JavaWeb中过滤器Filter的用法详解
目录
- 过滤器Filter
- 处理顺序
- 使用场景
- 自定义过滤器
- 源码分析
- FilterDef
- FilterMap
- 初始化过滤器
- 创建过滤器链 ApplicationFilterChain
- 执行过滤器链
过滤器Filter
过滤器通常对一些web资源进行拦截,做完一些处理器再交给下一个过滤器处理,直到所有的过滤器处理器,再调用servlet实例的service方法进行处理。过滤器可以对request进行处理也可以对response进行处理。
处理顺序
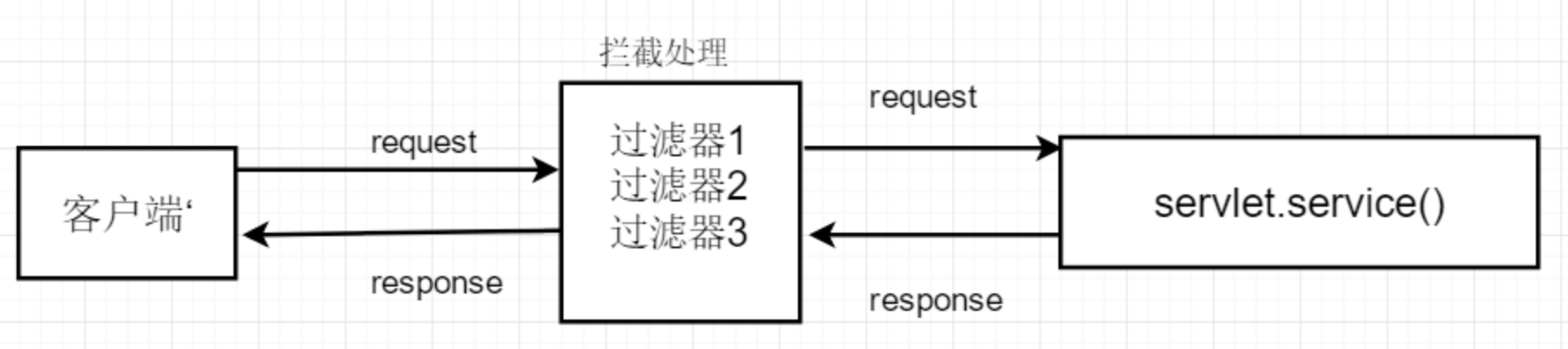
如果过滤器链顺序如上图所示,那么对request请求的处理顺序为1、2、3,对response响应的处理顺序为3、2、1.
使用场景
用户权限验证
防止乱码统一对请求和响应设置编码
对响应数据压缩等等
自定义过滤器
实现接口 Filter
public interface Filter {
// 由web容器调用在filter实例化后调用一次,可以用来配置filter的初始信息等
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException;
// 执行该过滤器逻辑,由ApplicationFilterChain过滤器链统一调用
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException;
// 有web容器调用进行销毁
public void destroy();
}
写一个简单的过滤器,当用户已登录或者请求的页面是首页时不进行过滤拦截继续请求下一个过滤器,否则跳转回首页进行登录。可以看到给LoginFilter类加了WebFilter注解,表明过滤器的名称、作用的servlet以及需要拦截的请求路径表达式,后续会将这个过滤器注册添加到web容器的过滤器链中。
@Slf4j(topic = "e")
@WebFilter(filterName = "loginFilter", servletNames = "dispatcher", urlPatterns = "*")
public class LoginFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
log.info("LoginFilter init");
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
log.info("LoginFilter doFilter");
HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) request;
HttpServletResponse res = (HttpServletResponse) response;
// 判断用户是否登录
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
String uri = req.getRequestURI();
log.info("requestUri:" + uri);
// 已经登录 | 首页 | 登录接口不拦截,其他情况重定向回首页
if (LoginUtil.isLogin(session.getAttribute("username"))) {
log.info("用户已登录");
chain.doFilter(req, res);
} else if (uri.equals(req.getContextPath() + "/") || uri.contains("login")) {
log.info("请求首页/登录接口");
chain.doFilter(req, res);
} else {
log.info("未登录请求转发到登录页");
RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = req.getRequestDispatcher("/");
requestDispatcher.forward(req, res);
}
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
当然也可以在web.xml文件中配置此过滤器同使用注解是相同的效果,如下:
<filter>
<filter-name>LoginFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.monian.study.filter.LoginFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>LoginFilter</filter-name>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
请求接口日志如下
源码分析
FilterDef
这个类定义了过滤器的名称、全限定名、初始化参数等信息,有了这些信息web容器就可以实例化这个过滤器并进行一些初始化的配置操作,用来生成后续的ApplicationFilterConfig对象
public class FilterDef implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private static final StringManager sm =
StringManager.getManager(Constants.PACKAGE_NAME);
// ------------------------------------------------------------- Properties
/**
* The description of this filter.
*/
private String description = null;
public String getDescription() {
return this.description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
/**
* The display name of this filter.
*/
private String displayName = null;
public String getDisplayName() {
return this.displayName;
}
public void setDisplayName(String displayName) {
this.displayName = displayName;
}
/**
* The filter instance associated with this definition
*/
private transient Filter filter = null;
public Filter getFilter() {
return filter;
}
public void setFilter(Filter filter) {
this.filter = filter;
}
/**
* The fully qualified name of the Java class that implements this filter.
*/
private String filterClass = null;
public String getFilterClass() {
return this.filterClass;
}
public void setFilterClass(String filterClass) {
this.filterClass = filterClass;
}
/**
* The name of this filter, which must be unique among the filters
* defined for a particular web application.
*/
private String filterName = null;
public String getFilterName() {
return this.filterName;
}
public void setFilterName(String filterName) {
if (filterName == null || filterName.equals("")) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
sm.getString("filterDef.invalidFilterName", filterName));
}
this.filterName = filterName;
}
/**
* The large icon associated with this filter.
*/
private String largeIcon = null;
public String getLargeIcon() {
return this.largeIcon;
}
public void setLargeIcon(String largeIcon) {
this.largeIcon = largeIcon;
}
/**
* The set of initialization parameters for this filter, keyed by
* parameter name.
*/
private final Map<String, String> parameters = new HashMap<>();
public Map<String, String> getParameterMap() {
return this.parameters;
}
/**
* The small icon associated with this filter.
*/
private String smallIcon = null;
public String getSmallIcon() {
return this.smallIcon;
}
public void setSmallIcon(String smallIcon) {
this.smallIcon = smallIcon;
}
private String asyncSupported = null;
public String getAsyncSupported() {
return asyncSupported;
}
public void setAsyncSupported(String asyncSupported) {
this.asyncSupported = asyncSupported;
}
// --------------------------------------------------------- Public Methods
/**
* Add an initialization parameter to the set of parameters associated
* with this filter.
*
* @param name The initialization parameter name
* @param value The initialization parameter value
*/
public void addInitParameter(String name, String value) {
if (parameters.containsKey(name)) {
// The spec does not define this but the TCK expects the first
// definition to take precedence
return;
}
parameters.put(name, value);
}
/**
* Render a String representation of this object.
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("FilterDef[");
sb.append("filterName=");
sb.append(this.filterName);
sb.append(", filterClass=");
sb.append(this.filterClass);
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
}
FilterMap
这个类主要定义了过滤器的名称、作用的serlvet、拦截的路径以及调度类型等信息,主要用来作为判断过滤器是否能应用在request上。
public class FilterMap extends XmlEncodingBase implements Serializable {
// ------------------------------------------------------------- Properties
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* The name of this filter to be executed when this mapping matches
* a particular request.
*/
public static final int ERROR = 1;
public static final int FORWARD = 2;
public static final int INCLUDE = 4;
public static final int REQUEST = 8;
public static final int ASYNC = 16;
// represents nothing having been set. This will be seen
// as equal to a REQUEST
private static final int NOT_SET = 0;
private int dispatcherMapping = NOT_SET;
private String filterName = null;
public String getFilterName() {
return this.filterName;
}
public void setFilterName(String filterName) {
this.filterName = filterName;
}
// 过滤器作用的servlet的名称
private String[] servletNames = new String[0];
public String[] getServletNames() {
if (matchAllServletNames) {
return new String[] {};
} else {
return this.servletNames;
}
}
public void addServletName(String servletName) {
if ("*".equals(servletName)) {
this.matchAllServletNames = true;
} else {
String[] results = new String[servletNames.length + 1];
System.arraycopy(servletNames, 0, results, 0, servletNames.length);
results[servletNames.length] = servletName;
servletNames = results;
}
}
/**
* The flag that indicates this mapping will match all url-patterns
*/
private boolean matchAllUrlPatterns = false;
public boolean getMatchAllUrlPatterns() {
return matchAllUrlPatterns;
}
/**
* The flag that indicates this mapping will match all servlet-names
*/
private boolean matchAllServletNames = false;
public boolean getMatchAllServletNames() {
return matchAllServletNames;
}
/**
* 过滤器作用拦截的路径
*/
private String[] urlPatterns = new String[0];
public String[] getURLPatterns() {
if (matchAllUrlPatterns) {
return new String[] {};
} else {
return this.urlPatterns;
}
}
public void addURLPattern(String urlPattern) {
addURLPatternDecoded(UDecoder.URLDecode(urlPattern, getCharset()));
}
public void addURLPatternDecoded(String urlPattern) {
if ("*".equals(urlPattern)) {
this.matchAllUrlPatterns = true;
} else {
String[] results = new String[urlPatterns.length + 1];
System.arraycopy(urlPatterns, 0, results, 0, urlPatterns.length);
results[urlPatterns.length] = UDecoder.URLDecode(urlPattern);
urlPatterns = results;
}
}
/**
* This method will be used to set the current state of the FilterMap
* representing the state of when filters should be applied.
* @param dispatcherString the dispatcher type which should
* match this filter
*/
public void setDispatcher(String dispatcherString) {
String dispatcher = dispatcherString.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
if (dispatcher.equals(DispatcherType.FORWARD.name())) {
// apply FORWARD to the global dispatcherMapping.
dispatcherMapping |= FORWARD;
} else if (dispatcher.equals(DispatcherType.INCLUDE.name())) {
// apply INCLUDE to the global dispatcherMapping.
dispatcherMapping |= INCLUDE;
} else if (dispatcher.equals(DispatcherType.REQUEST.name())) {
// apply REQUEST to the global dispatcherMapping.
dispatcherMapping |= REQUEST;
} else if (dispatcher.equals(DispatcherType.ERROR.name())) {
// apply ERROR to the global dispatcherMapping.
dispatcherMapping |= ERROR;
} else if (dispatcher.equals(DispatcherType.ASYNC.name())) {
// apply ERROR to the global dispatcherMapping.
dispatcherMapping |= ASYNC;
}
}
public int getDispatcherMapping() {
// per the SRV.6.2.5 absence of any dispatcher elements is
// equivalent to a REQUEST value
if (dispatcherMapping == NOT_SET) return REQUEST;
return dispatcherMapping;
}
public String[] getDispatcherNames() {
ArrayList<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
if ((dispatcherMapping & FORWARD) != 0) {
result.add(DispatcherType.FORWARD.name());
}
if ((dispatcherMapping & INCLUDE) != 0) {
result.add(DispatcherType.INCLUDE.name());
}
if ((dispatcherMapping & REQUEST) != 0) {
result.add(DispatcherType.REQUEST.name());
}
if ((dispatcherMapping & ERROR) != 0) {
result.add(DispatcherType.ERROR.name());
}
if ((dispatcherMapping & ASYNC) != 0) {
result.add(DispatcherType.ASYNC.name());
}
return result.toArray(new String[result.size()]);
}
// --------------------------------------------------------- Public Methods
/**
* Render a String representation of this object.
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("FilterMap[");
sb.append("filterName=");
sb.append(this.filterName);
for (int i = 0; i < servletNames.length; i++) {
sb.append(", servletName=");
sb.append(servletNames[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < urlPatterns.length; i++) {
sb.append(", urlPattern=");
sb.append(urlPatterns[i]);
}
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
}
初始化过滤器
org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext#filterStart
/**
* Configure and initialize the set of filters for this Context.
* 为此上下文配置和初始化过滤器
* @return <code>true</code> if all filter initialization completed
* successfully, or <code>false</code> otherwise.
*/
public boolean filterStart() {
if (getLogger().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLogger().debug("Starting filters");
}
// Instantiate and record a FilterConfig for each defined filter
boolean ok = true;
synchronized (filterConfigs) {
filterConfigs.clear();
// 遍历过滤器定义
for (Entry<String,FilterDef> entry : filterDefs.entrySet()) {
String name = entry.getKey();
if (getLogger().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLogger().debug(" Starting filter '" + name + "'");
}
try {
// 实例化应用过滤器配置
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig =
new ApplicationFilterConfig(this, entry.getValue());
filterConfigs.put(name, filterConfig);
} catch (Throwable t) {
t = ExceptionUtils.unwrapInvocationTargetException(t);
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
getLogger().error(sm.getString(
"standardContext.filterStart", name), t);
ok = false;
}
}
}
return ok;
}
通过构建ApplicationFilterConfig主要是实例化filter,以及初始化init(只会调用一次),并且该类实现了FilterConfig接口,可以通过ApplicationFilterConfig实例获取过滤器的名称、全限定名以及配置的一些初始化参数信息。
public final class ApplicationFilterConfig implements FilterConfig, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
static final StringManager sm =
StringManager.getManager(Constants.Package);
private transient Log log = LogFactory.getLog(ApplicationFilterConfig.class); // must not be static
/**
* Empty String collection to serve as the basis for empty enumerations.
*/
private static final List<String> emptyString = Collections.emptyList();
// ----------------------------------------------------------- Constructors
// 构造方法
ApplicationFilterConfig(Context context, FilterDef filterDef)
throws ClassCastException, ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException,
InstantiationException, ServletException, InvocationTargetException, NamingException,
IllegalArgumentException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {
super();
this.context = context;
this.filterDef = filterDef;
// 过滤器初始化
if (filterDef.getFilter() == null) {
getFilter();
} else {
this.filter = filterDef.getFilter();
getInstanceManager().newInstance(filter);
initFilter();
}
}
// ----------------------------------------------------- Instance Variables
/**
* The Context with which we are associated.
*/
private final transient Context context;
/**
* The application Filter we are configured for.
*/
private transient Filter filter = null;
/**
* The <code>FilterDef</code> that defines our associated Filter.
*/
private final FilterDef filterDef;
/**
* the InstanceManager used to create and destroy filter instances.
*/
private transient InstanceManager instanceManager;
/**
* JMX registration name
*/
private ObjectName oname;
// --------------------------------------------------- FilterConfig Methods
/**
* Return the name of the filter we are configuring.
*/
@Override
public String getFilterName() {
return filterDef.getFilterName();
}
/**
* @return The class of the filter we are configuring.
*/
public String getFilterClass() {
return filterDef.getFilterClass();
}
/**
* Return a <code>String</code> containing the value of the named
* initialization parameter, or <code>null</code> if the parameter
* does not exist.
*
* @param name Name of the requested initialization parameter
*/
@Override
public String getInitParameter(String name) {
Map<String,String> map = filterDef.getParameterMap();
if (map == null) {
return null;
}
return map.get(name);
}
/**
* Return an <code>Enumeration</code> of the names of the initialization
* parameters for this Filter.
*/
@Override
public Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames() {
Map<String,String> map = filterDef.getParameterMap();
if (map == null) {
return Collections.enumeration(emptyString);
}
return Collections.enumeration(map.keySet());
}
/**
* Return the ServletContext of our associated web application.
*/
@Override
public ServletContext getServletContext() {
return this.context.getServletContext();
}
/**
* Return a String representation of this object.
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("ApplicationFilterConfig[");
sb.append("name=");
sb.append(filterDef.getFilterName());
sb.append(", filterClass=");
sb.append(filterDef.getFilterClass());
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
// --------------------------------------------------------- Public Methods
public Map<String, String> getFilterInitParameterMap() {
return Collections.unmodifiableMap(filterDef.getParameterMap());
}
// -------------------------------------------------------- Package Methods
Filter getFilter() throws ClassCastException, ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException,
InstantiationException, ServletException, InvocationTargetException, NamingException,
IllegalArgumentException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {
// Return the existing filter instance, if any
if (this.filter != null)
return this.filter;
// 根据过滤器的全限定名通过反射实例化
String filterClass = filterDef.getFilterClass();
this.filter = (Filter) getInstanceManager().newInstance(filterClass);
// 初始化过滤器
initFilter();
return this.filter;
}
// 调用过滤器的init()方法,我们自定义的过滤器该init方法也由我们自定义
private void initFilter() throws ServletException {
if (context instanceof StandardContext &&
context.getSwallowOutput()) {
try {
SystemLogHandler.startCapture();
filter.init(this);
} finally {
String capturedlog = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture();
if (capturedlog != null && capturedlog.length() > 0) {
getServletContext().log(capturedlog);
}
}
} else {
filter.init(this);
}
// Expose filter via JMX
registerJMX();
}
/**
* Return the filter definition we are configured for.
*/
FilterDef getFilterDef() {
return this.filterDef;
}
private InstanceManager getInstanceManager() {
if (instanceManager == null) {
if (context instanceof StandardContext) {
instanceManager = ((StandardContext)context).getInstanceManager();
} else {
instanceManager = new DefaultInstanceManager(null,
new HashMap<String, Map<String, String>>(),
context,
getClass().getClassLoader());
}
}
return instanceManager;
}
}
创建过滤器链 ApplicationFilterChain
web容器会为request创建过滤器链,并且经过过滤器链中每个过滤器的处理后才会继续执行到servlet
org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterFactory#createFilterChain
public static ApplicationFilterChain createFilterChain(ServletRequest request,
Wrapper wrapper, Servlet servlet) {
// If there is no servlet to execute, return null
if (servlet == null)
return null;
// 创建并初始化一个拦截器对象
ApplicationFilterChain filterChain = null;
if (request instanceof Request) {
Request req = (Request) request;
if (Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
// Security: Do not recycle
filterChain = new ApplicationFilterChain();
} else {
// 从请求中取,复用过滤器链
filterChain = (ApplicationFilterChain) req.getFilterChain();
if (filterChain == null) {
filterChain = new ApplicationFilterChain();
req.setFilterChain(filterChain);
}
}
} else {
// Request dispatcher in use
filterChain = new ApplicationFilterChain();
}
// 设置servlet
filterChain.setServlet(servlet);
// 是否支持异步
filterChain.setServletSupportsAsync(wrapper.isAsyncSupported());
// Acquire the filter mappings for this Context
// 从上下文中获取过滤器映射信息
StandardContext context = (StandardContext) wrapper.getParent();
FilterMap filterMaps[] = context.findFilterMaps();
// If there are no filter mappings, we are done
// 未设置过滤器直接返回
if ((filterMaps == null) || (filterMaps.length == 0))
return filterChain;
// Acquire the information we will need to match filter mappings
// 从request获取dispatcher以匹配 (REQUEST)
DispatcherType dispatcher =
(DispatcherType) request.getAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_TYPE_ATTR);
// 获取请求路径
String requestPath = null;
Object attribute = request.getAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_REQUEST_PATH_ATTR);
if (attribute != null){
requestPath = attribute.toString();
}
// 获取servlet名称
String servletName = wrapper.getName();
// Add the relevant path-mapped filters to this filter chain
// 过滤器链中添加路径匹配的过滤器
for (int i = 0; i < filterMaps.length; i++) {
// 先匹配dispatcher类型,默认是REQUEST
if (!matchDispatcher(filterMaps[i] ,dispatcher)) {
continue;
}
// 再匹配请求路径
if (!matchFiltersURL(filterMaps[i], requestPath))
continue;
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = (ApplicationFilterConfig)
context.findFilterConfig(filterMaps[i].getFilterName());
if (filterConfig == null) {
// FIXME - log configuration problem
continue;
}
// 添加到过滤器链中
filterChain.addFilter(filterConfig);
}
// Add filters that match on servlet name second
// 在根据servlet名称匹配过滤器添加到过滤器链中
for (int i = 0; i < filterMaps.length; i++) {
if (!matchDispatcher(filterMaps[i] ,dispatcher)) {
continue;
}
if (!matchFiltersServlet(filterMaps[i], servletName))
continue;
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = (ApplicationFilterConfig)
context.findFilterConfig(filterMaps[i].getFilterName());
if (filterConfig == null) {
// FIXME - log configuration problem
continue;
}
filterChain.addFilter(filterConfig);
}
// Return the completed filter chain
// 返回完整的过滤器链对象
return filterChain;
}
执行过滤器链
ApplicationFilterChain执行过滤器方法
public final class ApplicationFilterChain implements FilterChain {
// Used to enforce requirements of SRV.8.2 / SRV.14.2.5.1
private static final ThreadLocal<ServletRequest> lastServicedRequest;
private static final ThreadLocal<ServletResponse> lastServicedResponse;
static {
if (ApplicationDispatcher.WRAP_SAME_OBJECT) {
lastServicedRequest = new ThreadLocal<>();
lastServicedResponse = new ThreadLocal<>();
} else {
lastServicedRequest = null;
lastServicedResponse = null;
}
}
// -------------------------------------------------------------- Constants
public static final int INCREMENT = 10;
// ----------------------------------------------------- Instance Variables
/**
* Filters.
*/
private ApplicationFilterConfig[] filters = new ApplicationFilterConfig[0];
/**
* The int which is used to maintain the current position
* in the filter chain.
*/
private int pos = 0;
/**
* The int which gives the current number of filters in the chain.
*/
private int n = 0;
/**
* The servlet instance to be executed by this chain.
*/
private Servlet servlet = null;
/**
* Does the associated servlet instance support async processing?
*/
private boolean servletSupportsAsync = false;
/**
* The string manager for our package.
*/
private static final StringManager sm =
StringManager.getManager(Constants.Package);
/**
* Static class array used when the SecurityManager is turned on and
* <code>doFilter</code> is invoked.
*/
private static final Class<?>[] classType = new Class[]{
ServletRequest.class, ServletResponse.class, FilterChain.class};
/**
* Static class array used when the SecurityManager is turned on and
* <code>service</code> is invoked.
*/
private static final Class<?>[] classTypeUsedInService = new Class[]{
ServletRequest.class, ServletResponse.class};
// ---------------------------------------------------- FilterChain Methods
/**
* Invoke the next filter in this chain, passing the specified request
* and response. If there are no more filters in this chain, invoke
* the <code>service()</code> method of the servlet itself.
*
* @param request The servlet request we are processing
* @param response The servlet response we are creating
*
* @exception IOException if an input/output error occurs
* @exception ServletException if a servlet exception occurs
*/
// 执行过滤器
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
try {
java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new java.security.PrivilegedExceptionAction<Void>() {
@Override
public Void run()
throws ServletException, IOException {
internalDoFilter(req,res);
return null;
}
}
);
} catch( PrivilegedActionException pe) {
Exception e = pe.getException();
if (e instanceof ServletException)
throw (ServletException) e;
else if (e instanceof IOException)
throw (IOException) e;
else if (e instanceof RuntimeException)
throw (RuntimeException) e;
else
throw new ServletException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
} else {
internalDoFilter(request,response);
}
}
private void internalDoFilter(ServletRequest request,
ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Call the next filter if there is one
// pos表示当前正在使用的过滤器在过滤器数组filters中的序号,每执行一次加1
// n表示过滤器数目
if (pos < n) {
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = filters[pos++];
try {
Filter filter = filterConfig.getFilter();
if (request.isAsyncSupported() && "false".equalsIgnoreCase(
filterConfig.getFilterDef().getAsyncSupported())) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.ASYNC_SUPPORTED_ATTR, Boolean.FALSE);
}
if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
Principal principal =
((HttpServletRequest) req).getUserPrincipal();
Object[] args = new Object[]{req, res, this};
SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege ("doFilter", filter, classType, args, principal);
} else {
// 调用doFilter执行过滤器的方法
filter.doFilter(request, response, this);
}
} catch (IOException | ServletException | RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
e = ExceptionUtils.unwrapInvocationTargetException(e);
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("filterChain.filter"), e);
}
return;
}
// We fell off the end of the chain -- call the servlet instance
// 当所有过滤器执行完后,调用servlet的service()方法
try {
if (ApplicationDispatcher.WRAP_SAME_OBJECT) {
lastServicedRequest.set(request);
lastServicedResponse.set(response);
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported() && !servletSupportsAsync) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.ASYNC_SUPPORTED_ATTR,
Boolean.FALSE);
}
// Use potentially wrapped request from this point
if ((request instanceof HttpServletRequest) &&
(response instanceof HttpServletResponse) &&
Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
Principal principal =
((HttpServletRequest) req).getUserPrincipal();
Object[] args = new Object[]{req, res};
SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege("service",
servlet,
classTypeUsedInService,
args,
principal);
} else {
servlet.service(request, response);
}
} catch (IOException | ServletException | RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
e = ExceptionUtils.unwrapInvocationTargetException(e);
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("filterChain.servlet"), e);
} finally {
if (ApplicationDispatcher.WRAP_SAME_OBJECT) {
lastServicedRequest.set(null);
lastServicedResponse.set(null);
}
}
}
/**
* The last request passed to a servlet for servicing from the current
* thread.
*
* @return The last request to be serviced.
*/
public static ServletRequest getLastServicedRequest() {
return lastServicedRequest.get();
}
/**
* The last response passed to a servlet for servicing from the current
* thread.
*
* @return The last response to be serviced.
*/
public static ServletResponse getLastServicedResponse() {
return lastServicedResponse.get();
}
// -------------------------------------------------------- Package Methods
/**
* Add a filter to the set of filters that will be executed in this chain.
*
* @param filterConfig The FilterConfig for the servlet to be executed
*/
// 添加过滤器配置信息到过滤器链
void addFilter(ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig) {
// Prevent the same filter being added multiple times
for(ApplicationFilterConfig filter:filters)
if(filter==filterConfig)
return;
if (n == filters.length) {
ApplicationFilterConfig[] newFilters =
new ApplicationFilterConfig[n + INCREMENT];
System.arraycopy(filters, 0, newFilters, 0, n);
filters = newFilters;
}
filters[n++] = filterConfig;
}
/**
* Release references to the filters and wrapper executed by this chain.
*/
void release() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
filters[i] = null;
}
n = 0;
pos = 0;
servlet = null;
servletSupportsAsync = false;
}
/**
* Prepare for reuse of the filters and wrapper executed by this chain.
*/
void reuse() {
pos = 0;
}
/**
* Set the servlet that will be executed at the end of this chain.
*
* @param servlet The Wrapper for the servlet to be executed
*/
void setServlet(Servlet servlet) {
this.servlet = servlet;
}
void setServletSupportsAsync(boolean servletSupportsAsync) {
this.servletSupportsAsync = servletSupportsAsync;
}
/**
* Identifies the Filters, if any, in this FilterChain that do not support
* async.
*
* @param result The Set to which the fully qualified class names of each
* Filter in this FilterChain that does not support async will
* be added
*/
public void findNonAsyncFilters(Set<String> result) {
for (int i = 0; i < n ; i++) {
ApplicationFilterConfig filter = filters[i];
if ("false".equalsIgnoreCase(filter.getFilterDef().getAsyncSupported())) {
result.add(filter.getFilterClass());
}
}
}
}
到此这篇关于JavaWeb中过滤器Filter的用法详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关JavaWeb过滤器Filter内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

