Android-实现切换Fragment页功能的实现代码
场景:使用Fragment实现切页。
类结构:
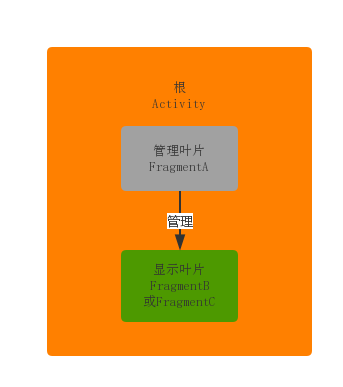
一:Activity
Activity中使用getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction()来填充一个Fragment(管理用的FragmentA)
Activity部分代码:
FragmentA fragment = FragmentA.newInstant(null); getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().add(R.id.f_tab_fragment,fragment).commit();
XML:
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/fl_container"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_above="@+id/f_tab_fragment"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/f_tab_fragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="52dp"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"/>
二:FragmentA
加载一个主FragmentA,作为管理其它子叶片FragmentX。
现在比如有两个子叶片FragmentB、FragmentC.
FragmentA 使用FragmentManager和FragmentTransaction管理FragmentB、FragmentC的切换
FragmentA代码:
public class FragmentA extends BaseFragment {
private static final String TAB_HOME = com.timediffproject.module.home.MyMainFragment.class.getName();
private static final String TAB_TEST = com.timediffproject.module.home.TestFragment.class.getName();
private BaseFragment mLastShowFragment;
private static TabFragment fragment;
public static TabFragment newInstant(Bundle bundle){
if (fragment == null){
fragment = new TabFragment();
fragment.setArguments(bundle);
}
return fragment;
}
@Override
public void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
initTabInfo();
}
private void initTabInfo(){
FragmentManager fm = getFragmentManager();
if (fm == null){
return;
}
FragmentTransaction ft = fm.beginTransaction();
BaseFragment home = (BaseFragment) fm.findFragmentByTag(TAB_HOME);
if (home != null){
ft.hide(home);
}
BaseFragment test = (BaseFragment) fm.findFragmentByTag(TAB_TEST);
if (test != null){
ft.hide(test);
}
ft.commit();
}
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater,ViewGroup container,Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_tab,container,false);
}
@Override
public void onViewCreated(View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState);
view.findViewById(R.id.btn_change_home).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
switchTo(TAB_HOME,null);
}
});
view.findViewById(R.id.btn_change_test).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
switchTo(TAB_TEST,null);
}
});
switchTo(TAB_HOME,null);
}
//切换Fragment的方式(FragmentB、FragmentC)
//tab为Fragment的类名(如:FragmentB.class.getName())
//R.id.fl_container是在Activity的布局里,不是在FragmentA的布局里
private void switchTo(String tab, Bundle bundle){
//初始化管理Fragment的类
FragmentManager fm = getFragmentManager();
if (fm == null){
return;
}
FragmentTransaction ft = fm.beginTransaction();
//从FragmentManager里寻找类名为tab的Fragment
BaseFragment fragment = (BaseFragment)fm.findFragmentByTag(tab);
if (fragment == null){
fragment = (BaseFragment) Fragment.instantiate(getActivity(),tab);
fragment.setArguments(bundle);
ft.add(R.id.fl_container,fragment,tab);
}else{
ft.show(fragment);
}
//隐藏现在正显示的Fragment
if (mLastShowFragment != null) {
ft.hide(mLastShowFragment);
}
//记录最后点击的Fragment
mLastShowFragment = fragment;
ft.commitAllowingStateLoss();
}
}
XML:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="52dp">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_change_home"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="切换home"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_change_test"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="切换test"
/>
</LinearLayout>
三:FragmentX(FragmentB、FragmentC)
子页的逻辑根据具体业务自己定义,实现与一般Fragmeng一样
例如:
public class TestFragment extends BaseFragment {
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_test,container,false);
}
@Override
public void onViewCreated(View view, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState);
}
}
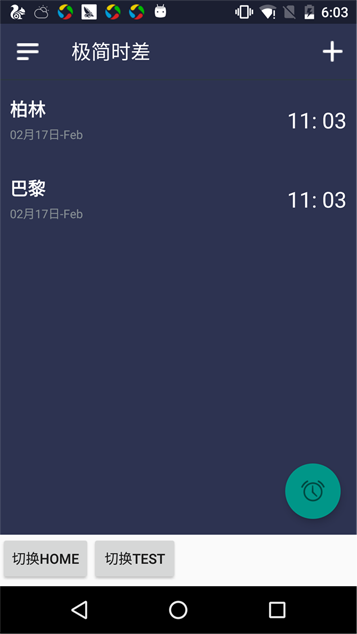
到这里,就可以简单的实现-用底部Tab切换Fragment实现切页的功能
附图:

PS:实现过程中出现的错误
java.lang.IllegalStateException: The specified child already has a parent. You must call removeView() on the child's parent first.
正确方式: 有关的fragment的初始化布局应该加上false,与父类布局建立关系。
原因:不加的话这个inflater出来的view系统会绑定一个未知父类,这时候当你把这个fragment又作为子页绑定给Activity或者另一个fragment时,就会出现以上错误。
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
//这里正确的写法是:
//return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_test,container,false);
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_test,container);
}
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。
赞 (0)

