详解IntelliJ IDEA 自带的 HTTP Client 接口调用插件吊打 Postman
1 前言
当我们在开发调试 Web 服务的时候,需要对接口进行调用测试;或者对接第三方系统时,需要调用远程第三方的接口进行联调。这时,相信大家首选的工具一般会是 Postman ,一款当今比较流行而且功能齐全的接口调用调试工具。如下所示:

不过我们一般使用 IntelliJ IDEA 代码编辑器来开发和调试 Web 服务,如果使用 Postman 工具来测试接口,不仅要在电脑上安装 Postman ,还需要在不同工具之间切换,比较麻烦。幸运地的是 IDEA 自带了一款简洁轻量级的接口调用插件,HTTP Client。

2 HTTP Client
HTTP Client 是 IDEA 自带的一款简洁轻量级的接口调用插件,通过它,我们能在 IDEA 上开发,调试,测试
RESTful Web 服务。
注意:确保 HTTP Client 插件是安装启动的,默认是已安装启动的。若没有安装,在 File - Settings - Plugins 路径下进行安装,如下:

2.1 创建 HTTP Client 文件
可以创建2种文件类型的 HTTP Client 文件,一种是临时文件(scratch files,不跟项目工程挂钩),一种是非临时文件(physical files,跟项目工程挂钩)。
如果你想创建的 HTTP Client 文件是为了临时调用接口测试用的,不需要保留记录供以后使用,则可以使用临时文件;如果想存档记录请求参数,请求结果等,后续再继续使用,或者随项目提交到远程git仓库,则建议使用非临时文件。
创建 HTTP Client 临时文件

打开后,显示界面和Postman差不多,不过这种风格的界面被弃用了,官方不推荐我们使用,在最新版本的 IDEA 中已经没有这个界面了。
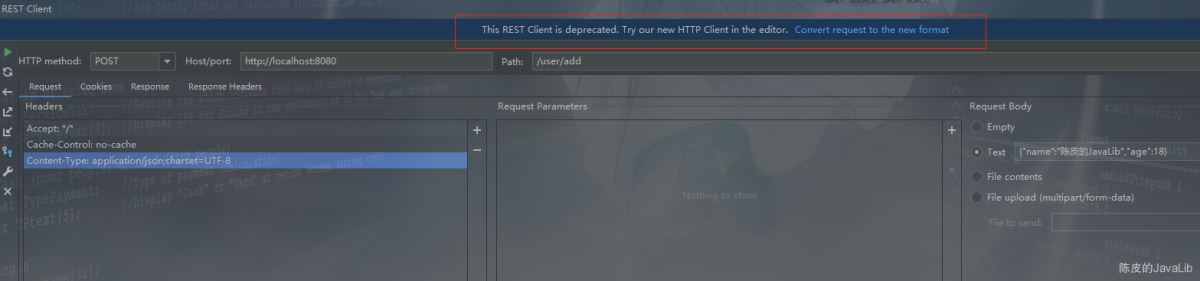
官方推荐我们使用编码式的风格界面,点击上个界面顶部的 Convert request to the new format ,即可打开新的 HTTP Client 界面。

创建 HTTP Client 非临时文件
可以在项目根目录下创建一个存储请求文件的文件夹,然后在里面创建 HTTP Client 请求文件,如下:

2.2 HTTP Client 特性
HTTP 请求存储在以.http或.rest为后缀的文件中,并且带有 API 小图标。

请求文件可以包含多个请求,多个请求中间用3个井号 ### 隔开;如果是临时文件,每次执行请求后,会在请求下方生成对应请求结果的文件链接,按住 Ctrl + 鼠标左键可以打开。
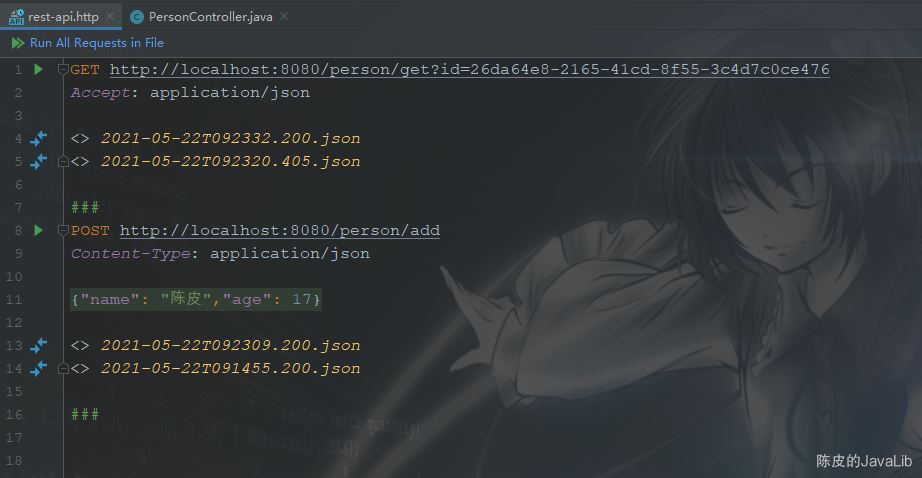
所有的请求结果,请求历史记录,cookies等信息会存放在 .idea 文件夹下,如下:

2.3 如何创建请求
使用右上角的快捷按钮创建请求,可以选择不同方式的请求,如下:

使用快捷键进行创建请求,例如输入 gtr 可以快速创建一个简单的 GET 请求,如下:
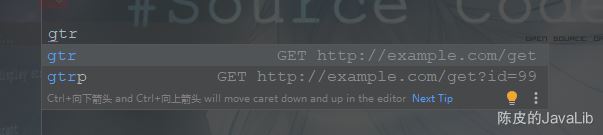
使用 Ctrl + J 快捷键可以查看创建 HTTP 请求的所有快捷键,如下:

通过 cURL 创建请求,点击右上角的 Convert form cURL 按钮,然后输入 cURL 地址即可自动转换,如下:


2.4 请求方式
GET
### GET request with a header
GET https://httpbin.org/ip
Accept: application/json
### GET request with parameter
GET https://httpbin.org/get?show_env=1
Accept: application/json
### GET request with environment variables
GET {{host}}/get?show_env={{show_env}}
Accept: application/json
### GET request with disabled redirects
# @no-redirect
GET http://httpbin.org/status/301
### GET request with dynamic variables
GET http://httpbin.org/anything?id={{$uuid}}&ts={{$timestamp}}
###
POST
### Send POST request with json body
POST https://httpbin.org/post
Content-Type: application/json
{
"id": 999,
"value": "content"
}
### Send POST request with body as parameters
POST https://httpbin.org/post
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
id=999&value=content
### Send a form with the text and file fields
POST https://httpbin.org/post
Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=WebAppBoundary
--WebAppBoundary
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="element-name"
Content-Type: text/plain
Name
--WebAppBoundary
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="data"; filename="data.json"
Content-Type: application/json
< ./request-form-data.json
--WebAppBoundary--
### Send request with dynamic variables in request's body
POST https://httpbin.org/post
Content-Type: application/json
{
"id": {{$uuid}},
"price": {{$randomInt}},
"ts": {{$timestamp}},
"value": "content"
}
###
PUT
PUT http://localhost:8080/person/put
Content-Type: application/json
{"name": "陈皮","age": 17}
PATCH
###
PATCH http://localhost:8080/person/put
Content-Type: application/json
{"name": "陈皮","age": 17}
鉴权方式
### Basic authorization.
GET https://httpbin.org/basic-auth/user/passwd
Authorization: Basic user passwd
### Basic authorization with variables.
GET https://httpbin.org/basic-auth/user/passwd
Authorization: Basic {{username}} {{password}}
### Digest authorization.
GET https://httpbin.org/digest-auth/realm/user/passwd
Authorization: Digest user passwd
### Digest authorization with variables.
GET https://httpbin.org/digest-auth/realm/user/passwd
Authorization: Digest {{username}} {{password}}
### Authorization by token, part 1. Retrieve and save token.
POST https://httpbin.org/post
Content-Type: application/json
{
"token": "my-secret-token"
}
> {% client.global.set("auth_token", response.body.json.token); %}
### Authorization by token, part 2. Use token to authorize.
GET https://httpbin.org/headers
Authorization: Bearer {{auth_token}}
###
断言方式
### Successful test: check response status is 200
GET https://httpbin.org/status/200
> {%
client.test("Request executed successfully", function() {
client.assert(response.status === 200, "Response status is not 200");
});
%}
### Failed test: check response status is 200
GET https://httpbin.org/status/404
> {%
client.test("Request executed successfully", function() {
client.assert(response.status === 200, "Response status is not 200");
});
%}
### Check response status and content-type
GET https://httpbin.org/get
> {%
client.test("Request executed successfully", function() {
client.assert(response.status === 200, "Response status is not 200");
});
client.test("Response content-type is json", function() {
var type = response.contentType.mimeType;
client.assert(type === "application/json", "Expected 'application/json' but received '" + type + "'");
});
%}
### Check response body
GET https://httpbin.org/get
> {%
client.test("Headers option exists", function() {
client.assert(response.body.hasOwnProperty("headers"), "Cannot find 'headers' option in response");
});
%}
###
以上就是IntelliJ IDEA 自带的 HTTP Client 接口调用插件吊打 Postman的详细内容,更多关于idea HTTP Client插件的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!

