SpringBoot @Scope与@RefreshScope注解使用详解
目录
- 前言
- @Scope注解
- @RefreshScope刷新bean
- 刷新Environment对象
- 重新创建RefreshBean
- @RefreshScope代理对象
前言
在SpringIOC中,我们熟知的BeanScope有单例(singleton)、原型(prototype), Bean的Scope影响了Bean的管理方式,例如创建Scope=singleton的Bean时,IOC会保存实例在一个Map中,保证这个Bean在一个IOC上下文有且仅有一个实例。SpringCloud新增了一个refresh范围的scope,同样用了一种独特的方式改变了Bean的管理方式,使得其可以通过外部化配置(.properties)的刷新,在应用不需要重启的情况下热加载新的外部化配置的值。
那么这个scope是如何做到热加载的呢?RefreshScope主要做了以下动作:
单独管理Bean生命周期创建Bean的时候如果是RefreshScope就缓存在一个专门管理的ScopeMap中,这样就可以管理Scope是Refresh的Bean的生命周期了重新创建Bean外部化配置刷新之后,会触发一个动作,这个动作将上面的ScopeMap中的Bean清空,这样,这些Bean就会重新被IOC容器创建一次,使用最新的外部化配置的值注入类中,达到热加载新值的效果下面我们深入源码,来验证我们上述的讲法。
@Scope注解
Spring管理的Bean默认是单例的
@Scope (“prototype”) 通过注解可以实现多个实例的解决
Spring定义了多种作用域,可以基于这些作用域创建bean,包括:
单例( singleton):在整个应用中,只创建bean的一个实例。也就是单例
原型(prototype):每次注入或者通过Spring应用上下文获取的时候:getBean,都会创建一个新的bean实例。多例,每次getBean的时候都会创建新的对象
request表示请求,即在一次http请求中,被注解的Bean都是同一个Bean,不同的请求是不同的Bean;
session表示会话,即在同一个会话中,被注解的Bean都是使用的同一个Bean,不同的会话使用不同的Bean。
创建一个Bean的时候,会去BeanFactory的doGetBean方法创建Bean,不同scope有不同的创建方式:
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean
protected <T> T doGetBean(final String name, @Nullable final Class<T> requiredType,
@Nullable final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException {
//....
// Create bean instance.
// 单例Bean的创建
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
//...
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
// 原型Bean的创建
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
// ...
try {
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
//...
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else {
// 由上面的RefreshScope注解可以知道,这里scopeName=refresh
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
// 获取Refresh的Scope对象
final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
// 让Scope对象去管理Bean
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
//...
}
}
//...
}
//...
}
这里可以看到几件事情:
单例和原型scope的Bean是硬编码单独处理的
除了单例和原型Bean,其他Scope是由Scope对象处理的
具体创建Bean的过程都是由IOC做的,只不过Bean的获取是通过Scope对象
通过scopeName获取对应的scope实例
@RefreshScope刷新bean
这里scope.get获取的Scope对象为RefreshScope,可以看到,创建Bean还是由IOC来做(createBean方法),但是获取Bean,都由RefreshScope对象的get方法去获取,其get方法在父类GenericScope中实现:
public Object get(String name, ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory) {
// 将Bean缓存下来
BeanLifecycleWrapper value = this.cache.put(name,
new BeanLifecycleWrapper(name, objectFactory));
this.locks.putIfAbsent(name, new ReentrantReadWriteLock());
try {
// 创建Bean,只会创建一次,后面直接返回创建好的Bean
return value.getBean();
}
catch (RuntimeException e) {
this.errors.put(name, e);
throw e;
}
}
首先这里将Bean包装起来缓存下来
这里scope.get获取的Scope对象为RefreshScope,可以看到,创建Bean还是由IOC来做(createBean方法),但是获取Bean,都由RefreshScope对象的get方法去获取,其get方法在父类GenericScope中实现。bean的生命周期也由GenericScope控制
public Object get(String name, ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory) {
// 将Bean缓存下来
BeanLifecycleWrapper value = this.cache.put(name,
new BeanLifecycleWrapper(name, objectFactory));
this.locks.putIfAbsent(name, new ReentrantReadWriteLock());
try {
// 创建Bean,只会创建一次,后面直接返回创建好的Bean
return value.getBean();
}
catch (RuntimeException e) {
this.errors.put(name, e);
throw e;
}
}
private final ScopeCache cache;
// 这里进入上面的 BeanLifecycleWrapper value = this.cache.put(name, new BeanLifecycleWrapper(name, objectFactory));
public BeanLifecycleWrapper put(String name, BeanLifecycleWrapper value) {
return (BeanLifecycleWrapper) this.cache.put(name, value);
}
这里的ScopeCache对象其实就是一个HashMap:
public class StandardScopeCache implements ScopeCache {
private final ConcurrentMap<String, Object> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>();
//...
public Object get(String name) {
return this.cache.get(name);
}
// 如果不存在,才会put进去
public Object put(String name, Object value) {
// result若不等于null,表示缓存存在了,不会进行put操作
Object result = this.cache.putIfAbsent(name, value);
if (result != null) {
// 直接返回旧对象
return result;
}
// put成功,返回新对象
return value;
}
}
这里就是将Bean包装成一个对象,缓存在一个Map中,下次如果再GetBean,还是那个旧的BeanWrapper。回到Scope的get方法,接下来就是调用BeanWrapper的getBean方法:
private Object bean;
public Object getBean() {
if (this.bean == null) {
synchronized (this.name) {
if (this.bean == null) {
this.bean = this.objectFactory.getObject();
}
}
}
return this.bean;
}
可以看出来,BeanWrapper中的bean变量即为实际Bean,如果第一次get肯定为空,就会调用BeanFactory的createBean方法创建Bean,创建出来之后就会一直保存下来。
由此可见,RefreshScope管理了Scope=Refresh的Bean的生命周期。
重新创建RefreshBean
当配置中心刷新配置之后,有两种方式可以动态刷新Bean的配置变量值,(SpringCloud-Bus还是Nacos差不多都是这么实现的):
向上下文发布一个RefreshEvent事件
Http访问/refresh这个EndPoint
不管是什么方式,最终都会调用ContextRefresher这个类的refresh方法,那么我们由此为入口来分析一下,热加载配置的原理:
// 这就是我们上面一直分析的Scope对象(实际上可以看作一个保存refreshBean的Map)
private RefreshScope scope;
public synchronized Set<String> refresh() {
// 更新上下文中Environment外部化配置值
Set<String> keys = refreshEnvironment();
// 调用scope对象的refreshAll方法
this.scope.refreshAll();
return keys;
}
我们一般是使用@Value、@ConfigurationProperties去获取配置变量值,其底层在IOC中则是通过上下文的Environment对象去获取property值,然后依赖注入利用反射Set到Bean对象中去的。
那么如果我们更新Environment里的Property值,然后重新创建一次RefreshBean,再进行一次上述的依赖注入,是不是就能完成配置热加载了呢?@Value的变量值就可以加载为最新的了。
这里说的刷新Environment对象并重新依赖注入则为上述两个方法做的事情:
Set keys = refreshEnvironment();
this.scope.refreshAll();
刷新Environment对象
刷新环境遍历指的的是将配置替换到当前的Environment,后面如果再根据配置创建对象就会使用新的配置设置属性。
例如org.springframework.cloud.endpoint.event.RefreshEventListener进行将配置文件刷新进入environment中的操作。
ConfigurableApplicationContext addConfigFilesToEnvironment() {
StandardEnvironment environment = copyEnvironment(
this.context.getEnvironment());
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = new SpringApplicationBuilder(Empty.class)
.bannerMode(Mode.OFF).web(WebApplicationType.NONE)
.environment(environment);
// Just the listeners that affect the environment (e.g. excluding logging
// listener because it has side effects)
builder.application()
.setListeners(Arrays.asList(new BootstrapApplicationListener(),
new ConfigFileApplicationListener()));
capture = builder.run();
}
可以看到,这里归根结底就是SpringBoot启动上下文那种方法,新做了一个Spring上下文,因为Spring启动后会对上下文中的Environment进行初始化,获取最新配置,所以这里利用Spring的启动,达到了获取最新的Environment对象的目的。然后去替换旧的上下文中的Environment对象中的配置值即可。
重新创建RefreshBean
经过上述刷新Environment对象的动作,此时上下文中的配置值已经是最新的了。思路回到ContextRefresher的refresh方法,接下来会调用Scope对象的refreshAll方法:
public void refreshAll() {
// 销毁Bean
super.destroy();
this.context.publishEvent(new RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent());
}
public void destroy() {
List<Throwable> errors = new ArrayList<Throwable>();
// 缓存清空
Collection<BeanLifecycleWrapper> wrappers = this.cache.clear();
// ...
}
还记得上面的管理RefreshBean生命周期那一节关于缓存的讨论吗,cache变量是一个Map保存着RefreshBean实例,这里直接就将Map清空了。
思路回到BeanFactory的doGetBean的流程中,从IOC容器中获取RefreshBean是交给RefreshScope的get方法做的:
public Object get(String name, ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory) {
// 由于刚刚清空了缓存Map,这里就会put一个新的BeanLifecycleWrapper实例
BeanLifecycleWrapper value = this.cache.put(name,
new BeanLifecycleWrapper(name, objectFactory));
this.locks.putIfAbsent(name, new ReentrantReadWriteLock());
try {
// 在这里是新的BeanLifecycleWrapper实例调用getBean方法
return value.getBean();
}
catch (RuntimeException e) {
this.errors.put(name, e);
throw e;
}
}
public Object getBean() {
// 由于是新的BeanLifecycleWrapper实例,这里一定为null
if (this.bean == null) {
synchronized (this.name) {
if (this.bean == null) {
// 调用IOC容器的createBean,再创建一个Bean出来
this.bean = this.objectFactory.getObject();
}
}
}
return this.bean;
}
可以看到,此时RefreshBean被IOC容器重新创建一个出来了,经过IOC的依赖注入功能,@Value的就是一个新的配置值了。到这里热加载功能实现基本结束。
根据以上分析,我们可以看出只要每次我们都从IOC容器中getBean,那么拿到的RefreshBean一定是带有最新配置值的Bean。
@RefreshScope代理对象
@Scope 的注册 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader#registerBean
public void registerBean(...){
...
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(abd);
abd.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
...
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
读取@Scope元数据, AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver#resolveScopeMetadata
public ScopeMetadata resolveScopeMetadata(BeanDefinition definition) {
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(
annDef.getMetadata(), Scope.class);
if (attributes != null) {
metadata.setScopeName(attributes.getString("value"));
ScopedProxyMode proxyMode = attributes.getEnum("proxyMode");
if (proxyMode == null || proxyMode == ScopedProxyMode.DEFAULT) {
proxyMode = this.defaultProxyMode;
}
metadata.setScopedProxyMode(proxyMode);
}
}
Scope实例对象通过ScopedProxyFactoryBean创建,其中通过AOP使其实现ScopedObject接口,这里不再展开
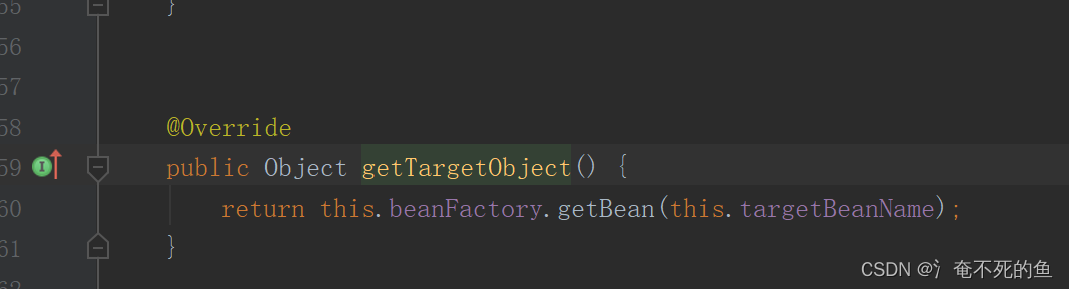
每次使用@RefreshScope的bean的get方法时都会重新通过this.beanFactory.getBean(this.targetBeanName);
如果被清空了的话,那么会重新创建bean会使用,刷新后的environment的配置注入属性,实现动态刷新。
到此这篇关于SpringBoot @Scope与@RefreshScope注解使用详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot @Scope与@RefreshScope内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

