详解使用Spring MVC统一异常处理实战
1 描述
在J2EE项目的开发中,不管是对底层的数据库操作过程,还是业务层的处理过程,还是控制层的处理过程,都不可避免会遇到各种可预知的、不可预知的异常需要处理。每个过程都单独处理异常,系统的代码耦合度高,工作量大且不好统一,维护的工作量也很大。
那么,能不能将所有类型的异常处理从各处理过程解耦出来,这样既保证了相关处理过程的功能较单一,也实现了异常信息的统一处理和维护?答案是肯定的。下面将介绍使用Spring MVC统一处理异常的解决和实现过程。
2 分析
Spring MVC处理异常有3种方式:
(1)使用Spring MVC提供的简单异常处理器SimpleMappingExceptionResolver;
(2)实现Spring的异常处理接口HandlerExceptionResolver 自定义自己的异常处理器;
(3)使用@ExceptionHandler注解实现异常处理;
3 实战
3.1 引言
为了验证Spring MVC的3种异常处理方式的实际效果,我们需要开发一个测试项目,从Dao层、Service层、Controller层分别抛出不同的异常,然后分别集成3种方式进行异常处理,从而比较3种方式的优缺点。
3.2 实战项目
3.2.1 项目结构
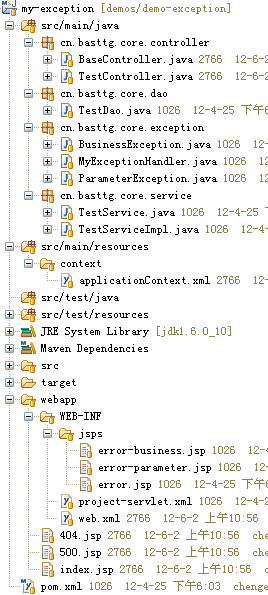
3.2.2 Dao层代码
@Repository("testDao")
public class TestDao {
public void exception(Integer id) throws Exception {
switch(id) {
case 1:
throw new BusinessException("12", "dao12");
case 2:
throw new BusinessException("22", "dao22");
case 3:
throw new BusinessException("32", "dao32");
case 4:
throw new BusinessException("42", "dao42");
case 5:
throw new BusinessException("52", "dao52");
default:
throw new ParameterException("Dao Parameter Error");
}
}
}
3.2.3 Service层代码
public interface TestService {
public void exception(Integer id) throws Exception;
public void dao(Integer id) throws Exception;
}
@Service("testService")
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService {
@Resource
private TestDao testDao;
public void exception(Integer id) throws Exception {
switch(id) {
case 1:
throw new BusinessException("11", "service11");
case 2:
throw new BusinessException("21", "service21");
case 3:
throw new BusinessException("31", "service31");
case 4:
throw new BusinessException("41", "service41");
case 5:
throw new BusinessException("51", "service51");
default:
throw new ParameterException("Service Parameter Error");
}
}
@Override
public void dao(Integer id) throws Exception {
testDao.exception(id);
}
}
3.2.4 Controller层代码
@Controller
public class TestController {
@Resource
private TestService testService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/controller.do", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void controller(HttpServletResponse response, Integer id) throws Exception {
switch(id) {
case 1:
throw new BusinessException("10", "controller10");
case 2:
throw new BusinessException("20", "controller20");
case 3:
throw new BusinessException("30", "controller30");
case 4:
throw new BusinessException("40", "controller40");
case 5:
throw new BusinessException("50", "controller50");
default:
throw new ParameterException("Controller Parameter Error");
}
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/service.do", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void service(HttpServletResponse response, Integer id) throws Exception {
testService.exception(id);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/dao.do", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void dao(HttpServletResponse response, Integer id) throws Exception {
testService.dao(id);
}
}
3.2.5 JSP页面代码
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"%> <html> <head> <title>Maven Demo</title> </head> <body> <h1>所有的演示例子</h1> <h3>[url=./dao.do?id=1]Dao正常错误[/url]</h3> <h3>[url=./dao.do?id=10]Dao参数错误[/url]</h3> <h3>[url=./dao.do?id=]Dao未知错误[/url]</h3> <h3>[url=./service.do?id=1]Service正常错误[/url]</h3> <h3>[url=./service.do?id=10]Service参数错误[/url]</h3> <h3>[url=./service.do?id=]Service未知错误[/url]</h3> <h3>[url=./controller.do?id=1]Controller正常错误[/url]</h3> <h3>[url=./controller.do?id=10]Controller参数错误[/url]</h3> <h3>[url=./controller.do?id=]Controller未知错误[/url]</h3> <h3>[url=./404.do?id=1]404错误[/url]</h3> </body> </html>
3.3 集成异常处理
3.3.1 使用SimpleMappingExceptionResolver实现异常处理
1、在Spring的配置文件applicationContext.xml中增加以下内容:
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver">
<!-- 定义默认的异常处理页面,当该异常类型的注册时使用 -->
<property name="defaultErrorView" value="error"></property>
<!-- 定义异常处理页面用来获取异常信息的变量名,默认名为exception -->
<property name="exceptionAttribute" value="ex"></property>
<!-- 定义需要特殊处理的异常,用类名或完全路径名作为key,异常也页名作为值 -->
<property name="exceptionMappings">
<props>
<prop key="cn.basttg.core.exception.BusinessException">error-business</prop>
<prop key="cn.basttg.core.exception.ParameterException">error-parameter</prop>
<!-- 这里还可以继续扩展对不同异常类型的处理 -->
</props>
</property>
</bean>
2、启动测试项目,经验证,Dao层、Service层、Controller层抛出的异常(业务异常BusinessException、参数异常ParameterException和其它的异常Exception)都能准确显示定义的异常处理页面,达到了统一异常处理的目标。
3、从上面的集成过程可知,使用SimpleMappingExceptionResolver进行异常处理,具有集成简单、有良好的扩展性、对已有代码没有入侵性等优点,但该方法仅能获取到异常信息,若在出现异常时,对需要获取除异常以外的数据的情况不适用。
3.3.2 实现HandlerExceptionResolver 接口自定义异常处理器
1、增加HandlerExceptionResolver 接口的实现类MyExceptionHandler,代码如下:
public class MyExceptionHandler implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler,
Exception ex) {
Map<String, Object> model = new HashMap<String, Object>();
model.put("ex", ex);
// 根据不同错误转向不同页面
if(ex instanceof BusinessException) {
return new ModelAndView("error-business", model);
}else if(ex instanceof ParameterException) {
return new ModelAndView("error-parameter", model);
} else {
return new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
}
}
2、在Spring的配置文件applicationContext.xml中增加以下内容:
<bean id="exceptionHandler" class="cn.basttg.core.exception.MyExceptionHandler"/>
3、启动测试项目,经验证,Dao层、Service层、Controller层抛出的异常(业务异常BusinessException、参数异常ParameterException和其它的异常Exception)都能准确显示定义的异常处理页面,达到了统一异常处理的目标。
4、从上面的集成过程可知,使用实现HandlerExceptionResolver接口的异常处理器进行异常处理,具有集成简单、有良好的扩展性、对已有代码没有入侵性等优点,同时,在异常处理时能获取导致出现异常的对象,有利于提供更详细的异常处理信息。
3.3.3 使用@ExceptionHandler注解实现异常处理
1、增加BaseController类,并在类中使用@ExceptionHandler注解声明异常处理,代码如下:
public class BaseController {
/** 基于@ExceptionHandler异常处理 */
@ExceptionHandler
public String exp(HttpServletRequest request, Exception ex) {
request.setAttribute("ex", ex);
// 根据不同错误转向不同页面
if(ex instanceof BusinessException) {
return "error-business";
}else if(ex instanceof ParameterException) {
return "error-parameter";
} else {
return "error";
}
}
}
2、修改代码,使所有需要异常处理的Controller都继承该类,如下所示,修改后的TestController类继承于BaseController:
public class TestController extends BaseController
3、启动测试项目,经验证,Dao层、Service层、Controller层抛出的异常(业务异常BusinessException、参数异常ParameterException和其它的异常Exception)都能准确显示定义的异常处理页面,达到了统一异常处理的目标。
4、从上面的集成过程可知,使用@ExceptionHandler注解实现异常处理,具有集成简单、有扩展性好(只需要将要异常处理的Controller类继承于BaseController即可)、不需要附加Spring配置等优点,但该方法对已有代码存在入侵性(需要修改已有代码,使相关类继承于BaseController),在异常处理时不能获取除异常以外的数据。
3.4 未捕获异常的处理
对于Unchecked Exception而言,由于代码不强制捕获,往往被忽略,如果运行期产生了Unchecked Exception,而代码中又没有进行相应的捕获和处理,则我们可能不得不面对尴尬的404、500……等服务器内部错误提示页面。
我们需要一个全面而有效的异常处理机制。目前大多数服务器也都支持在Web.xml中通过<error-page>(Websphere/Weblogic)或者<error-code>(Tomcat)节点配置特定异常情况的显示页面。修改web.xml文件,增加以下内容:
<!-- 出错页面定义 --> <error-page> <exception-type>java.lang.Throwable</exception-type> <location>/500.jsp</location> </error-page> <error-page> <error-code>500</error-code> <location>/500.jsp</location> </error-page> <error-page> <error-code>404</error-code> <location>/404.jsp</location> </error-page> <!-- 这里可继续增加服务器错误号的处理及对应显示的页面 -->
4 解决结果
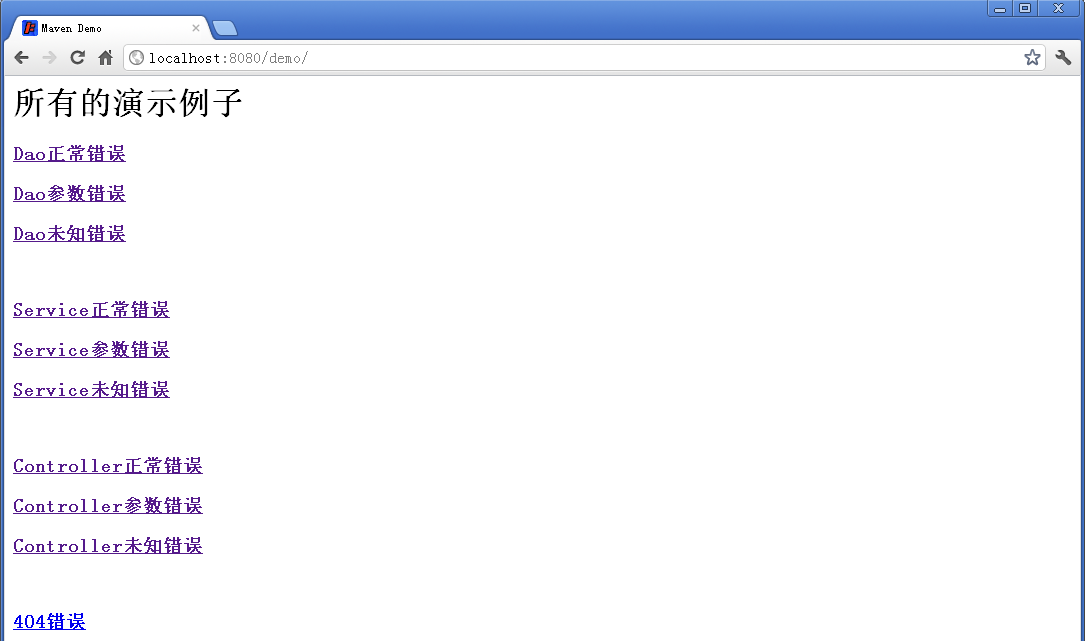
1、运行测试项目显示的首页,如下图所示:
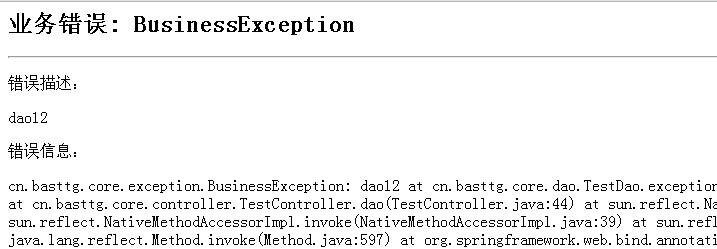
2、业务错误显示的页面,如下图所示:
3、参数错误显示的页面,如下图所示:
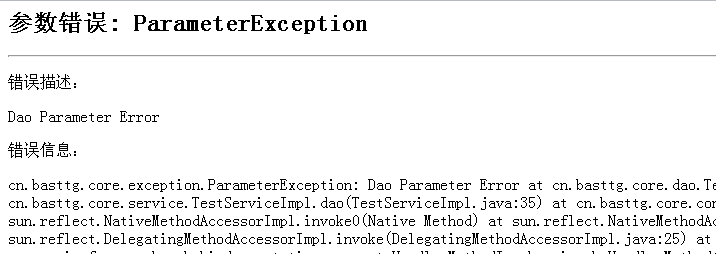
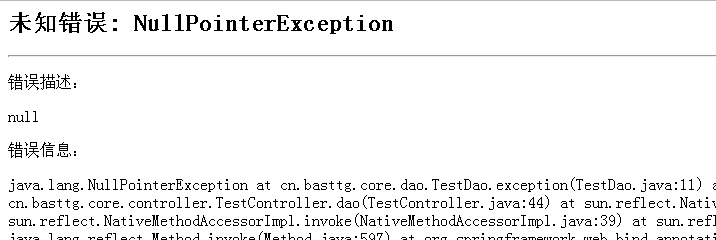
4、未知错误显示的页面,如下图所示:
5、服务器内部错误页面,如下图所示:

5 总结
综合上述可知,Spring MVC集成异常处理3种方式都可以达到统一异常处理的目标。从3种方式的优缺点比较,若只需要简单的集成异常处理,推荐使用SimpleMappingExceptionResolver即可;若需要集成的异常处理能够更具个性化,提供给用户更详细的异常信息,推荐自定义实现HandlerExceptionResolver接口的方式;若不喜欢Spring配置文件或要实现“零配置”,且能接受对原有代码的适当入侵,则建议使用@ExceptionHandler注解方式。
6 源代码
源代码项目如下所示,为Maven项目,若需运行,请自行获取相关的依赖包。
点击这里获取源代码
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。

