Java自定义线程池的实现示例
目录
- 一、Java语言本身也是多线程,回顾Java创建线程方式如下:
- 二、JDK线程池工具类.
- 三、业界知名自定义线程池扩展使用.
一、Java语言本身也是多线程,回顾Java创建线程方式如下:
1、继承Thread类,(Thread类实现Runnable接口),来个类图加深印象。
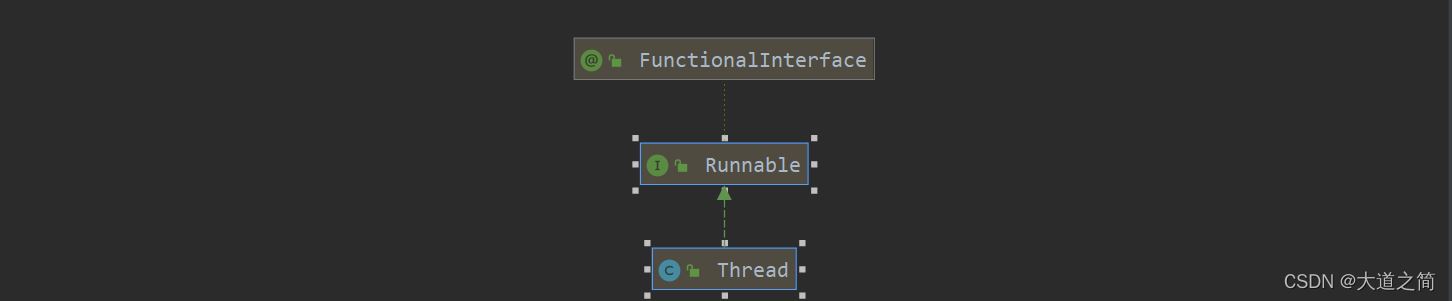
2、实现Runnable接口实现无返回值、实现run()方法,啥时候run,黑话了。
3、实现Callable接口重写call()+FutureTask获取.
public class CustomThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 自定义线程
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Custom Run");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
},"custom-thread-1").start();
}
}

4、基于线程池集中管理创建线程系列周期.【本篇文章重点介绍】
二、JDK线程池工具类.
1、Executors工具类,是JDK中Doug Lea大佬实现供开发者使用。
随着JDK版本迭代逐渐加入了基于工作窃取算法的线程池了,阿里编码规范也推荐开发者自定义线程池,禁止生产直接使用Executos线程池工具类,因此很有可能造成OOM异常。同时在某些类型的线程池里面,使用无界队列还会导致maxinumPoolSize、keepAliveTime、handler等参数失效。因此目前在大厂的开发规范中会强调禁止使用Executors来创建线程池。这里说道阻塞队列。LinkedBlockingQueue。

2、自定义线程池工具类基于ThreadPoolExecutor实现,那个JDK封装的线程池工具类也是基于这个ThreadPoolExecutor实现的。
public class ConstomThreadPool extends ThreadPoolExecutor{
/**
*
* @param corePoolSize 核心线程池
* @param maximumPoolSize 线程池最大数量
* @param keepAliveTime 线程存活时间
* @param unit TimeUnit
* @param workQueue 工作队列,自定义大小
* @param poolName 线程工厂自定义线程名称
*/
public ConstomThreadPool(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, String poolName) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue);
setThreadFactory(new CustomThreadFactory(poolName, false));
}
}
自定义线程工厂类,这样线程命名有开发者控制实现了,这样参数可以做到可配置化,生产环境可以供不同业务模块使用,如果系统配置值不生效,就给一个默认值,更加满足业务需要.
/**
* 自定义线程工厂
*/
public class CustomThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
/**
* 线程前缀,采用AtomicInteger实现线程编号线程安全自增
*/
private final AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(1);
/**
* 线程命名前缀
*/
private final String namePrefix;
/**
* 线程工厂创建的线程是否是守护线程
*/
private final boolean isDaemon;
public CustomThreadFactory(String prefix, boolean daemin) {
if (StringUtils.isNoneBlank(prefix)) {
this.namePrefix = prefix;
} else {
this.namePrefix = "thread_pool";
}
// 是否是守护线程
isDaemon = daemin;
}
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread thread = new Thread(r, namePrefix + "-" + atomicInteger.getAndIncrement());
thread.setDaemon(isDaemon);
// 设置线程优先级
if (thread.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY) {
thread.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
}
return thread;
}
}
这里Spring框架提供的自定义线程池工厂类,当然了一些开源包也会提供这样的轮子,这个比较简单了.
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class CustomizableThreadFactory extends CustomizableThreadCreator implements ThreadFactory {
/**
* Create a new CustomizableThreadFactory with default thread name prefix.
*/
public CustomizableThreadFactory() {
super();
}
/**
* Create a new CustomizableThreadFactory with the given thread name prefix.
* @param threadNamePrefix the prefix to use for the names of newly created threads
*/
public CustomizableThreadFactory(String threadNamePrefix) {
super(threadNamePrefix);
}
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable runnable) {
return createThread(runnable);
}
}
3、SpringBoot框架提供的自定义线程池,基于异步注解@Async名称和一些业务自定义配置项,很好的实现了业务间线程池的隔离。
@Configuration
public class ThreadPoolConfig {
/**
*
* @return ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
*/
@Bean("serviceTaskA")
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor serviceTaskA() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(2);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(2);
executor.setQueueCapacity(10);
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("service-a");
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
return executor;
}
/**
*
* @return ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
*/
@Bean("serviceTaskB")
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor serviceTaskB() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(2);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(2);
executor.setQueueCapacity(10);
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("service-b");
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
return executor;
}
}
整体来看是Spring框架对JDK的线程池做了封装,公开发者使用,毕竟框架嘛,肯定是把方便留给开发者。

4、并发流线程池。
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(4);
list.add("A");
list.add("B");
list.add("C");
list.add("D");
list.parallelStream().forEach(string -> {
string = string + "paralleStream";
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":-> "+string);
});
运行实例:
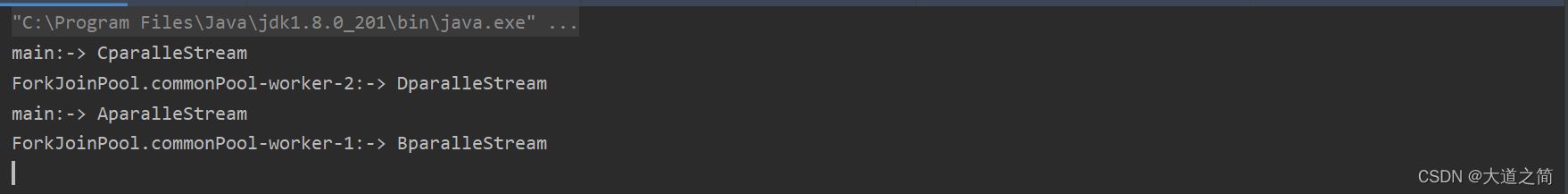
说明:并发流默认使用系统公共的线程池ForkJoinWorkerThread,供整个程序使用。
类图如下,基于分治法,双端窃取算法实现的一种线程池。

ForkJoin实现的了自己的线程工厂命名。

也可以自定义并发流线程,然后提交任务,一般并发流适用于短暂耗时业务,避免拖垮整个线程池业务.
5、实现一个基于系统公用线程池工具类,运行这个系统中的异步业务.
public final class CustomExecutors {
/**
* 核心线程数大小
*/
private static final int CORE_POOL_SIZE=5;
/**
* 核心线程池大小
*/
private static final int MAX_POOL_SIZE=10;
/**
* 线程存活时间
*/
private static final int KEEP_ALIVE_TIME=60;
/**
* 工作队列大小
*/
private static final LinkedBlockingQueue queue=new LinkedBlockingQueue(100);
/**
* 自定义线程池名前缀
*/
private static final String POOL_PREFIX_NAME="Custom-Common-Pool";
private CustomExecutors(){
//throw new XXXXException("un support create pool!");
}
private static ConstomThreadPool constomThreadPool;
/**
* 静态块初始化只执行一次,不关闭,整个系统公用一个线程池
*/
static {
constomThreadPool=new ConstomThreadPool(CORE_POOL_SIZE,MAX_POOL_SIZE,KEEP_ALIVE_TIME,TimeUnit.SECONDS,queue,POOL_PREFIX_NAME);
}
/**
* 单例模式获取线程池
* @return ExecutorService
*/
private static ExecutorService getInstance(){
return constomThreadPool;
}
private static Future<?> submit(Runnable task){
return constomThreadPool.submit(task);
}
private static <T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result){
return constomThreadPool.submit(task,result);
}
private static <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task){
return constomThreadPool.submit(task);
}
private static void execute(Runnable task){
constomThreadPool.execute(task);
}
}
三、业界知名自定义线程池扩展使用.
1、org.apache.tomcat.util.threads;【Tomcat线程池】

2、XXL-JOB分布式任务调度框架的快慢线程池,线程池任务隔离.
public class JobTriggerPoolHelper {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JobTriggerPoolHelper.class);
// ---------------------- trigger pool ----------------------
// fast/slow thread pool
private ThreadPoolExecutor fastTriggerPool = null;
private ThreadPoolExecutor slowTriggerPool = null;
public void start(){
fastTriggerPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
10,
XxlJobAdminConfig.getAdminConfig().getTriggerPoolFastMax(),
60L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(1000),
new ThreadFactory() {
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "xxl-job, admin JobTriggerPoolHelper-fastTriggerPool-" + r.hashCode());
}
});
slowTriggerPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
10,
XxlJobAdminConfig.getAdminConfig().getTriggerPoolSlowMax(),
60L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(2000),
new ThreadFactory() {
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "xxl-job, admin JobTriggerPoolHelper-slowTriggerPool-" + r.hashCode());
}
});
}
public void stop() {
//triggerPool.shutdown();
fastTriggerPool.shutdownNow();
slowTriggerPool.shutdownNow();
logger.info(">>>>>>>>> xxl-job trigger thread pool shutdown success.");
}
// job timeout count
private volatile long minTim = System.currentTimeMillis()/60000; // ms > min
private volatile ConcurrentMap<Integer, AtomicInteger> jobTimeoutCountMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* add trigger
*/
public void addTrigger(final int jobId,
final TriggerTypeEnum triggerType,
final int failRetryCount,
final String executorShardingParam,
final String executorParam,
final String addressList) {
// choose thread pool
ThreadPoolExecutor triggerPool_ = fastTriggerPool;
AtomicInteger jobTimeoutCount = jobTimeoutCountMap.get(jobId);
if (jobTimeoutCount!=null && jobTimeoutCount.get() > 10) { // job-timeout 10 times in 1 min
triggerPool_ = slowTriggerPool;
}
// trigger
triggerPool_.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// do trigger
XxlJobTrigger.trigger(jobId, triggerType, failRetryCount, executorShardingParam, executorParam, addressList);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
// check timeout-count-map
long minTim_now = System.currentTimeMillis()/60000;
if (minTim != minTim_now) {
minTim = minTim_now;
jobTimeoutCountMap.clear();
}
// incr timeout-count-map
long cost = System.currentTimeMillis()-start;
if (cost > 500) { // ob-timeout threshold 500ms
AtomicInteger timeoutCount = jobTimeoutCountMap.putIfAbsent(jobId, new AtomicInteger(1));
if (timeoutCount != null) {
timeoutCount.incrementAndGet();
}
}
}
}
});
}
// ---------------------- helper ----------------------
private static JobTriggerPoolHelper helper = new JobTriggerPoolHelper();
public static void toStart() {
helper.start();
}
public static void toStop() {
helper.stop();
}
/**
* @param jobId
* @param triggerType
* @param failRetryCount
* >=0: use this param
* <0: use param from job info config
* @param executorShardingParam
* @param executorParam
* null: use job param
* not null: cover job param
*/
public static void trigger(int jobId, TriggerTypeEnum triggerType, int failRetryCount, String executorShardingParam, String executorParam, String addressList) {
helper.addTrigger(jobId, triggerType, failRetryCount, executorShardingParam, executorParam, addressList);
}
}
①、定义两个线程池,一个是fastTriggerPool,另一个是slowTriggerPool。
②、定义一个容器ConcurrentMap,存放每个任务的执行慢次数,60秒后自动清空该容器。
③、在线程的run()方法中计算每个任务的耗时,如果大于500ms,则任务的慢执行次数+1。

3、基于线程池动态监控动态线程池

引用图片,线程池常见问题

还有比较多啦,例如ES的基于JDK的线程池,Dubbo中等。
到此这篇关于Java自定义线程池的实现示例的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java自定义线程池内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

