详解Android 蓝牙通信方式总结
1.摘要
Android手机间通过蓝牙方式进行通信,有两种常见的方式,一种是socket方式,另一种是通过Gatt Server(Android 5.0以后)通信,socket方式最为简单,但是很多低功耗的蓝牙设备,如单片机上的蓝牙模块可能不支持;而Gatt方式相对比较复杂。其实无论是socket方式还是Gatt,Android设备间蓝牙通信都是一种C/S(client-server)模式。
本文基于两种通信方式,进行详细展开,并推荐了开源项目,建议配合学习。
关键词
(1)Bluetooth
蓝牙(Bluetooth):蓝牙,是一种支持设备短距离通信(一般10m内)的无线电技术,能在包括移动电话、PDA、无线耳机、笔记本电脑、相关外设等众多设备之间进行无线信息交换。利用“蓝牙”技术,能够有效地简化移动通信终端设备之间的通信,也能够成功地简化设备与因特网Internet之间的通信,从而使数据传输变得更加迅速高效,为无线通信拓宽道路。
(2) UUID
UUID(Universally Unique Identifier):用于标识蓝牙服务以及通讯特征访问属性,不同的蓝牙服务和属性使用不同的访问方法。
(3)服务UUID
服务UUID(Service UUID):不同的服务(Service)应该有不同的编号(UUID),用以区分不同的服务(Service)。
(4)特征值UUID
特征值UUID(Characteristic UUID):特性(Characteristic) 是依附于某个服务(Service)的
(5)属性(Property) (5.1)Read: 读属性
Read: 读属性,具有这个属性的特性是可读的,也就是说这个属性允许手机来读取一些信息。手机可以发送指令来读取某个具有读属性UUID的信息。
(5.2)Notify: 通知属性
Notify: 通知属性, 具有这个属性的特性是可以发送通知的,也就是说具有这个属性的特性(Characteristic)可以主动发送信息给手机。
(5.3)Write: 写属性
Write: 写属性, 具有这个属性的特性是可以接收写入数据的。通常手机发送数据给蓝模块就是通过这个属性完成的。这个属性在Write 完成后,会发送写入完成结果的反馈给手机,然后手机再可以写入下一包或处理后续业务,这个属性在写入一包数据后,需要等待应用层返回写入结果,速度比较慢。
(5.4)WriteWithout Response:写属性
WriteWithout Response:写属性,从字面意思上看,只是写,不需要返回写的结果,这个属性的特点是不需要应用层返回,完全依靠协议层完成,速度快,但是写入速度超过协议处理速度的时候,会丢包。
(6) GATT
GATT(Generic Attribute Profile):中文名叫通用属性协议,它定义了services和characteristic两种东西来完成低功耗蓝牙设备之间的数据传输。它是建立在通用数据协议Attribute Protocol (ATT),之上的,ATT把services和characteristic以及相关的数据保存在一张简单的查找表中,该表使用16-bit的id作为索引。
(7)profile
profile可以理解为一种规范,一个标准的通信协议,它存在于从机中。蓝牙组织规定了一些标准的profile,例如 HID OVER GATT ,防丢器 ,心率计等。每个profile中会包含多个service,每个service代表从机的一种能力。
2. Bluetooth Socket
推荐开源项目:https://github.com/Zweo/Bluetooth(https://github.com/zolty-lionheart/Bluetooth)
以该项目demo为例介绍
蓝牙端口监听接口和TCP端口类似:Socket和ServerSocket类。在服务器端,使用BluetoothServerSocket类来创建一个 监听服务端口。当一个连接被BluetoothServerSocket所接受,它会返回一个新的BluetoothSocket来管理该连接。在客户 端,使用一个单独的BluetoothSocket类去初始化一个外接连接和管理该连接。
最通常使用的蓝牙端口是RFCOMM,它是被Android API支持的类型。RFCOMM是一个面向连接,通过蓝牙模块进行的数据流传输方式,它也被称为串行端口规范(Serial Port Profile,SPP)。
为了创建一个BluetoothSocket去连接到一个已知设备,使用方法 BluetoothDevice.createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord()。然后调用connect()方法去尝试一个 面向远程设备的连接。这个调用将被阻塞指导一个连接已经建立或者该链接失效。
为了创建一个BluetoothSocket作为服务端(或者“主机”),查看BluetoothServerSocket文档。
每当该端口连接成功,无论它初始化为客户端,或者被接受作为服务器端,通过getInputStream()和getOutputStream()来打开IO流,从而获得各自的InputStream和OutputStream对象
BluetoothSocket类线程安全。特别的,close()方法总会马上放弃外界操作并关闭服务器端口。
注意:需要BLUETOOTH权限。
2.1 Server端
private static final String UUIDString = "00001101-0000-1000-8000-00805F9B34FB";
//开启服务器
private class ServerThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
/* 创建一个蓝牙服务器
* 参数分别:服务器名称、UUID */
mServerSocket = bluetoothAdapter.listenUsingRfcommWithServiceRecord(PROTOCOL_SCHEME_RFCOMM, UUID.fromString(UUIDString));
while (true){
Log.d("server", "wait cilent connect...");
Message msg = new Message();
msg.obj = "请稍候,正在等待客户端的连接...";
msg.what = WAITING_FOR_CLIENT;
linkDetectedHandler.sendMessage(msg);
/* 接受客户端的连接请求 */
BluetoothSocket socket = mServerSocket.accept();
socketMap.put(socket.getRemoteDevice().getAddress(), socket);
// remoteDeviceMap.put(socket.getRemoteDevice().getAddress(),socket.getRemoteDevice());
Log.d("server", "accept success !");
Message msg2 = new Message();
String info = "客户端已经连接上!可以发送信息。";
msg2.obj = info;
msg.what = CONNECTED_CLIENT;
linkDetectedHandler.sendMessage(msg2);
//启动接受数据
ReadThread mreadThread = new ReadThread(socket.getRemoteDevice().getAddress());
readThreadMap.put(socket.getRemoteDevice().getAddress(),mreadThread);
mreadThread.start();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.2 Server
//开启客户端
private class ClientThread extends Thread {
private String remoteAddress;
public ClientThread(String remoteAddress) {
this.remoteAddress = remoteAddress;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//创建一个Socket连接:只需要服务器在注册时的UUID号
BluetoothDevice device = bluetoothAdapter.getRemoteDevice(remoteAddress);
BluetoothSocket socket = device.createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(UUID.fromString(UUIDString));
//连接
Message msg2 = new Message();
msg2.obj = "请稍候,正在连接服务器:" + remoteAddress;
msg2.what = IS_CONNECTING_SERVER;
linkDetectedHandler.sendMessage(msg2);
socket.connect();
socketMap.put(remoteAddress, socket);
Message msg = new Message();
msg.obj = remoteAddress;
msg.what = CONNECTED_SERVER;
linkDetectedHandler.sendMessage(msg);
//启动接受数据
ReadThread mreadThread = new ReadThread(remoteAddress);
readThreadMap.put(remoteAddress,mreadThread);
mreadThread.start();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
socketMap.remove(remoteAddress);
Log.e("connect", e.getMessage(), e);
Message msg = new Message();
msg.obj = "连接服务端异常!断开连接重新试一试。"+e.getMessage();
msg.what = CONNECT_SERVER_ERROR;
linkDetectedHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
}
}
3. Bluetooth GATT
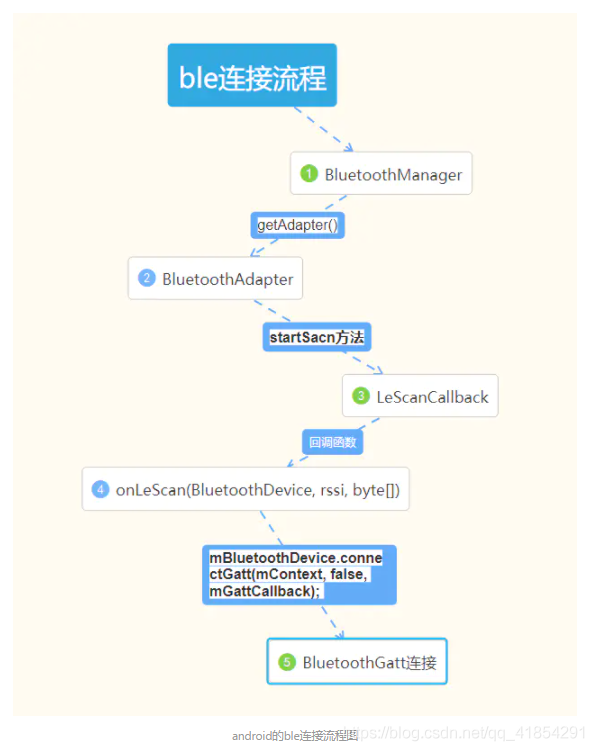
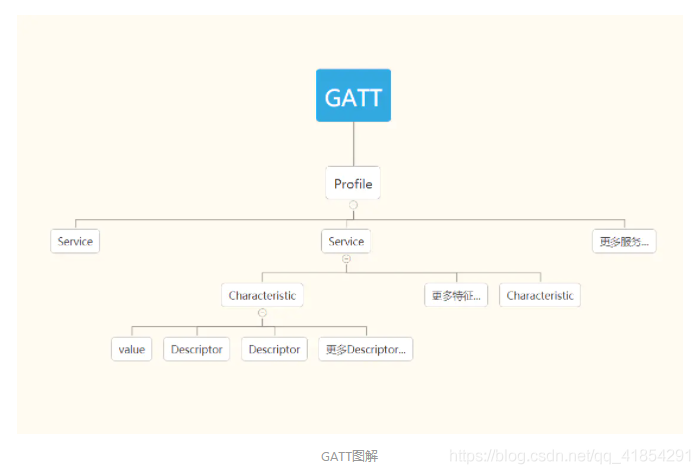
推荐开源项目:https://github.com/dingpwen/bl_communication(https://github.com/zolty-lionheart/bl_communication)
以该项目demo为例介绍
3.1 Server
private fun setupServer() {
val gattService = BluetoothGattService(Constants.BLE_SERVICE_UUID, BluetoothGattService.SERVICE_TYPE_PRIMARY)
val characteristicRead = BluetoothGattCharacteristic(Constants.BLE_READ_UUID, BluetoothGattCharacteristic.PROPERTY_READ, BluetoothGattCharacteristic.PERMISSION_READ)
val descriptor = BluetoothGattDescriptor(Constants.BLE_DESC_UUID, BluetoothGattCharacteristic.PERMISSION_WRITE)
characteristicRead.addDescriptor(descriptor)
gattService.addCharacteristic(characteristicRead)
val characteristicWrite = BluetoothGattCharacteristic(Constants.BLE_WRITE_UUID, BluetoothGattCharacteristic.PROPERTY_WRITE or
BluetoothGattCharacteristic.PROPERTY_READ or BluetoothGattCharacteristic.PROPERTY_NOTIFY,
BluetoothGattCharacteristic.PERMISSION_WRITE)
gattService.addCharacteristic(characteristicWrite)
Log.d("wenpd", "startGattServer:stagattServicetus=$gattService")
mGattServer.addService(gattService)
}
3.2 Client
private class GattClientCallback extends BluetoothGattCallback {
@Override
public void onConnectionStateChange(BluetoothGatt gatt, int status, int newState) {
super.onConnectionStateChange(gatt, status, newState);
if (status == BluetoothGatt.GATT_FAILURE) {
disconnectGattServer();
return;
} else if (status != BluetoothGatt.GATT_SUCCESS) {
disconnectGattServer();
return;
}
if (newState == BluetoothProfile.STATE_CONNECTED) {
mConnected = true;
gatt.discoverServices();
} else if (newState == BluetoothProfile.STATE_DISCONNECTED) {
disconnectGattServer();
}
}
@Override
public void onServicesDiscovered(BluetoothGatt gatt, int status) {
super.onServicesDiscovered(gatt, status);
Log.d(TAG, "onServicesDiscovered status:" + status);
if (status != BluetoothGatt.GATT_SUCCESS) {
return;
}
BluetoothGattService service = gatt.getService(Constants.SERVICE_UUID);
BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic = service.getCharacteristic(Constants.CHARACTERISTIC_UUID);
characteristic.setWriteType(BluetoothGattCharacteristic.WRITE_TYPE_DEFAULT);
mInitialized = gatt.setCharacteristicNotification(characteristic, true);
}
@Override
public void onCharacteristicChanged(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic) {
super.onCharacteristicChanged(gatt, characteristic);
byte[] messageBytes = characteristic.getValue();
/*for(int i = 0, j = messageBytes.length -1; i < j; ++i, --j) {
byte temp = messageBytes[i];
messageBytes[i] = messageBytes[j];
messageBytes[j] = temp;
}*/
String messageString = new String(messageBytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
Log.d(TAG,"Received message: " + messageString);
setReceivedData(messageString);
}
}
参考文献
1.Android Phone蓝牙通信方式总结(Socket与Gatt)
2.Bluetooth之BluetoothSocket
3.全面且简单明了的蓝牙服务及UUID介绍
4.Android BLE蓝牙开发-读写数据 获取UUID
到此这篇关于详解Android 蓝牙通信方式总结的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Android 蓝牙通信内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

