Spring AspectJ 实现AOP的方法你了解吗
目录
- 1、什么是 AspectJ?
- 2、切入点表达式
- AOP 切入点表达式支持多种形式的定义规则:
- 2、Aspect 通知类型
- 3、AOP具体实例
- ①、创建接口
- ②、创建实现类
- ③、创建切面类(包含各种通知)
- ④、创建spring配置文件applicationContext.xml
- ⑤、测试
- 4、测试异常通知
- 5、测试环绕通知
- 总结
1、什么是 AspectJ?
AspectJ是一个面向切面的框架,它扩展了Java语言。AspectJ定义了AOP语法,也可以说 AspectJ 是一个基于 Java 语言的 AOP 框架。通常我们在使用 Spring AOP 的时候,都会导入 AspectJ 的相关 jar 包。

在 spring2.0以后,spring新增了对AspectJ 切点表达式的支持;Aspect1.5新增注解功能,通过 JDK5的注解技术,能直接在类中定义切面;新版本的 spring 框架,也都建议使用 AspectJ 来实现 AOP。所以说在 spring AOP 的核心包 Spring-aop-3.2.jar 里面也有对 AspectJ 的支持。
2、切入点表达式
上一篇博客中,我们在spring配置文件中配置如下:
<!-- 切入点表达式 --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.ys.aop.*.*(..))" id="myPointCut"/>
那么它表达的意思是 返回值任意,包名为 com.ys.aop 下的任意类名中的任意方法名,参数任意。那么这到底是什么意思呢?
首先 execution 是 AspectJ 框架定义的一个切入点函数,其语法形式如下:
execution(modifiers-pattern? ref-type-pattern declaring-type-pattern? name-pattern(param-pattern) throws-pattern?) 类修饰符 返回值 方法所在的包 方法名 方法抛出的异常
简单点来说就是:
语法:execution(修饰符 返回值 包.类.方法名(参数) throws异常)
具体解释我们用下面一张思维导图来看:
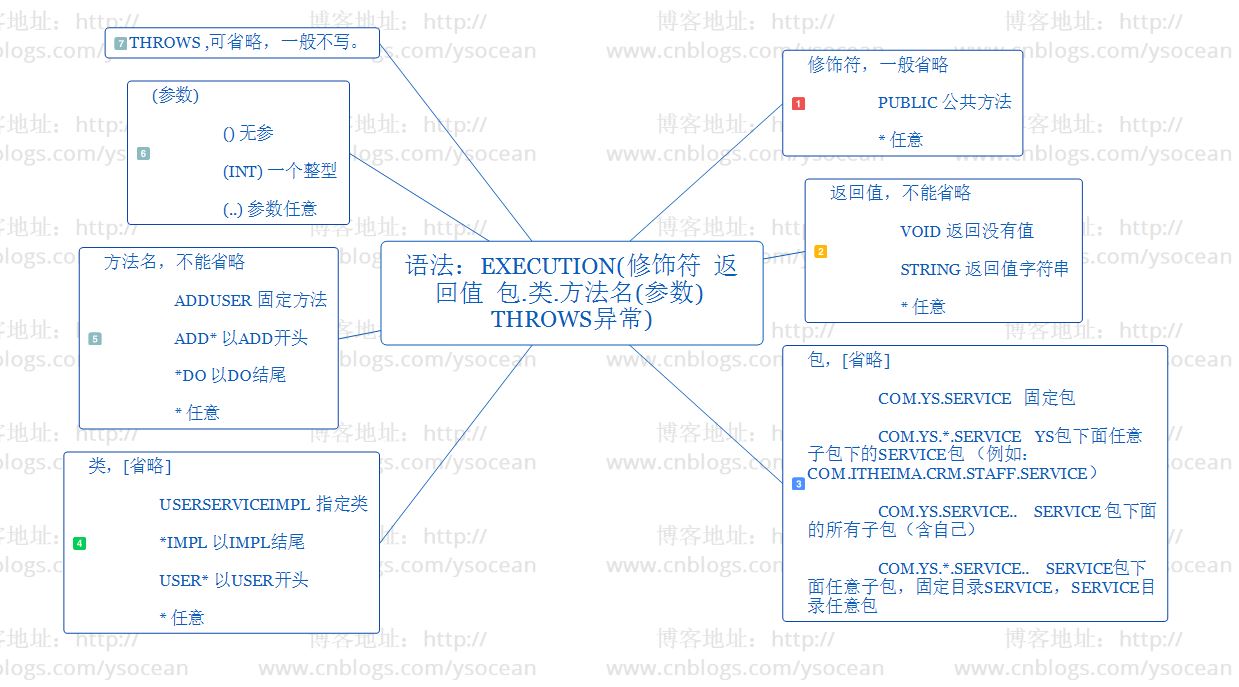
注意:如果切入点表达式有多个不同目录呢? 可以通过 || 来表示或的关系。
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.ys.*Service1.*(..)) ||
execution(* com.ys.*Service2.*(..))" id="myPointCut"/>
表示匹配 com.ys包下的,以 Service1结尾或者以Service2结尾的类的任意方法。
AOP 切入点表达式支持多种形式的定义规则:
1、execution:匹配方法的执行(常用)
execution(public *.*(..))
2.within:匹配包或子包中的方法(了解)
within(com.ys.aop..*)
3.this:匹配实现接口的代理对象中的方法(了解)
this(com.ys.aop.user.UserDAO)
4.target:匹配实现接口的目标对象中的方法(了解)
target(com.ys.aop.user.UserDAO)
5.args:匹配参数格式符合标准的方法(了解)
args(int,int)
6.bean(id) 对指定的bean所有的方法(了解)
bean('userServiceId')
2、Aspect 通知类型
Aspect 通知类型,定义了类型名称以及方法格式。类型如下:
before:前置通知(应用:各种校验)
在方法执行前执行,如果通知抛出异常,阻止方法运行
afterReturning:后置通知(应用:常规数据处理)
方法正常返回后执行,如果方法中抛出异常,通知无法执行
必须在方法执行后才执行,所以可以获得方法的返回值。
around:环绕通知(应用:十分强大,可以做任何事情)
方法执行前后分别执行,可以阻止方法的执行
必须手动执行目标方法
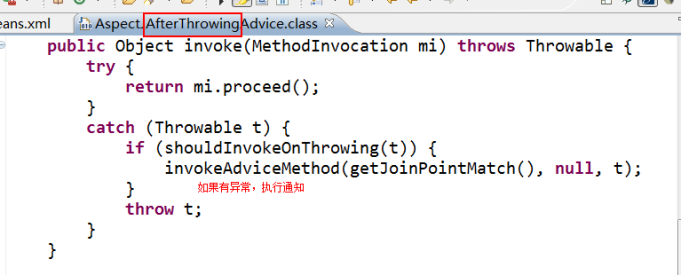
afterThrowing:抛出异常通知(应用:包装异常信息)
方法抛出异常后执行,如果方法没有抛出异常,无法执行
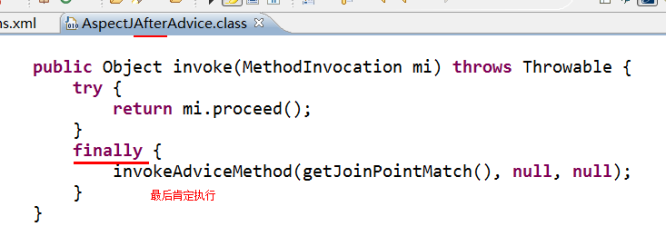
after:最终通知(应用:清理现场)
方法执行完毕后执行,无论方法中是否出现异常
这里最重要的是around,环绕通知,它可以代替上面的任意通知。
在程序中表示的意思如下:
try{
//前置:before
//手动执行目标方法
//后置:afterRetruning
} catch(){
//抛出异常 afterThrowing
} finally{
//最终 after
}
对应的 jar 包如下:
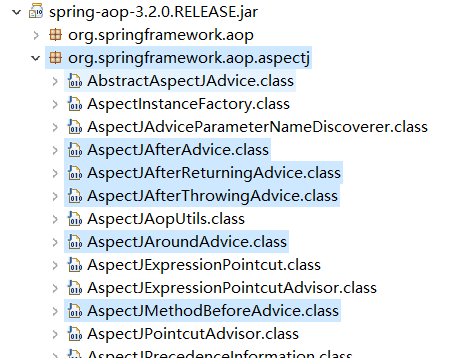
我们可以查看源码:
3、AOP具体实例
①、创建接口
package com.ys.aop;
public interface UserService {
//添加 user
public void addUser();
//删除 user
public void deleteUser();
}
②、创建实现类
package com.ys.aop;
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
@Override
public void addUser() {
System.out.println("增加 User");
}
@Override
public void deleteUser() {
System.out.println("删除 User");
}
}
③、创建切面类(包含各种通知)
package com.ys.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
public class MyAspect {
/**
* JoinPoint 能获取目标方法的一些基本信息
* @param joinPoint
*/
public void myBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("前置通知 : " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
}
public void myAfterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object ret){
System.out.println("后置通知 : " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName() + " , -->" + ret);
}
public void myAfter(){
System.out.println("最终通知");
}
}
④、创建spring配置文件applicationContext.xml
我们首先测试前置通知、后置通知、最终通知
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--1、 创建目标类 -->
<bean id="userService" class="com.ys.aop.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<!--2、创建切面类(通知) -->
<bean id="myAspect" class="com.ys.aop.MyAspect"></bean>
<!--3、aop编程
3.1 导入命名空间
3.2 使用 <aop:config>进行配置
proxy-target-class="true" 声明时使用cglib代理
如果不声明,Spring 会自动选择cglib代理还是JDK动态代理
<aop:pointcut> 切入点 ,从目标对象获得具体方法
<aop:advisor> 特殊的切面,只有一个通知 和 一个切入点
advice-ref 通知引用
pointcut-ref 切入点引用
3.3 切入点表达式
execution(* com.ys.aop.*.*(..))
选择方法 返回值任意 包 类名任意 方法名任意 参数任意
-->
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="myAspect">
<!-- 切入点表达式 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.ys.aop.*.*(..))" id="myPointCut"/>
<!-- 3.1 前置通知
<aop:before method="" pointcut="" pointcut-ref=""/>
method : 通知,及方法名
pointcut :切入点表达式,此表达式只能当前通知使用。
pointcut-ref : 切入点引用,可以与其他通知共享切入点。
通知方法格式:public void myBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint){
参数1:org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint 用于描述连接点(目标方法),获得目标方法名等
-->
<aop:before method="myBefore" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/>
<!-- 3.2后置通知 ,目标方法后执行,获得返回值
<aop:after-returning method="" pointcut-ref="" returning=""/>
returning 通知方法第二个参数的名称
通知方法格式:public void myAfterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object ret){
参数1:连接点描述
参数2:类型Object,参数名 returning="ret" 配置的
-->
<aop:after-returning method="myAfterReturning" pointcut-ref="myPointCut" returning="ret" />
<!-- 3.3 最终通知 -->
<aop:after method="myAfter" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
⑤、测试
@Test
public void testAop(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService useService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
useService.addUser();
}
控制台打印:
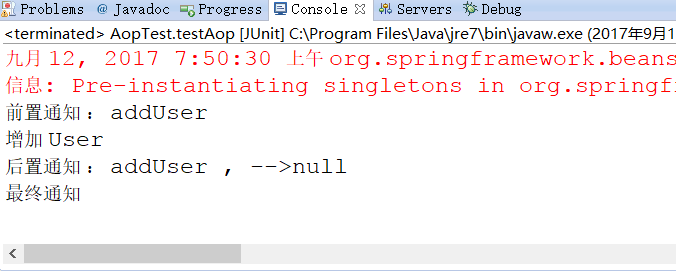
注意,后置通知的返回值为 null,是因为我们的目标方法 addUser() 没有返回值。如果有返回值,这里就是addUser() 的返回值。
4、测试异常通知
目标接口保持不变,目标类我们手动引入异常:
public void addUser() {
int i = 1/0;//显然这里会抛出除数不能为 0
System.out.println("增加 User");
}
接着配置切面:MyAspect.java
public void myAfterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint,Throwable e){
System.out.println("抛出异常通知 : " + e.getMessage());
}public void myAfterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint,Throwable e){
System.out.println("抛出异常通知 : " + e.getMessage());
}
接着在 applicationContext.xml 中配置如下:
<!-- 3.4 抛出异常
<aop:after-throwing method="" pointcut-ref="" throwing=""/>
throwing :通知方法的第二个参数名称
通知方法格式:public void myAfterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint,Throwable e){
参数1:连接点描述对象
参数2:获得异常信息,类型Throwable ,参数名由throwing="e" 配置
-->
<aop:after-throwing method="myAfterThrowing" pointcut-ref="myPointCut" throwing="e"/>
测试:
@Test
public void testAop(){
String str = "com/ys/execption/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(str);
UserService useService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
useService.addUser();
}
控制台打印:

5、测试环绕通知
目标接口和目标类保持不变,切面MyAspect 修改如下:
public class MyAspect {
public Object myAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("前置通知");
//手动执行目标方法
Object obj = joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("后置通知");
return obj;
}
}
applicationContext.xml 配置如下:
<!-- 环绕通知
<aop:around method="" pointcut-ref=""/>
通知方法格式:public Object myAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
返回值类型:Object
方法名:任意
参数:org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint
抛出异常
执行目标方法:Object obj = joinPoint.proceed();
-->
<aop:around method="myAround" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/>
测试:
@Test
public void testAop(){
String str = "com/ys/around/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(str);
UserService useService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
useService.addUser();
}
印结果:

那么至此,通过 xml 配置的方式我们讲解了Spring AOP 的配置。下一章将通过注解的方式来实现。
总结
本篇文章就到这里了,希望能够给你带来帮助,也希望您能够多多关注我们的更多内容!

