基于Java回顾之I/O的使用详解
工作后,使用的技术随着项目的变化而变化,时而C#,时而Java,当然还有其他一些零碎的技术。总体而言,C#的使用时间要更长一些,其次是Java。我本身对语言没有什么倾向性,能干活的语言,就是好语言。而且从面向对象的角度来看,我觉得C#和Java对我来说,没什么区别。
这篇文章主要回顾Java中和I/O操作相关的内容,I/O也是编程语言的一个基础特性,Java中的I/O分为两种类型,一种是顺序读取,一种是随机读取。
我们先来看顺序读取,有两种方式可以进行顺序读取,一种是InputStream/OutputStream,它是针对字节进行操作的输入输出流;另外一种是Reader/Writer,它是针对字符进行操作的输入输出流。
下面我们画出InputStream的结构
FileInputStream:操作文件,经常和BufferedInputStream一起使用
PipedInputStream:可用于线程间通信
ObjectInputStream:可用于对象序列化
ByteArrayInputStream:用于处理字节数组的输入
LineNumberInputStream:可输出当前行数,并且可以在程序中进行修改
下面是OutputStream的结构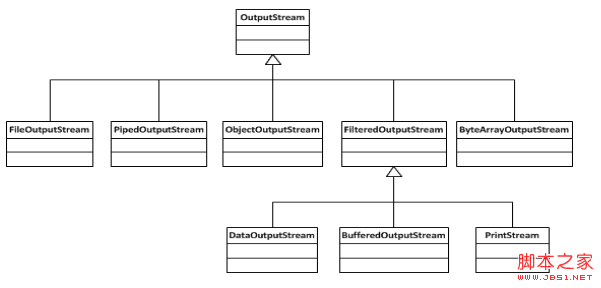
PrintStream:提供了类似print和println的接口去输出数据
下面我们来看如何使用Stream的方式来操作输入输出
使用FileInputStream读取文件信息
public static byte[] readFileByFileInputStream(File file) throws IOException
{
ByteArrayOutputStream output = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
FileInputStream fis = null;
try
{
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int bytesRead = 0;
while((bytesRead = fis.read(buffer, 0, buffer.length)) != -1)
{
output.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
System.out.println("Error occurs during reading " + file.getAbsoluteFile());
}
finally
{
if (fis !=null) fis.close();
if (output !=null) output.close();
}
return output.toByteArray();
}
使用BufferedInputStream读取文件
代码如下:
public static byte[] readFileByBufferedInputStream(File file) throws Exception
{
FileInputStream fis = null;
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream output = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
try
{
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int bytesRead = 0;
while((bytesRead = bis.read(buffer, 0, buffer.length)) != -1)
{
output.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
System.out.println("Error occurs during reading " + file.getAbsoluteFile());
}
finally
{
if (fis != null) fis.close();
if (bis != null) bis.close();
if (output != null) output.close();
}
return output.toByteArray();
}
使用FileOutputStream复制文件
public static void copyFileByFileOutputStream(File file) throws IOException
{
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try
{
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
fos = new FileOutputStream(file.getName() + ".bak");
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int bytesRead = 0;
while((bytesRead = fis.read(buffer,0,buffer.length)) != -1)
{
fos.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
fos.flush();
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
System.out.println("Error occurs during copying " + file.getAbsoluteFile());
}
finally
{
if (fis != null) fis.close();
if (fos != null) fos.close();
}
}
使用BufferedOutputStream复制文件
public static void copyFilebyBufferedOutputStream(File file)throws IOException
{
FileInputStream fis = null;
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try
{
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
fos = new FileOutputStream(file.getName() + ".bak");
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int bytesRead = 0;
while((bytesRead = bis.read(buffer, 0, buffer.length)) != -1)
{
bos.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
bos.flush();
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
System.out.println("Error occurs during copying " + file.getAbsoluteFile());
}
finally
{
if (fis != null) fis.close();
if (bis != null) bis.close();
if (fos != null) fos.close();
if (bos != null) bos.close();
}
}
这里的代码对异常的处理非常不完整,稍后我们会给出完整严谨的代码。
下面我们来看Reader的结构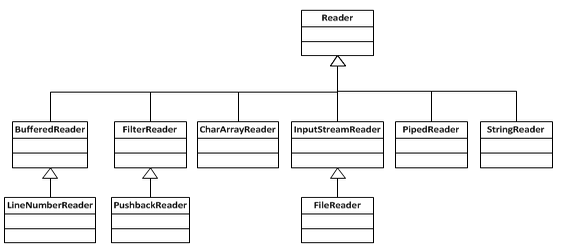
这里的Reader基本上和InputStream能够对应上。
Writer的结构如下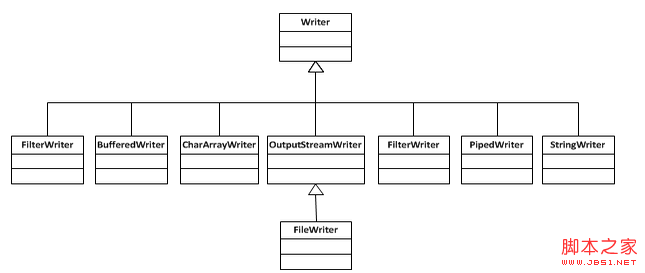
下面我们来看一些使用Reader或者Writer的例子
使用BufferedReader读取文件内容
public static String readFile(String file)throws IOException
{
BufferedReader br = null;
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
try
{
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String line = null;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null)
{
sb.append(line);
}
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
System.out.println("Error occurs during reading " + file);
}
finally
{
if (br != null) br.close();
}
return sb.toString();
}
使用BufferedWriter复制文件
public static void copyFile(String file) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try
{
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file + ".bak"));
String line = null;
while((line = br.readLine())!= null)
{
bw.write(line);
}
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
System.out.println("Error occurs during copying " + file);
}
finally
{
if (br != null) br.close();
if (bw != null) bw.close();
}
}
下面我们来看如何对文件进行随机访问,Java中主要使用RandomAccessFile来对文件进行随机操作。
创建大小固定的文件
public static void createFile(String file, int size) throws IOException
{
File temp = new File(file);
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(temp, "rw");
raf.setLength(size);
raf.close();
}
向文件中随机插入数据
public static void writeFile(String file, byte[] content, int startPos, int contentLength) throws IOException
{
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(new File(file), "rw");
raf.seek(startPos);
raf.write(content, 0, contentLength);
raf.close();
}
接下里,我们来看一些其他的常用操作
移动文件
public static boolean moveFile(String sourceFile, String destFile)
{
File source = new File(sourceFile);
if (!source.exists()) throw new RuntimeException("source file does not exist.");
File dest = new File(destFile);
if (!(new File(dest.getPath()).exists())) new File(dest.getParent()).mkdirs();
return source.renameTo(dest);
}
复制文件
public static void copyFile(String sourceFile, String destFile) throws IOException
{
File source = new File(sourceFile);
if (!source.exists()) throw new RuntimeException("File does not exist.");
if (!source.isFile()) throw new RuntimeException("It is not file.");
if (!source.canRead()) throw new RuntimeException("File cound not be read.");
File dest = new File(destFile);
if (dest.exists())
{
if (dest.isDirectory()) throw new RuntimeException("Destination is a folder.");
else
{
dest.delete();
}
}
else
{
File parentFolder = new File(dest.getParent());
if (!parentFolder.exists()) parentFolder.mkdirs();
if (!parentFolder.canWrite()) throw new RuntimeException("Destination can not be written.");
}
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try
{
fis = new FileInputStream(source);
fos = new FileOutputStream(dest);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int bytesRead = 0;
while((bytesRead = fis.read(buffer, 0, buffer.length)) != -1)
{
fos.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
fos.flush();
}
catch(IOException ex)
{
System.out.println("Error occurs during copying " + sourceFile);
}
finally
{
if (fis != null) fis.close();
if (fos != null) fos.close();
}
}
复制文件夹
public static void copyDir(String sourceDir, String destDir) throws IOException
{
File source = new File(sourceDir);
if (!source.exists()) throw new RuntimeException("Source does not exist.");
if (!source.canRead()) throw new RuntimeException("Source could not be read.");
File dest = new File(destDir);
if (!dest.exists()) dest.mkdirs();
File[] arrFiles = source.listFiles();
for(int i = 0; i < arrFiles.length; i++)
{
if (arrFiles[i].isFile())
{
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(arrFiles[i]));
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(destDir + "/" + arrFiles[i].getName()));
String line = null;
while((line = reader.readLine()) != null) writer.write(line);
writer.flush();
reader.close();
writer.close();
}
else
{
copyDir(sourceDir + "/" + arrFiles[i].getName(), destDir + "/" + arrFiles[i].getName());
}
}
}
删除文件夹
public static void del(String filePath)
{
File file = new File(filePath);
if (file == null || !file.exists()) return;
if (file.isFile())
{
file.delete();
}
else
{
File[] arrFiles = file.listFiles();
if (arrFiles.length > 0)
{
for(int i = 0; i < arrFiles.length; i++)
{
del(arrFiles[i].getAbsolutePath());
}
}
file.delete();
}
}
获取文件夹大小
public static long getFolderSize(String dir)
{
long size = 0;
File file = new File(dir);
if (!file.exists()) throw new RuntimeException("dir does not exist.");
if (file.isFile()) return file.length();
else
{
String[] arrFileName = file.list();
for (int i = 0; i < arrFileName.length; i++)
{
size += getFolderSize(dir + "/" + arrFileName[i]);
}
}
return size;
}
将大文件切分成多个小文件
public static void splitFile(String filePath, long unit) throws IOException
{
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()) throw new RuntimeException("file does not exist.");
long size = file.length();
if (unit >= size) return;
int count = size % unit == 0 ? (int)(size/unit) : (int)(size/unit) + 1;
String newFile = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
FileInputStream fis =null;
byte[] buffer = new byte[(int)unit];
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
long startPos = 0;
String countFile = filePath + "_Count";
PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter( new File(countFile)));
writer.println(filePath + "\t" + size);
for (int i = 1; i <= count; i++)
{
newFile = filePath + "_" + i;
startPos = (i - 1) * unit;
System.out.println("Creating " + newFile);
fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(newFile));
int bytesRead = fis.read(buffer, 0, buffer.length);
if (bytesRead != -1)
{
fos.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
writer.println(newFile + "\t" + startPos + "\t" + bytesRead);
}
fos.flush();
fos.close();
System.out.println("StartPos:" + i*unit + "; EndPos:" + (i*unit + bytesRead));
}
writer.flush();
writer.close();
fis.close();
}
将多个小文件合并成一个大文件
public static void linkFiles(String countFile) throws IOException
{
File file = new File(countFile);
if (!file.exists()) throw new RuntimeException("Count file does not exist.");
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String line = reader.readLine();
String newFile = line.split("\t")[0];
long size = Long.parseLong(line.split("\t")[1]);
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(newFile, "rw");
raf.setLength(size);
FileInputStream fis = null;
byte[] buffer = null;
while((line = reader.readLine()) != null)
{
String[] arrInfo = line.split("\t");
fis = new FileInputStream(new File(arrInfo[0]));
buffer = new byte[Integer.parseInt(arrInfo[2])];
long startPos = Long.parseLong(arrInfo[1]);
fis.read(buffer, 0, Integer.parseInt(arrInfo[2]));
raf.seek(startPos);
raf.write(buffer, 0, Integer.parseInt(arrInfo[2]));
fis.close();
}
raf.close();
}
执行外部命令
public static void execExternalCommand(String command, String argument)
{
Process process = null;
try
{
process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command + " " + argument);
InputStream is = process.getInputStream();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
String line = null;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null)
{
System.out.println(line);
}
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
System.err.println(ex.getMessage());
}
finally
{
if (process != null) process.destroy();
}
}

