Springboot整合camunda+mysql的集成流程分析
一、创建springboot工程
使用IDEA工具,选择File->New->Project,选择Spring Initialzr

输入springboot工程基本信息,本示例命名为“camunda-demo1”, jdk版本选择8

在选择springboot组件的时候,需要选择Spring Web、JDBC API、MySql Driver 这三个组件。点击下一步完成即可。

二、修改maven配置
2.1、修改springboot版本号
由于camunda版本与springboot版本有匹配关系,所以需要修改springboot版本为2.4.3,
官方推荐Camunda7.1.5版本使用Spring Boot 2.4.x版本
具体配置参考camunda官方说明文档:https://docs.camunda.org/manual/7.15/user-guide/spring-boot-integration/version-compatibility/
Pom.xm代码片段:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.4.3</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
2.2、引入camunda包
由于本示例要使用camunda流程引擎、web界面、Rest服务接口,所以需要导入camunda-bpm-spring-boot-starter、camunda-bpm-spring-boot-starter-rest、camunda-bpm-spring-boot-starter-webapp这三个依赖包,如果仅仅是使用流程引擎,只需要引入camunda-bpm-spring-boot-starter就可以了。
完整的pom.xml文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.4.3</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <groupId>com.example</groupId> <artifactId>camunda-demo1</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>camunda-demo1</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.camunda.bpm.springboot</groupId> <artifactId>camunda-bpm-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>7.15.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.camunda.bpm.springboot</groupId> <artifactId>camunda-bpm-spring-boot-starter-rest</artifactId> <version>7.15.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.camunda.bpm.springboot</groupId> <artifactId>camunda-bpm-spring-boot-starter-webapp</artifactId> <version>7.15.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
三、修改application.yaml配置
打开工程目录下的main\resources\application.yaml文件,如果没有该文件,手动新建一个,录入如下信息。
# Find more available configuration properties on the following pages of the documentation. # https://docs.camunda.org/manual/latest/user-guide/camunda-bpm-run/#configure-camunda-bpm-run # https://docs.camunda.org/manual/latest/user-guide/spring-boot-integration/configuration/#camunda-engine-properties camunda.bpm: generic-properties.properties: javaSerializationFormatEnabled: true admin-user: id: demo password: demo run: # https://docs.camunda.org/manual/latest/user-guide/camunda-bpm-run/#cross-origin-resource-sharing cors: enabled: true allowed-origins: "*" # datasource configuration is required spring.datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/camunda715?characterEncoding=UTF-8&useUnicode=true&useSSL=false&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver username: root password: root # By default, Spring Boot serves static content from any directories called /static or /public or /resources or # /META-INF/resources in the classpath. To prevent users from accidentally sharing files, this is disabled here by setting static locations to NULL. # https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/htmlsingle/#boot-features-spring-mvc-static-content spring.web.resources: static-locations: NULL
本示例使用的是mysql数据库,数据库URL、username、 password 跟后面数据库信息保存一致。
四、创建mysql数据库
Camunda默认使用已预先配置好的H2数据库,本示例使用mysql数据库,需要提前创建mysql数据库并导入Camunda建表脚本。
为Camunda平台创建一个数据库模式,名称为camunda715

导入SQL脚本。执行创建所有必需的表和默认索引的SQL DDL脚本。这些脚本可以在configuration/sql/create文件夹中找到。共2个脚本,都需要导入。

导入完成后的表结构,共40张表:

详细配置方法参考:https://lowcode.blog.csdn.net/article/details/117564836
五、启动springboot工程
创建springboot工程的时候,自动生成了SpringBootApplication启动类,运行改类启动即可。
package com.example.demo1;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class CamundaDemo1Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CamundaDemo1Application.class, args);
}
}

六、登录访问camunda
访问:http://localhost:8080,
默认账号密码demo/demo

登录成功后进入camunda控制台
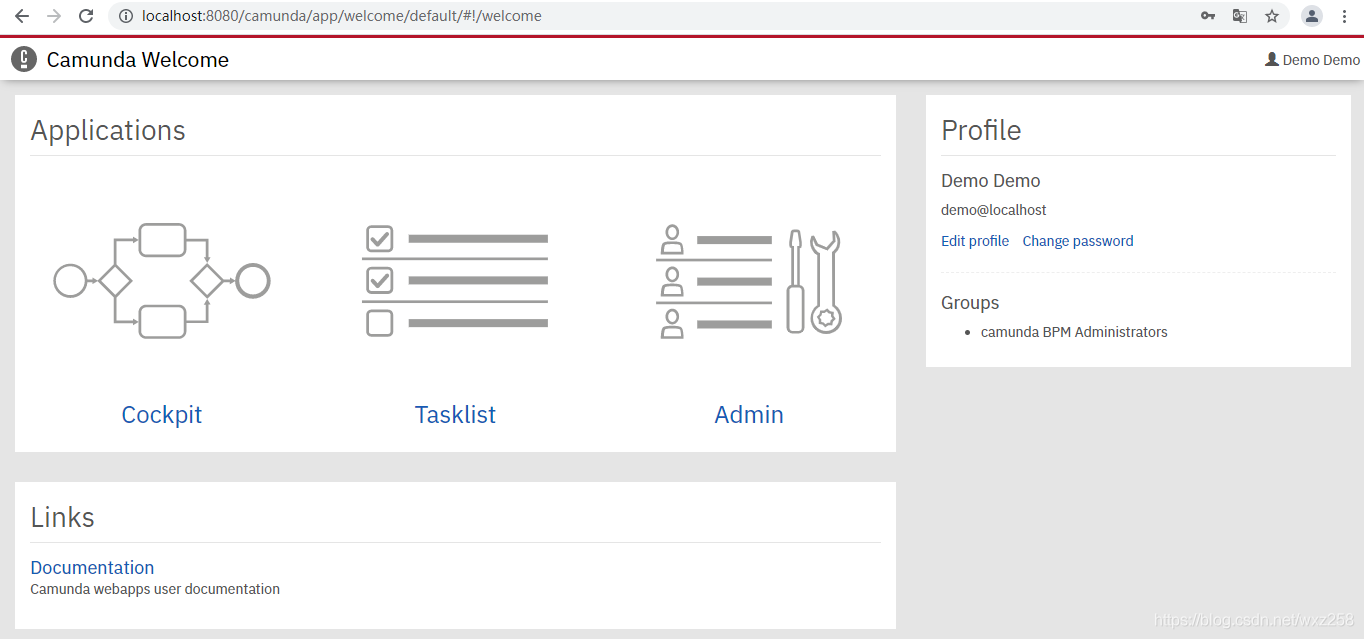
至此,完成了springboot2.4.3+camunda7.15+mysql的集成,后续的如何设计流程、如何启动流程、如何审批流程等操作,跟非springboot方式是一致的,请参考前面的文章。
https://lowcode.blog.csdn.net/article/details/117518828
https://lowcode.blog.csdn.net/article/details/118055189
以上就是Springboot整合camunda+mysql的集成实现方法的详细内容,更多关于Springboot整合camunda的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!

