C++之默认参数详解
目录
- 一、C++ 默认参数
- 1.举例
- 1.单个参数
- 2.多个参数
- 2.规则
- 总结
一、C++ 默认参数
通常情况下,函数在调用时,形参从实参那里取得值。对于多次调用同一函数同一实参时,C++给出了更简单的处理办法。给形参以默认值,这样就不用从实参那里取值了。
1.举例
1.单个参数
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
void weatherForcast(char * w="sunny")
{
time_t t = time(0);
char tmp[64];
strftime(tmp,sizeof(tmp), "%Y/%m/%d %X %A ",localtime(&t) );
cout<<tmp<< "today is weahter "<<w<<endl;
}
int main()
{
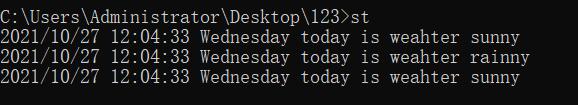
//sunny windy cloudy foggy rainy
weatherForcast();
weatherForcast("rainny");
weatherForcast();
return 0;
}
2.多个参数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
float volume(float length, float weight = 4,float high = 5)
{
return length*weight*high;
}
int main()
{
float v = volume(10);
float v1 = volume(10,20);
float v2 = volume(10,20,30);
cout<<v<<endl;
cout<<v1<<endl;
cout<<v2<<endl;
return 0;
}

2.规则
1.规定默认参数必须从函数参数的右边向左边使用
正确声明: void fun1(int a, int b=10); void fun2(int a, int b=10, int c=20); 错误声明: void fun3(int a=5, int b, int c); void fun4(int a, int b=5, int c);
2.默认参数不能在声明和定义中同时出现
错误
声明:
void fun1(int a=10);
定义:
void fun1(int a=10){......}
正确
声明:
void fun2(int a=10);
定义:
void fun2(int a){......}
或者
声明:
void fun2(int a);
定义:
void fun2(int a=10){......}
3.函数声明和定义一体时,默认参数在定义或声明处都可以。声明在前,定义在后的话,默认参数在声明处
4.一个函数,不能又作重载,又作默认参数的函数。当你少写一个参数时,系统无法确认时重载还是默认函数。
void print(int a)
{
}
void print(int a,int b =10)
{
}
int main()
{
print(10);
return 0;
}
error:main.cpp:14: error: call of overloaded 'print(int)' is ambiguous
print(10);
总结
本篇文章就到这里了,希望能够给你带来帮助,也希望您能够多多关注我们的更多内容!
赞 (0)

