C++全面细致讲解复数类
目录
- 一、复数类应该具有的操作
- 二、利用操作符重载
- 三、注意事项
- 四、小结
一、复数类应该具有的操作
- 运算:+,- ,*,/
- 比较:== ,! =
- 赋值:=
- 求模:modulus
二、利用操作符重载
统一复数与实数的运算方式
统—复数与实数的比较方式

下面来看一下复数类的实现:
Complex.h:
#ifndef _COMPLEX_H_
#define _COMPLEX_H_
class Complex
{
double a;
double b;
public:
Complex(double a = 0, double b = 0);
double getA();
double getB();
double getModulus();
Complex operator + (const Complex& c);
Complex operator - (const Complex& c);
Complex operator * (const Complex& c);
Complex operator / (const Complex& c);
bool operator == (const Complex& c);
bool operator != (const Complex& c);
Complex& operator = (const Complex& c);
};
#endif
Complex.cpp:
#include "Complex.h"
#include "math.h"
Complex::Complex(double a, double b)
{
this->a = a;
this->b = b;
}
double Complex::getA()
{
return a;
}
double Complex::getB()
{
return b;
}
double Complex::getModulus()
{
return sqrt(a * a + b * b);
}
Complex Complex::operator + (const Complex& c)
{
double na = a + c.a;
double nb = b + c.b;
Complex ret(na, nb);
return ret;
}
Complex Complex::operator - (const Complex& c)
{
double na = a - c.a;
double nb = b - c.b;
Complex ret(na, nb);
return ret;
}
Complex Complex::operator * (const Complex& c)
{
double na = a * c.a - b * c.b;
double nb = a * c.b + b * c.a;
Complex ret(na, nb);
return ret;
}
Complex Complex::operator / (const Complex& c)
{
double cm = c.a * c.a + c.b * c.b;
double na = (a * c.a + b * c.b) / cm;
double nb = (b * c.a - a * c.b) / cm;
Complex ret(na, nb);
return ret;
}
bool Complex::operator == (const Complex& c)
{
return (a == c.a) && (b == c.b);
}
bool Complex::operator != (const Complex& c)
{
return !(*this == c);
}
Complex& Complex::operator = (const Complex& c)
{
if( this != &c )
{
a = c.a;
b = c.b;
}
return *this;
}
test.cpp:
#include <stdio.h>
#include "Complex.h"
int main()
{
Complex c1(1, 2);
Complex c2(3, 6);
Complex c3 = c2 - c1;
Complex c4 = c1 * c3;
Complex c5 = c2 / c1;
printf("c3.a = %f, c3.b = %f\n", c3.getA(), c3.getB());
printf("c4.a = %f, c4.b = %f\n", c4.getA(), c4.getB());
printf("c5.a = %f, c5.b = %f\n", c5.getA(), c5.getB());
Complex c6(2, 4);
printf("c3 == c6 : %d\n", c3 == c6);
printf("c3 != c4 : %d\n", c3 != c4);
(c3 = c2) = c1;
printf("c1.a = %f, c1.b = %f\n", c1.getA(), c1.getB());
printf("c2.a = %f, c2.b = %f\n", c2.getA(), c2.getB());
printf("c3.a = %f, c3.b = %f\n", c3.getA(), c3.getB());
return 0;
}
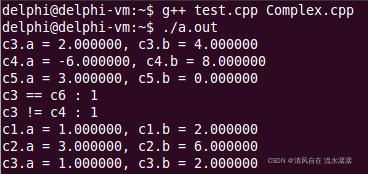
输出结果如下:
三、注意事项
- C++ 规定赋值操作符(=)只能重载为成员函数
- 操作符重载不能改变原操作符的优先级
- 操作符重载不能改变操作数的个数
- 操作符重载不应改变操作符的原有语义
四、小结
- 复数的概念可以通过自定义类实现
- 复数中的运算操作可以通过操作符重载实现
- 赋值操作符只能通过成员函数实现
- 操作符重载的本质为函数定义
到此这篇关于C++全面细致讲解复数类的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C++复数类内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!
赞 (0)

