springboot集成rabbitMQ之对象传输的方法
rabbitMQ的安装方法网上有很多教程,这里就不重复了。
在springboot上使用rabbitMQ传输字符串和对象,本文所给出的例子是在两个不同的项目之间进行对象和和字符串的传输。
rabbitMQ的依赖(在两个项目中一样的配置):
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
pom配置文件(在两个项目中一样的配置):
spring.application.name: demo1 //项目名 spring.rabbitmq.host: 192.168.1.111 //写自己的ip spring.rabbitmq.port: 5672 spring.rabbitmq.username: guest spring.rabbitmq.password: guest spring.rabbitmq.virtual-host: / spring.rabbitmq.publisher-confirms: true spring.rabbitmq.publisher-returns: true spring.rabbitmq.template.mandatory: true
字符转的相互传输(本例使用的topic类型)
1>. 首先,在生产者(项目A)中写配置文件,其中生成队列queue,交换机exchange并且进行绑定binding
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @Author:fdh
* @Description:
* @Date: Create in 16:13 2017/12/22
*/
@Configuration
public class senderConfigration {
/**
*@Description: 新建队列 topic.messages
*@Data:16:14 2017/12/22
*/
@Bean(name = "messages")
public Queue queueMessages(){
return new Queue("topic.messages");
}
/**
*@Description: 定义交换器
*@Data:16:15 2017/12/22
*/
@Bean
public TopicExchange exchange(){
return new TopicExchange("exchange");
}
/**
*@Description: 交换机与消息队列进行绑定 队列messages绑定交换机with topic.messages
*@Data:16:18 2017/12/22
*/
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeMessages(@Qualifier("messages") Queue queueMessages,TopicExchange exchange){
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueMessages).to(exchange).with("topic.messages");
}
}
2>. 第二步(项目A),生产者把消息发送到消息队列,
/**
* @Author:fdh
* @Description:
* @Date: Create in 14:15 2017/12/22
*/
@Controller
public class RabbitController {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/sendss")
public void send1(){
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange","topic.messages","hello topic.messages RabbitMQ");
}
}
3>. 接下来,在消费者(项目B)端写一个监听器,交换器会根据绑定的routing key(topic.messages)把生产者生产的消息放到匹配的消息队列中,监听器会监听相应的消息队列来获取路由到该消息队列上的消息。
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
/**
* @ Author:fdh
* @ Description: 消息队列监听器
* @ Date: Create in 14:19 2017/12/22
*/
@Component
public class Receiver {
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic.messages")
public void process2(String str1) throws ClassNotFoundException{
System.out.println("messages :"+str1);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"接收到来自topic.message队列的消息: "+str1);
}
这样,一个简单的字符串的传输便写好了,下面打开刚才定义的mapping: 192.168.1.111:8080/sendss
在消费者端的console窗口便会看到打印的消息

以上就是一个简单的传输字符串的例子了。
2. 下面重点介绍一下消费者和生产者之间对象的传输。
对象的传输,要现在生产者(A)中进行序列化,即把对象转化为字节数组进行传输,在消费者中,再把转化的字节数组反序列化为对象。序列化和反序列化的方法很多,这里采用的是java的Serializable 接口
1>. 在生产者(项目A)和消费者(项目B)的项目中创建实体类。
!注意!:新建实体类Boy.java 该实体类在项目A、B中的位置,必须一致,即包名必须一致,在本项目中,Boy.java 在项目A、B中都是: import com.fengdonghao.shiro.bean.Boy;
实体类也要一致。
package com.fengdonghao.shiro.bean;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @Author:fdh
* @Description:
* @Date:Create in11:14 2017/12/16
*/
@Entity
public class Boy implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID=1L;
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Boy{" +
"age=" + age +
", id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
//此处省略getter 和setter 方法
}
2>. 在生产者(A)中配置 消息队列,交换器,并进行绑定binding,和在 例子1中的第一步是一样的
3>. 在生产者(A)中的RabbitController.java 中另写一个mapping,如下
@RequestMapping("/send")
public void sendMessage() {
Boy boy= new Boy();
boy.setName("tim");
boy.setAge(11);
System.out.println(boy);
//以下是序列化操作
//Write Obj to File
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("E:\\WebPackage\\a.txt")));//把序列化之后的字节数组暂时存放在该目录下
oos.writeObject(boy);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
IOUtils.closeQuietly(oos);
}
rabbitMQService.send("对象已序列化");
4>. 在消费者(B)中对字节数组进行反序列化。
在Receiver中,重新编写例1重点的监听器
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic.messages")
public void process2(String str1) {
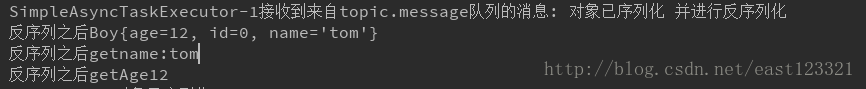
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"接收到来自topic.message队列的消息: "+str1+" 并进行反序列化");
File file = new File("E:\\WebPackage\\a.txt");//消费者和生产者中路径要保持一致,才能读取文件,进行解析
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
Boy newUser = (Boy) ois.readObject();
System.out.println("反序列之后:"+newUser);
System.out.println("反序列之后getname:"+newUser.getName());
System.out.println("反序列之后getAge"+newUser.getAge());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
IOUtils.closeQuietly(ois);
try {
FileUtils.forceDelete(file);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("messages :"+str1);
}
验证mapping: ip:8080/send
结果如下:
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。

