开启缓存支持即可。
例如,使用Redis作为缓存技术,只需要导入spring-boot-starter-data-redis的Maven坐标即可。
实际测试
使用Spring Cache(默认缓存ConcurrentMapCacheManager)
创建Spring Boot项目,使用MybatisX插件生成对应的mapper、service、实体类等,导入相关依赖,修改配置文件,创建数据库
pom.xml如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.4.5</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.itheima</groupId>
<artifactId>cache_demo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.20</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.76</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-lang</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang</artifactId>
<version>2.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.23</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.4.5</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
application.yml如下:
server:
port: 8080
spring:
application:
#应用的名称,可选
name: cache_demo
datasource:
druid:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/cache_demo?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true
username: root
password: 123456
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
#在映射实体或者属性时,将数据库中表名和字段名中的下划线去掉,按照驼峰命名法映射
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
global-config:
db-config:
id-type: ASSIGN_ID
数据库SQL如下:
/* Navicat Premium Data Transfer Source Server : Aiw Source Server Type : MySQL Source Server Version : 50528 Source Host : localhost:3306 Source Schema : cache_demo Target Server Type : MySQL Target Server Version : 50528 File Encoding : 65001 */ SET NAMES utf8mb4; SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0; -- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for user -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`; CREATE TABLE `user` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL, `name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, `age` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL, `address` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Compact; -- ---------------------------- -- Records of user -- ---------------------------- INSERT INTO `user` VALUES (1568896554487369729, 'Aiw', 22, '湖北省'); SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
在启动类上添加@EnableCaching注解
package com.itheima;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
@Slf4j
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching // 开启缓存注解功能
public class CacheDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CacheDemoApplication.class,args);
log.info("项目启动成功...");
}
}
创建UserController
package com.itheima.controller;
import com.itheima.entity.User;
import com.itheima.service.UserService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
@Slf4j
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private CacheManager cacheManager;
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
/**
* CachePut:将方法返回值放入缓存
* value:缓存的名称,每个缓存名称下面可以有多个key
* key:缓存的key
*/
@CachePut(value = "userCache", key = "#user.id")
@PostMapping
public User save(User user) {
userService.save(user);
return user;
}
/**
* CacheEvict:清理指定缓存
* value:缓存的名称,每个缓存名称下面可以有多个key
* key:缓存的key
*/
@CacheEvict(value = "userCache", key = "#p0")
//@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#root.args[0]")
//@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#id")
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public void delete(@PathVariable Long id) {
userService.removeById(id);
}
//@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#p0.id")
//@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#user.id")
//@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#root.args[0].id")
@CacheEvict(value = "userCache", key = "#result.id")
@PutMapping
public User update(User user) {
userService.updateById(user);
return user;
}
/**
* Cacheable:在方法执行前spring先查看缓存中是否有数据,如果有数据,则直接返回缓存数据;若没有数据,调用方法并将方法返回值放到缓存中
* value:缓存的名称,每个缓存名称下面可以有多个key
* key:缓存的key
* condition:条件,满足条件时才缓存数据
* unless:满足条件则不缓存
*/
@Cacheable(value = "userCache", key = "#id", unless = "#result == null")
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public User getById(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.getById(id);
}
@Cacheable(value = "userCache", key = "#user.id + '_' + #user.name")
@GetMapping("/list")
public List<User> list(User user) {
return userService.lambdaQuery()
.eq(Objects.nonNull(user.getId()), User::getId, user.getId())
.eq(Objects.nonNull(user.getName()), User::getName, user.getName())
.list();
}
}
以上不同写法均等价
使用ApiPost进行接口测试
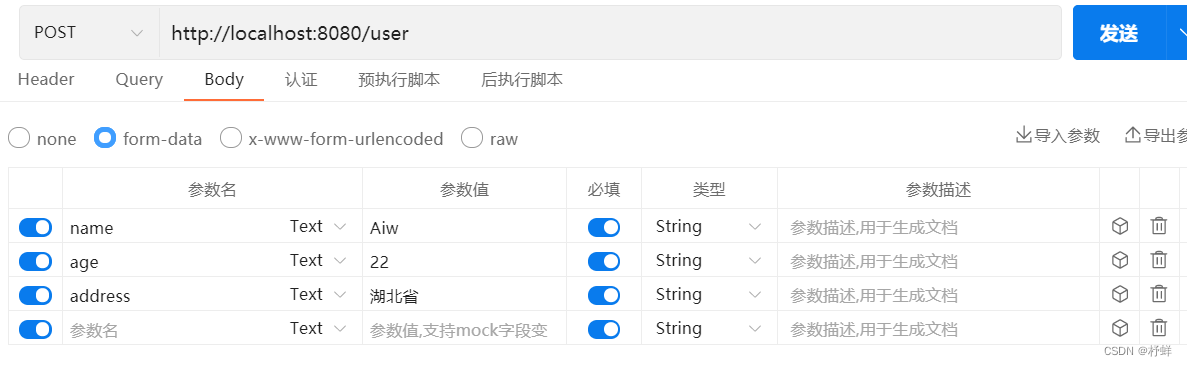
打断点调试,发送请求,可以看到已存入缓存

该缓存底层基于Map实现,默认ConcurrentHashMap基于内存,重启服务会清空缓存数据
使用Spring Cache(redis缓存RedisCacheManager)
导入Maven坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
修改配置文件
server:
port: 8080
spring:
application:
#应用的名称,可选
name: cache_demo
datasource:
druid:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/cache_demo?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true
username: root
password: 123456
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
# password: root@123456
database: 0
cache:
redis:
time-to-live: 1800000 #设置缓存过期时间(单位:秒),可选
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
#在映射实体或者属性时,将数据库中表名和字段名中的下划线去掉,按照驼峰命名法映射
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
global-config:
db-config:
id-type: ASSIGN_ID
启动项目,再次请求接口
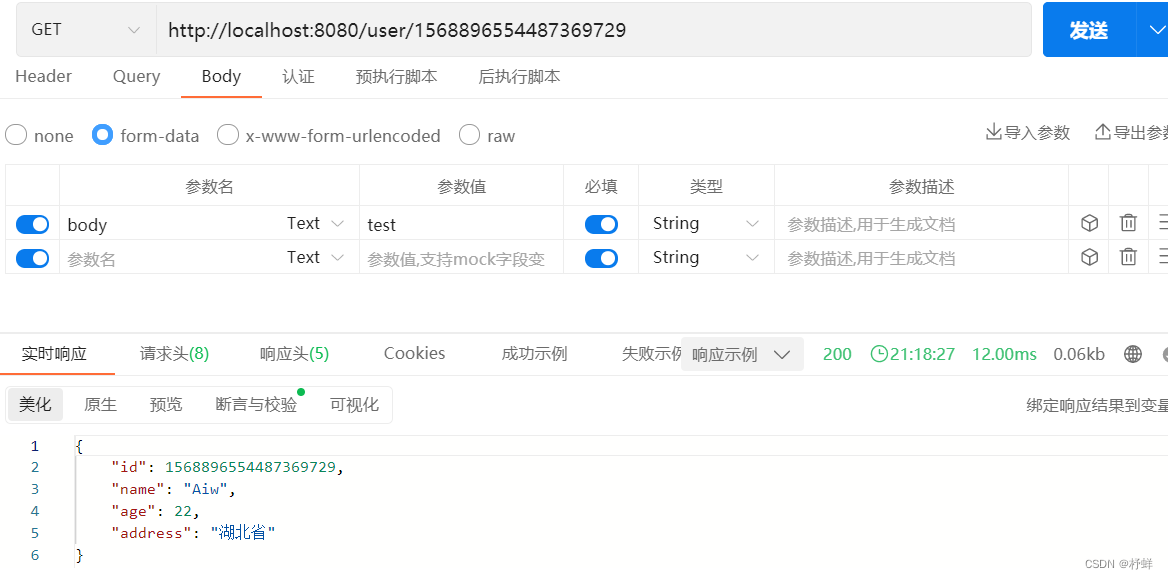
启动redis命令行窗口,查看

当请求不存在的id时,不会执行缓存操作(@Cacheable注解的unless条件起作用)
到此这篇关于Spring Cache框架应用介绍的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Spring Cache框架内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

