Tensorflow深度学习使用CNN分类英文文本
目录
- 前言
- 源码与数据
- 源码
- 数据
- train.py 源码及分析
- data_helpers.py 源码及分析
- text_cnn.py 源码及分析
前言
本文同时也是学习唐宇迪老师深度学习课程的一些理解与记录。
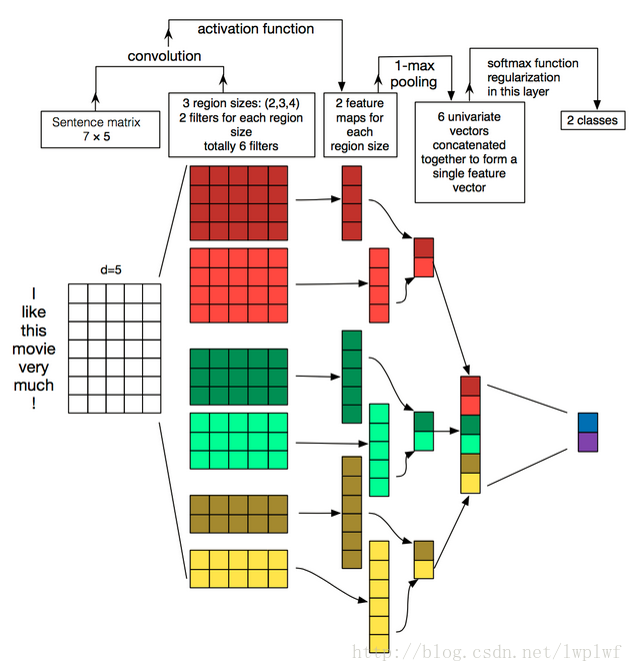
文中代码是实现在TensorFlow下使用卷积神经网络(CNN)做英文文本的分类任务(本次是垃圾邮件的二分类任务),当然垃圾邮件分类是一种应用环境,模型方法也可以推广到其它应用场景,如电商商品好评差评分类、正负面新闻等。
源码与数据
源码
- data_helpers.py
- train.py
- text_cnn.py
- eval.py(Save the evaluations to a csv, in case the user wants to inspect,analyze, or otherwise use the classifications generated by the neural net)
数据
- rt-polarity.neg
- rt-polarity.pos

train.py 源码及分析
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import os
import time
import datetime
import data_helpers
from text_cnn import TextCNN
from tensorflow.contrib import learn
# Parameters
# ==================================================
# Data loading params
# 语料文件路径定义
tf.flags.DEFINE_float("dev_sample_percentage", .1, "Percentage of the training data to use for validation")
tf.flags.DEFINE_string("positive_data_file", "./data/rt-polaritydata/rt-polarity.pos", "Data source for the positive data.")
tf.flags.DEFINE_string("negative_data_file", "./data/rt-polaritydata/rt-polarity.neg", "Data source for the negative data.")
# Model Hyperparameters
# 定义网络超参数
tf.flags.DEFINE_integer("embedding_dim", 128, "Dimensionality of character embedding (default: 128)")
tf.flags.DEFINE_string("filter_sizes", "3,4,5", "Comma-separated filter sizes (default: '3,4,5')")
tf.flags.DEFINE_integer("num_filters", 128, "Number of filters per filter size (default: 128)")
tf.flags.DEFINE_float("dropout_keep_prob", 0.5, "Dropout keep probability (default: 0.5)")
tf.flags.DEFINE_float("l2_reg_lambda", 0.0, "L2 regularization lambda (default: 0.0)")
# Training parameters
# 训练参数
tf.flags.DEFINE_integer("batch_size", 32, "Batch Size (default: 32)")
tf.flags.DEFINE_integer("num_epochs", 200, "Number of training epochs (default: 200)") # 总训练次数
tf.flags.DEFINE_integer("evaluate_every", 100, "Evaluate model on dev set after this many steps (default: 100)") # 每训练100次测试一下
tf.flags.DEFINE_integer("checkpoint_every", 100, "Save model after this many steps (default: 100)") # 保存一次模型
tf.flags.DEFINE_integer("num_checkpoints", 5, "Number of checkpoints to store (default: 5)")
# Misc Parameters
tf.flags.DEFINE_boolean("allow_soft_placement", True, "Allow device soft device placement") # 加上一个布尔类型的参数,要不要自动分配
tf.flags.DEFINE_boolean("log_device_placement", False, "Log placement of ops on devices") # 加上一个布尔类型的参数,要不要打印日志
# 打印一下相关初始参数
FLAGS = tf.flags.FLAGS
FLAGS._parse_flags()
print("\nParameters:")
for attr, value in sorted(FLAGS.__flags.items()):
print("{}={}".format(attr.upper(), value))
print("")
# Data Preparation
# ==================================================
# Load data
print("Loading data...")
x_text, y = data_helpers.load_data_and_labels(FLAGS.positive_data_file, FLAGS.negative_data_file)
# Build vocabulary
max_document_length = max([len(x.split(" ")) for x in x_text]) # 计算最长邮件
vocab_processor = learn.preprocessing.VocabularyProcessor(max_document_length) # tensorflow提供的工具,将数据填充为最大长度,默认0填充
x = np.array(list(vocab_processor.fit_transform(x_text)))
# Randomly shuffle data
# 数据洗牌
np.random.seed(10)
# np.arange生成随机序列
shuffle_indices = np.random.permutation(np.arange(len(y)))
x_shuffled = x[shuffle_indices]
y_shuffled = y[shuffle_indices]
# 将数据按训练train和测试dev分块
# Split train/test set
# TODO: This is very crude, should use cross-validation
dev_sample_index = -1 * int(FLAGS.dev_sample_percentage * float(len(y)))
x_train, x_dev = x_shuffled[:dev_sample_index], x_shuffled[dev_sample_index:]
y_train, y_dev = y_shuffled[:dev_sample_index], y_shuffled[dev_sample_index:]
print("Vocabulary Size: {:d}".format(len(vocab_processor.vocabulary_)))
print("Train/Dev split: {:d}/{:d}".format(len(y_train), len(y_dev))) # 打印切分的比例
# Training
# ==================================================
with tf.Graph().as_default():
session_conf = tf.ConfigProto(
allow_soft_placement=FLAGS.allow_soft_placement,
log_device_placement=FLAGS.log_device_placement)
sess = tf.Session(config=session_conf)
with sess.as_default():
# 卷积池化网络导入
cnn = TextCNN(
sequence_length=x_train.shape[1],
num_classes=y_train.shape[1], # 分几类
vocab_size=len(vocab_processor.vocabulary_),
embedding_size=FLAGS.embedding_dim,
filter_sizes=list(map(int, FLAGS.filter_sizes.split(","))), # 上面定义的filter_sizes拿过来,"3,4,5"按","分割
num_filters=FLAGS.num_filters, # 一共有几个filter
l2_reg_lambda=FLAGS.l2_reg_lambda) # l2正则化项
# Define Training procedure
global_step = tf.Variable(0, name="global_step", trainable=False)
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-3) # 定义优化器
grads_and_vars = optimizer.compute_gradients(cnn.loss)
train_op = optimizer.apply_gradients(grads_and_vars, global_step=global_step)
# Keep track of gradient values and sparsity (optional)
grad_summaries = []
for g, v in grads_and_vars:
if g is not None:
grad_hist_summary = tf.summary.histogram("{}/grad/hist".format(v.name), g)
sparsity_summary = tf.summary.scalar("{}/grad/sparsity".format(v.name), tf.nn.zero_fraction(g))
grad_summaries.append(grad_hist_summary)
grad_summaries.append(sparsity_summary)
grad_summaries_merged = tf.summary.merge(grad_summaries)
# Output directory for models and summaries
timestamp = str(int(time.time()))
out_dir = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.curdir, "runs", timestamp))
print("Writing to {}\n".format(out_dir))
# Summaries for loss and accuracy
# 损失函数和准确率的参数保存
loss_summary = tf.summary.scalar("loss", cnn.loss)
acc_summary = tf.summary.scalar("accuracy", cnn.accuracy)
# Train Summaries
# 训练数据保存
train_summary_op = tf.summary.merge([loss_summary, acc_summary, grad_summaries_merged])
train_summary_dir = os.path.join(out_dir, "summaries", "train")
train_summary_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(train_summary_dir, sess.graph)
# Dev summaries
# 测试数据保存
dev_summary_op = tf.summary.merge([loss_summary, acc_summary])
dev_summary_dir = os.path.join(out_dir, "summaries", "dev")
dev_summary_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(dev_summary_dir, sess.graph)
# Checkpoint directory. Tensorflow assumes this directory already exists so we need to create it
checkpoint_dir = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(out_dir, "checkpoints"))
checkpoint_prefix = os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, "model")
if not os.path.exists(checkpoint_dir):
os.makedirs(checkpoint_dir)
saver = tf.train.Saver(tf.global_variables(), max_to_keep=FLAGS.num_checkpoints) # 前面定义好参数num_checkpoints
# Write vocabulary
vocab_processor.save(os.path.join(out_dir, "vocab"))
# Initialize all variables
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) # 初始化所有变量
# 定义训练函数
def train_step(x_batch, y_batch):
"""
A single training step
"""
feed_dict = {
cnn.input_x: x_batch,
cnn.input_y: y_batch,
cnn.dropout_keep_prob: FLAGS.dropout_keep_prob # 参数在前面有定义
}
_, step, summaries, loss, accuracy = sess.run(
[train_op, global_step, train_summary_op, cnn.loss, cnn.accuracy], feed_dict)
time_str = datetime.datetime.now().isoformat() # 取当前时间,python的函数
print("{}: step {}, loss {:g}, acc {:g}".format(time_str, step, loss, accuracy))
train_summary_writer.add_summary(summaries, step)
# 定义测试函数
def dev_step(x_batch, y_batch, writer=None):
"""
Evaluates model on a dev set
"""
feed_dict = {
cnn.input_x: x_batch,
cnn.input_y: y_batch,
cnn.dropout_keep_prob: 1.0 # 神经元全部保留
}
step, summaries, loss, accuracy = sess.run(
[global_step, dev_summary_op, cnn.loss, cnn.accuracy], feed_dict)
time_str = datetime.datetime.now().isoformat()
print("{}: step {}, loss {:g}, acc {:g}".format(time_str, step, loss, accuracy))
if writer:
writer.add_summary(summaries, step)
# Generate batches
batches = data_helpers.batch_iter(list(zip(x_train, y_train)), FLAGS.batch_size, FLAGS.num_epochs)
# Training loop. For each batch...
# 训练部分
for batch in batches:
x_batch, y_batch = zip(*batch) # 按batch把数据拿进来
train_step(x_batch, y_batch)
current_step = tf.train.global_step(sess, global_step) # 将Session和global_step值传进来
if current_step % FLAGS.evaluate_every == 0: # 每FLAGS.evaluate_every次每100执行一次测试
print("\nEvaluation:")
dev_step(x_dev, y_dev, writer=dev_summary_writer)
print("")
if current_step % FLAGS.checkpoint_every == 0: # 每checkpoint_every次执行一次保存模型
path = saver.save(sess, './', global_step=current_step) # 定义模型保存路径
print("Saved model checkpoint to {}\n".format(path))
data_helpers.py 源码及分析
import numpy as np
import re
import itertools
from collections import Counter
def clean_str(string):
"""
Tokenization/string cleaning for all datasets except for SST.
Original taken from https://github.com/yoonkim/CNN_sentence/blob/master/process_data.py
"""
# 清理数据替换掉无词义的符号
string = re.sub(r"[^A-Za-z0-9(),!?\'\`]", " ", string)
string = re.sub(r"\'s", " \'s", string)
string = re.sub(r"\'ve", " \'ve", string)
string = re.sub(r"n\'t", " n\'t", string)
string = re.sub(r"\'re", " \'re", string)
string = re.sub(r"\'d", " \'d", string)
string = re.sub(r"\'ll", " \'ll", string)
string = re.sub(r",", " , ", string)
string = re.sub(r"!", " ! ", string)
string = re.sub(r"\(", " \( ", string)
string = re.sub(r"\)", " \) ", string)
string = re.sub(r"\?", " \? ", string)
string = re.sub(r"\s{2,}", " ", string)
return string.strip().lower()
def load_data_and_labels(positive_data_file, negative_data_file):
"""
Loads MR polarity data from files, splits the data into words and generates labels.
Returns split sentences and labels.
"""
# Load data from files
positive = open(positive_data_file, "rb").read().decode('utf-8')
negative = open(negative_data_file, "rb").read().decode('utf-8')
# 按回车分割样本
positive_examples = positive.split('\n')[:-1]
negative_examples = negative.split('\n')[:-1]
# 去空格
positive_examples = [s.strip() for s in positive_examples]
negative_examples = [s.strip() for s in negative_examples]
#positive_examples = list(open(positive_data_file, "rb").read().decode('utf-8'))
#positive_examples = [s.strip() for s in positive_examples]
#negative_examples = list(open(negative_data_file, "rb").read().decode('utf-8'))
#negative_examples = [s.strip() for s in negative_examples]
# Split by words
x_text = positive_examples + negative_examples
x_text = [clean_str(sent) for sent in x_text] # 字符过滤,实现函数见clean_str()
# Generate labels
positive_labels = [[0, 1] for _ in positive_examples]
negative_labels = [[1, 0] for _ in negative_examples]
y = np.concatenate([positive_labels, negative_labels], 0) # 将两种label连在一起
return [x_text, y]
# 创建batch迭代模块
def batch_iter(data, batch_size, num_epochs, shuffle=True): # shuffle=True洗牌
"""
Generates a batch iterator for a dataset.
"""
# 每次只输出shuffled_data[start_index:end_index]这么多
data = np.array(data)
data_size = len(data)
num_batches_per_epoch = int((len(data)-1)/batch_size) + 1 # 每一个epoch有多少个batch_size
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# Shuffle the data at each epoch
if shuffle:
shuffle_indices = np.random.permutation(np.arange(data_size)) # 洗牌
shuffled_data = data[shuffle_indices]
else:
shuffled_data = data
for batch_num in range(num_batches_per_epoch):
start_index = batch_num * batch_size # 当前batch的索引开始
end_index = min((batch_num + 1) * batch_size, data_size) # 判断下一个batch是不是超过最后一个数据了
yield shuffled_data[start_index:end_index]
text_cnn.py 源码及分析
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
# 定义CNN网络实现的类
class TextCNN(object):
"""
A CNN for text classification.
Uses an embedding layer, followed by a convolutional, max-pooling and softmax layer.
"""
def __init__(self, sequence_length, num_classes, vocab_size,
embedding_size, filter_sizes, num_filters, l2_reg_lambda=0.0): # 把train.py中TextCNN里定义的参数传进来
# Placeholders for input, output and dropout
self.input_x = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, sequence_length], name="input_x") # input_x输入语料,待训练的内容,维度是sequence_length,"N个词构成的N维向量"
self.input_y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, num_classes], name="input_y") # input_y输入语料,待训练的内容标签,维度是num_classes,"正面 || 负面"
self.dropout_keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name="dropout_keep_prob") # dropout_keep_prob dropout参数,防止过拟合,训练时用
# Keeping track of l2 regularization loss (optional)
l2_loss = tf.constant(0.0) # 先不用,写0
# Embedding layer
# 指定运算结构的运行位置在cpu非gpu,因为"embedding"无法运行在gpu
# 通过tf.name_scope指定"embedding"
with tf.device('/cpu:0'), tf.name_scope("embedding"): # 指定cpu
self.W = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([vocab_size, embedding_size], -1.0, 1.0), name="W") # 定义W并初始化
self.embedded_chars = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.W, self.input_x)
self.embedded_chars_expanded = tf.expand_dims(self.embedded_chars, -1) # 加一个维度,转换为4维的格式
# Create a convolution + maxpool layer for each filter size
pooled_outputs = []
# filter_sizes卷积核尺寸,枚举后遍历
for i, filter_size in enumerate(filter_sizes):
with tf.name_scope("conv-maxpool-%s" % filter_size):
# Convolution Layer
filter_shape = [filter_size, embedding_size, 1, num_filters] # 4个参数分别为filter_size高h,embedding_size宽w,channel为1,filter个数
W = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(filter_shape, stddev=0.1), name="W") # W进行高斯初始化
b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[num_filters]), name="b") # b给初始化为一个常量
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(
self.embedded_chars_expanded,
W,
strides=[1, 1, 1, 1],
padding="VALID", # 这里不需要padding
name="conv")
# Apply nonlinearity 激活函数
# 可以理解为,正面或者负面评价有一些标志词汇,这些词汇概率被增强,即一旦出现这些词汇,倾向性分类进正或负面评价,
# 该激励函数可加快学习进度,增加稀疏性,因为让确定的事情更确定,噪声的影响就降到了最低。
h = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv, b), name="relu")
# Maxpooling over the outputs
# 池化
pooled = tf.nn.max_pool(
h,
ksize=[1, sequence_length - filter_size + 1, 1, 1], # (h-filter+2padding)/strides+1=h-f+1
strides=[1, 1, 1, 1],
padding='VALID', # 这里不需要padding
name="pool")
pooled_outputs.append(pooled)
# Combine all the pooled features
num_filters_total = num_filters * len(filter_sizes)
self.h_pool = tf.concat(3, pooled_outputs)
self.h_pool_flat = tf.reshape(self.h_pool, [-1, num_filters_total]) # 扁平化数据,跟全连接层相连
# Add dropout
# drop层,防止过拟合,参数为dropout_keep_prob
# 过拟合的本质是采样失真,噪声权重影响了判断,如果采样足够多,足够充分,噪声的影响可以被量化到趋近事实,也就无从过拟合。
# 即数据越大,drop和正则化就越不需要。
with tf.name_scope("dropout"):
self.h_drop = tf.nn.dropout(self.h_pool_flat, self.dropout_keep_prob)
# Final (unnormalized) scores and predictions
# 输出层
with tf.name_scope("output"):
W = tf.get_variable(
"W",
shape=[num_filters_total, num_classes], #前面连扁平化后的池化操作
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer()) # 定义初始化方式
b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[num_classes]), name="b")
# 损失函数导入
l2_loss += tf.nn.l2_loss(W)
l2_loss += tf.nn.l2_loss(b)
# xw+b
self.scores = tf.nn.xw_plus_b(self.h_drop, W, b, name="scores") # 得分函数
self.predictions = tf.argmax(self.scores, 1, name="predictions") # 预测结果
# CalculateMean cross-entropy loss
with tf.name_scope("loss"):
# loss,交叉熵损失函数
losses = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=self.scores, labels=self.input_y)
self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(losses) + l2_reg_lambda * l2_loss
# Accuracy
with tf.name_scope("accuracy"):
# 准确率,求和计算算数平均值
correct_predictions = tf.equal(self.predictions, tf.argmax(self.input_y, 1))
self.accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_predictions, "float"), name="accuracy")
以上就是Tensorflow深度学习CNN实现英文文本分类的详细内容,更多关于Tensorflow实现CNN分类英文文本的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!
赞 (0)

