springboot运行时新增/更新外部接口的实现方法
最近有个需求:需要让现有springboot项目可以加载外部的jar包实现新增、更新接口逻辑。本着拿来主义的思维网上找了半天没有找到类似的东西,唯一有点相似的还是spring-loaded但是这个东西据我网上了解有如下缺点:
1、使用java agent启动,个人倾向于直接使用pom依赖的方式
2、不支持新增字段,新增方法,估计也不支持mybatis的xml加载那些吧,没了解过
3、只适合在开发环境IDE中使用,没法生产使用
无奈之下,我只能自己实现一个了,我需要实现的功能如下
1、加载外部扩展jar包中的新接口,多次加载需要能完全更新
2、应该能加载mybatis、mybatis-plus中放sql的xml文件
3、应该能加载@Mapper修饰的mybatis的接口资源
4、需要能加载其它被spring管理的Bean资源
5、需要能在加载完成后更新swagger文档
总而言之就是要实现一个能够扩展完整接口的容器,其实类似于热加载也不同于热加载,热部署是监控本地的class文件的改变,然后使用自动重启或者重载,热部署领域比较火的就是devtools和jrebel,前者使用自动重启的方式,监控你的classes改变了,然后使用反射调用你的main方法重启一下,后者使用重载的方式,因为收费,具体原理也没了解过,估计就是不重启,只加载变过的class吧。而本文实现的是加载外部的jar包,这个jar包只要是个可访问的URL资源就可以了。虽然和热部署不一样,但是从方案上可以借鉴,本文就是使用重载的方式,也就是只会更新扩展包里的资源。
先来一个自定义的模块类加载器
package com.rdpaas.dynamic.core;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.net.URL;
import java.net.URLClassLoader;
import java.security.AccessController;
import java.security.PrivilegedExceptionAction;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.jar.JarEntry;
import java.util.jar.JarFile;
/**
* 动态加载外部jar包的自定义类加载器
* @author rongdi
* @date 2021-03-06
* @blog https://www.cnblogs.com/rongdi
*/
public class ModuleClassLoader extends URLClassLoader {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ModuleClassLoader.class);
private final static String CLASS_SUFFIX = ".class";
private final static String XML_SUFFIX = ".xml";
private final static String MAPPER_SUFFIX = "mapper/";
//属于本类加载器加载的jar包
private JarFile jarFile;
private Map<String, byte[]> classBytesMap = new HashMap<>();
private Map<String, Class<?>> classesMap = new HashMap<>();
private Map<String, byte[]> xmlBytesMap = new HashMap<>();
public ModuleClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader, URL... urls) {
super(urls, classLoader);
URL url = urls[0];
String path = url.getPath();
try {
jarFile = new JarFile(path);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
byte[] buf = classBytesMap.get(name);
if (buf == null) {
return super.findClass(name);
}
if(classesMap.containsKey(name)) {
return classesMap.get(name);
}
/**
* 这里应该算是骚操作了,我不知道市面上有没有人这么做过,反正我是想了好久,遇到各种因为spring要生成代理对象
* 在他自己的AppClassLoader找不到原对象导致的报错,注意如果你限制你的扩展包你不会有AOP触碰到的类或者@Transactional这种
* 会产生代理的类,那么其实你不用这么骚,直接在这里调用defineClass把字节码装载进去就行了,不会有什么问题,最多也就是
* 在加载mybatis的xml那里前后加三句话,
* 1、获取并使用一个变量保存当前线程类加载器
* 2、将自定义类加载器设置到当前线程类加载器
* 3、还原当前线程类加载器为第一步保存的类加载器
* 这样之后mybatis那些xml里resultType,resultMap之类的需要访问扩展包的Class的就不会报错了。
* 不过直接用现在这种骚操作,更加一劳永逸,不会有mybatis的问题了
*/
return loadClass(name,buf);
}
/**
* 使用反射强行将类装载的归属给当前类加载器的父类加载器也就是AppClassLoader,如果报ClassNotFoundException
* 则递归装载
* @param name
* @param bytes
* @return
*/
private Class<?> loadClass(String name, byte[] bytes) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Object[] args = new Object[]{name, bytes, 0, bytes.length};
try {
/**
* 拿到当前类加载器的parent加载器AppClassLoader
*/
ClassLoader parent = this.getParent();
/**
* 首先要明确反射是万能的,仿造org.springframework.cglib.core.ReflectUtils的写法,强行获取被保护
* 的方法defineClass的对象,然后调用指定类加载器的加载字节码方法,强行将加载归属塞给它,避免被spring的AOP或者@Transactional
* 触碰到的类需要生成代理对象,而在AppClassLoader下加载不到外部的扩展类而报错,所以这里强行将加载外部扩展包的类的归属给
* AppClassLoader,让spring的cglib生成代理对象时可以加载到原对象
*/
Method classLoaderDefineClass = (Method) AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction() {
@Override
public Object run() throws Exception {
return ClassLoader.class.getDeclaredMethod("defineClass",
String.class, byte[].class, Integer.TYPE, Integer.TYPE);
}
});
if(!classLoaderDefineClass.isAccessible()) {
classLoaderDefineClass.setAccessible(true);
}
return (Class<?>)classLoaderDefineClass.invoke(parent,args);
} catch (Exception e) {
if(e instanceof InvocationTargetException) {
String message = ((InvocationTargetException) e).getTargetException().getCause().toString();
/**
* 无奈,明明ClassNotFoundException是个异常,非要抛个InvocationTargetException,导致
* 我这里一个不太优雅的判断
*/
if(message.startsWith("java.lang.ClassNotFoundException")) {
String notClassName = message.split(":")[1];
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(notClassName)) {
throw new ClassNotFoundException(message);
}
notClassName = notClassName.trim();
byte[] bytes1 = classBytesMap.get(notClassName);
if(bytes1 == null) {
throw new ClassNotFoundException(message);
}
/**
* 递归装载未找到的类
*/
Class<?> notClass = loadClass(notClassName, bytes1);
if(notClass == null) {
throw new ClassNotFoundException(message);
}
classesMap.put(notClassName,notClass);
return loadClass(name,bytes);
}
} else {
logger.error("",e);
}
}
return null;
}
public Map<String,byte[]> getXmlBytesMap() {
return xmlBytesMap;
}
/**
* 方法描述 初始化类加载器,保存字节码
*/
public Map<String, Class> load() {
Map<String, Class> cacheClassMap = new HashMap<>();
//解析jar包每一项
Enumeration<JarEntry> en = jarFile.entries();
InputStream input = null;
try {
while (en.hasMoreElements()) {
JarEntry je = en.nextElement();
String name = je.getName();
//这里添加了路径扫描限制
if (name.endsWith(CLASS_SUFFIX)) {
String className = name.replace(CLASS_SUFFIX, "").replaceAll("/", ".");
input = jarFile.getInputStream(je);
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int bufferSize = 4096;
byte[] buffer = new byte[bufferSize];
int bytesNumRead = 0;
while ((bytesNumRead = input.read(buffer)) != -1) {
baos.write(buffer, 0, bytesNumRead);
}
byte[] classBytes = baos.toByteArray();
classBytesMap.put(className, classBytes);
} else if(name.endsWith(XML_SUFFIX) && name.startsWith(MAPPER_SUFFIX)) {
input = jarFile.getInputStream(je);
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int bufferSize = 4096;
byte[] buffer = new byte[bufferSize];
int bytesNumRead = 0;
while ((bytesNumRead = input.read(buffer)) != -1) {
baos.write(buffer, 0, bytesNumRead);
}
byte[] xmlBytes = baos.toByteArray();
xmlBytesMap.put(name, xmlBytes);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error("",e);
} finally {
if (input != null) {
try {
input.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//将jar中的每一个class字节码进行Class载入
for (Map.Entry<String, byte[]> entry : classBytesMap.entrySet()) {
String key = entry.getKey();
Class<?> aClass = null;
try {
aClass = loadClass(key);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
logger.error("",e);
}
cacheClassMap.put(key, aClass);
}
return cacheClassMap;
}
public Map<String, byte[]> getClassBytesMap() {
return classBytesMap;
}
}
然后再来个加载mybatis的xml资源的类,本类解析xml部分是参考网上资料
package com.rdpaas.dynamic.core;
import org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLMapperBuilder;
import org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLMapperEntityResolver;
import org.apache.ibatis.executor.ErrorContext;
import org.apache.ibatis.executor.keygen.SelectKeyGenerator;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement;
import org.apache.ibatis.parsing.XNode;
import org.apache.ibatis.parsing.XPathParser;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.*;
/**
* mybatis的mapper.xml和@Mapper加载类
* @author rongdi
* @date 2021-03-06
* @blog https://www.cnblogs.com/rongdi
*/
public class MapperLoader {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MapperLoader.class);
private Configuration configuration;
/**
* 刷新外部mapper,包括文件和@Mapper修饰的接口
* @param sqlSessionFactory
* @param xmlBytesMap
* @return
*/
public Map<String,Object> refresh(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory, Map<String, byte[]> xmlBytesMap) {
Configuration configuration = sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration();
this.configuration = configuration;
/**
* 这里用来区分mybatis-plus和mybatis,mybatis-plus的Configuration是继承自mybatis的子类
*/
boolean isSupper = configuration.getClass().getSuperclass() == Configuration.class;
Map<String,Object> mapperMap = new HashMap<>();
try {
/**
* 遍历外部传入的xml字节码map
*/
for(Map.Entry<String,byte[]> entry:xmlBytesMap.entrySet()) {
String resource = entry.getKey();
byte[] bytes = entry.getValue();
/**
* 使用反射强行拿出configuration中的loadedResources属性
*/
Field loadedResourcesField = isSupper
? configuration.getClass().getSuperclass().getDeclaredField("loadedResources")
: configuration.getClass().getDeclaredField("loadedResources");
loadedResourcesField.setAccessible(true);
Set loadedResourcesSet = ((Set) loadedResourcesField.get(configuration));
/**
* 加载mybatis中的xml
*/
XPathParser xPathParser = new XPathParser(new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes), true, configuration.getVariables(),
new XMLMapperEntityResolver());
/**
* 解析mybatis的xml的根节点,
*/
XNode context = xPathParser.evalNode("/mapper");
/**
* 拿到namespace,namespace就是指Mapper接口的全限定名
*/
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
Field field = configuration.getMapperRegistry().getClass().getDeclaredField("knownMappers");
field.setAccessible(true);
/**
* 拿到存放Mapper接口和对应代理子类的映射map,
*/
Map mapConfig = (Map) field.get(configuration.getMapperRegistry());
/**
* 拿到Mapper接口对应的class对象
*/
Class nsClass = Resources.classForName(namespace);
/**
* 先删除各种
*/
mapConfig.remove(nsClass);
loadedResourcesSet.remove(resource);
configuration.getCacheNames().remove(namespace);
/**
* 清掉namespace下各种缓存
*/
cleanParameterMap(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"), namespace);
cleanResultMap(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"), namespace);
cleanKeyGenerators(context.evalNodes("insert|update|select|delete"), namespace);
cleanSqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"), namespace);
/**
* 加载并解析对应xml
*/
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes),
sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration(), resource,
sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getSqlFragments());
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
/**
* 构造MapperFactoryBean,注意这里一定要传入sqlSessionFactory,
* 这块逻辑通过debug源码试验了很久
*/
MapperFactoryBean mapperFactoryBean = new MapperFactoryBean(nsClass);
mapperFactoryBean.setSqlSessionFactory(sqlSessionFactory);
/**
* 放入map,返回出去给ModuleApplication去加载
*/
mapperMap.put(namespace,mapperFactoryBean);
logger.info("refresh: '" + resource + "', success!");
}
return mapperMap;
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("refresh error",e.getMessage());
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 清理parameterMap
*
* @param list
* @param namespace
*/
private void cleanParameterMap(List<XNode> list, String namespace) {
for (XNode parameterMapNode : list) {
String id = parameterMapNode.getStringAttribute("id");
configuration.getParameterMaps().remove(namespace + "." + id);
}
}
/**
* 清理resultMap
*
* @param list
* @param namespace
*/
private void cleanResultMap(List<XNode> list, String namespace) {
for (XNode resultMapNode : list) {
String id = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("id", resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
configuration.getResultMapNames().remove(id);
configuration.getResultMapNames().remove(namespace + "." + id);
clearResultMap(resultMapNode, namespace);
}
}
private void clearResultMap(XNode xNode, String namespace) {
for (XNode resultChild : xNode.getChildren()) {
if ("association".equals(resultChild.getName()) || "collection".equals(resultChild.getName())
|| "case".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
if (resultChild.getStringAttribute("select") == null) {
configuration.getResultMapNames()
.remove(resultChild.getStringAttribute("id", resultChild.getValueBasedIdentifier()));
configuration.getResultMapNames().remove(namespace + "."
+ resultChild.getStringAttribute("id", resultChild.getValueBasedIdentifier()));
if (resultChild.getChildren() != null && !resultChild.getChildren().isEmpty()) {
clearResultMap(resultChild, namespace);
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 清理selectKey
*
* @param list
* @param namespace
*/
private void cleanKeyGenerators(List<XNode> list, String namespace) {
for (XNode context : list) {
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
configuration.getKeyGeneratorNames().remove(id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX);
configuration.getKeyGeneratorNames().remove(namespace + "." + id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX);
Collection<MappedStatement> mappedStatements = configuration.getMappedStatements();
List<MappedStatement> objects = new ArrayList<>();
Iterator<MappedStatement> it = mappedStatements.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Object object = it.next();
if (object instanceof MappedStatement) {
MappedStatement mappedStatement = (MappedStatement) object;
if (mappedStatement.getId().equals(namespace + "." + id)) {
objects.add(mappedStatement);
}
}
}
mappedStatements.removeAll(objects);
}
}
/**
* 清理sql节点缓存
*
* @param list
* @param namespace
*/
private void cleanSqlElement(List<XNode> list, String namespace) {
for (XNode context : list) {
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
configuration.getSqlFragments().remove(id);
configuration.getSqlFragments().remove(namespace + "." + id);
}
}
}
上面需要注意的是,处理好xml还需要将XXMapper接口也放入spring容器中,但是接口是没办法直接转成spring的BeanDefinition的,因为接口没办法实例化,而BeanDefinition作为对象的模板,肯定不允许接口直接放进去,通过看mybatis-spring源码,可以看出这些接口都会被封装成MapperFactoryBean放入spring容器中实例化时就调用getObject方法生成Mapper的代理对象。下面就是将各种资源装载spring容器的代码了
package com.rdpaas.dynamic.core;
import com.rdpaas.dynamic.utils.ReflectUtil;
import com.rdpaas.dynamic.utils.SpringUtil;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.plugin.core.PluginRegistry;
import org.springframework.util.MultiValueMap;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.RequestMappingInfo;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ResponseMessageBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.schema.ModelRef;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.service.Contact;
import springfox.documentation.service.ResponseMessage;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spi.service.DocumentationPlugin;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.DocumentationPluginsBootstrapper;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.DocumentationPluginsManager;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.*;
/**
* 基于spring的应用上下文提供一些工具方法
* @author rongdi
* @date 2021-03-06
* @blog https://www.cnblogs.com/rongdi
*/
public class ModuleApplication {
private final static String SINGLETON = "singleton";
private final static String DYNAMIC_DOC_PACKAGE = "dynamic.swagger.doc.package";
private Set<RequestMappingInfo> extMappingInfos = new HashSet<>();
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
/**
* 使用spring上下文拿到指定beanName的对象
*/
public <T> T getBean(String beanName) {
return (T) ((ConfigurableApplicationContext) applicationContext).getBeanFactory().getBean(beanName);
}
/**
* 使用spring上下文拿到指定类型的对象
*/
public <T> T getBean(Class<T> clazz) {
return (T) ((ConfigurableApplicationContext) applicationContext).getBeanFactory().getBean(clazz);
}
/**
* 加载一个外部扩展jar,包括springmvc接口资源,mybatis的@mapper和mapper.xml和spring bean等资源
* @param url jar url
* @param applicationContext spring context
* @param sqlSessionFactory mybatis的session工厂
*/
public void reloadJar(URL url, ApplicationContext applicationContext,SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) throws Exception {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
URL[] urls = new URL[]{url};
/**
* 这里实际上是将spring的ApplicationContext的类加载器当成parent传给了自定义类加载器,很明自定义的子类加载器自己加载
* 的类,parent类加载器直接是获取不到的,所以在自定义类加载器做了特殊的骚操作
*/
ModuleClassLoader moduleClassLoader = new ModuleClassLoader(applicationContext.getClassLoader(), urls);
/**
* 使用模块类加载器加载url资源的jar包,直接返回类的全限定名和Class对象的映射,这些Class对象是
* jar包里所有.class结尾的文件加载后的结果,同时mybatis的xml加载后,无奈的放入了
* moduleClassLoader.getXmlBytesMap(),不是很优雅
*/
Map<String, Class> classMap = moduleClassLoader.load();
MapperLoader mapperLoader = new MapperLoader();
/**
* 刷新mybatis的xml和Mapper接口资源,Mapper接口其实就是xml的namespace
*/
Map<String, Object> extObjMap = mapperLoader.refresh(sqlSessionFactory, moduleClassLoader.getXmlBytesMap());
/**
* 将各种资源放入spring容器
*/
registerBeans(applicationContext, classMap, extObjMap);
}
/**
* 装载bean到spring中
*
* @param applicationContext
* @param cacheClassMap
*/
public void registerBeans(ApplicationContext applicationContext, Map<String, Class> cacheClassMap,Map<String,Object> extObjMap) throws Exception {
/**
* 将applicationContext转换为ConfigurableApplicationContext
*/
ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext = (ConfigurableApplicationContext) applicationContext;
/**
* 获取bean工厂并转换为DefaultListableBeanFactory
*/
DefaultListableBeanFactory defaultListableBeanFactory = (DefaultListableBeanFactory) configurableApplicationContext.getBeanFactory();
/**
* 有一些对象想给spring管理,则放入spring中,如mybatis的@Mapper修饰的接口的代理类
*/
if(extObjMap != null && !extObjMap.isEmpty()) {
extObjMap.forEach((beanName,obj) ->{
/**
* 如果已经存在,则销毁之后再注册
*/
if(defaultListableBeanFactory.containsSingleton(beanName)) {
defaultListableBeanFactory.destroySingleton(beanName);
}
defaultListableBeanFactory.registerSingleton(beanName,obj);
});
}
for (Map.Entry<String, Class> entry : cacheClassMap.entrySet()) {
String className = entry.getKey();
Class<?> clazz = entry.getValue();
if (SpringUtil.isSpringBeanClass(clazz)) {
//将变量首字母置小写
String beanName = StringUtils.uncapitalize(className);
beanName = beanName.substring(beanName.lastIndexOf(".") + 1);
beanName = StringUtils.uncapitalize(beanName);
/**
* 已经在spring容器就删了
*/
if (defaultListableBeanFactory.containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
defaultListableBeanFactory.removeBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
/**
* 使用spring的BeanDefinitionBuilder将Class对象转成BeanDefinition
*/
BeanDefinitionBuilder beanDefinitionBuilder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(clazz);
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionBuilder.getRawBeanDefinition();
//设置当前bean定义对象是单利的
beanDefinition.setScope(SINGLETON);
/**
* 以指定beanName注册上面生成的BeanDefinition
*/
defaultListableBeanFactory.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
}
/**
* 刷新springmvc,让新增的接口生效
*/
refreshMVC((ConfigurableApplicationContext) applicationContext);
}
/**
* 刷新springMVC,这里花了大量时间调试,找不到开放的方法,只能取个巧,在更新RequestMappingHandlerMapping前先记录之前
* 所有RequestMappingInfo,记得这里一定要copy一下,然后刷新后再记录一次,计算出差量存放在成员变量Set中,然后每次开头判断
* 差量那里是否有内容,有就先unregiester掉
*/
private void refreshMVC(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) throws Exception {
Map<String, RequestMappingHandlerMapping> map = applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getBeansOfType(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class);
/**
* 先拿到RequestMappingHandlerMapping对象
*/
RequestMappingHandlerMapping mappingHandlerMapping = map.get("requestMappingHandlerMapping");
/**
* 重新注册mapping前先判断是否存在了,存在了就先unregister掉
*/
if(!extMappingInfos.isEmpty()) {
for(RequestMappingInfo requestMappingInfo:extMappingInfos) {
mappingHandlerMapping.unregisterMapping(requestMappingInfo);
}
}
/**
* 获取刷新前的RequestMappingInfo
*/
Map<RequestMappingInfo, HandlerMethod> preMappingInfoHandlerMethodMap = mappingHandlerMapping.getHandlerMethods();
/**
* 这里注意一定要拿到拷贝,不然刷新后内容就一致了,就没有差量了
*/
Set<RequestMappingInfo> preRequestMappingInfoSet = new HashSet(preMappingInfoHandlerMethodMap.keySet());
/**
* 这里是刷新springmvc上下文
*/
applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getBeansOfType(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class)
.forEach((key,value) ->{
value.afterPropertiesSet();
});
/**
* 获取刷新后的RequestMappingInfo
*/
Map<RequestMappingInfo, HandlerMethod> afterMappingInfoHandlerMethodMap = mappingHandlerMapping.getHandlerMethods();
Set<RequestMappingInfo> afterRequestMappingInfoSet = afterMappingInfoHandlerMethodMap.keySet();
/**
* 填充差量部分RequestMappingInfo
*/
fillSurplusRequestMappingInfos(preRequestMappingInfoSet,afterRequestMappingInfoSet);
/**
* 这里真的是不讲武德了,每次调用value.afterPropertiesSet();如下urlLookup都会产生重复,暂时没找到开放方法去掉重复,这里重复会导致
* 访问的时候报错Ambiguous handler methods mapped for
* 目标是去掉RequestMappingHandlerMapping -> RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping -> AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
* -> mappingRegistry -> urlLookup重复的RequestMappingInfo,这里的.getClass().getSuperclass().getSuperclass()相信会
* 很懵逼,如果单独通过getClass().getDeclaredMethod("getMappingRegistry",new Class[]{})是无论如何都拿不到父类的非public非
* protected方法的,因为这个方法不属于子类,只有父类才可以访问到,只有你拿得到你才有资格不讲武德的使用method.setAccessible(true)强行
* 访问
*/
Method method = ReflectUtil.getMethod(mappingHandlerMapping,"getMappingRegistry",new Class[]{});
method.setAccessible(true);
Object mappingRegistryObj = method.invoke(mappingHandlerMapping,new Object[]{});
Field field = mappingRegistryObj.getClass().getDeclaredField("urlLookup");
field.setAccessible(true);
MultiValueMap<String, RequestMappingInfo> multiValueMap = (MultiValueMap)field.get(mappingRegistryObj);
multiValueMap.forEach((key,list) -> {
clearMultyMapping(list);
});
}
/**
* 填充差量的RequestMappingInfo,因为已经重写过hashCode和equals方法所以可以直接用对象判断是否存在
* @param preRequestMappingInfoSet
* @param afterRequestMappingInfoSet
*/
private void fillSurplusRequestMappingInfos(Set<RequestMappingInfo> preRequestMappingInfoSet,Set<RequestMappingInfo> afterRequestMappingInfoSet) {
for(RequestMappingInfo requestMappingInfo:afterRequestMappingInfoSet) {
if(!preRequestMappingInfoSet.contains(requestMappingInfo)) {
extMappingInfos.add(requestMappingInfo);
}
}
}
/**
* 简单的逻辑,删除List里重复的RequestMappingInfo,已经写了toString,直接使用mappingInfo.toString()就可以区分重复了
* @param mappingInfos
*/
private void clearMultyMapping(List<RequestMappingInfo> mappingInfos) {
Set<String> containsList = new HashSet<>();
for(Iterator<RequestMappingInfo> iter = mappingInfos.iterator();iter.hasNext();) {
RequestMappingInfo mappingInfo = iter.next();
String flag = mappingInfo.toString();
if(containsList.contains(flag)) {
iter.remove();
} else {
containsList.add(flag);
}
}
}
}
上述有两个地方很虐心,第一个就是刷新springmvc那里,提供的刷新springmvc上下文的方式不友好不说,刷新上下文后RequestMappingHandlerMapping -> RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping -> AbstractHandlerMethodMapping -> mappingRegistry -> urlLookup属性中会存在重复的路径如下
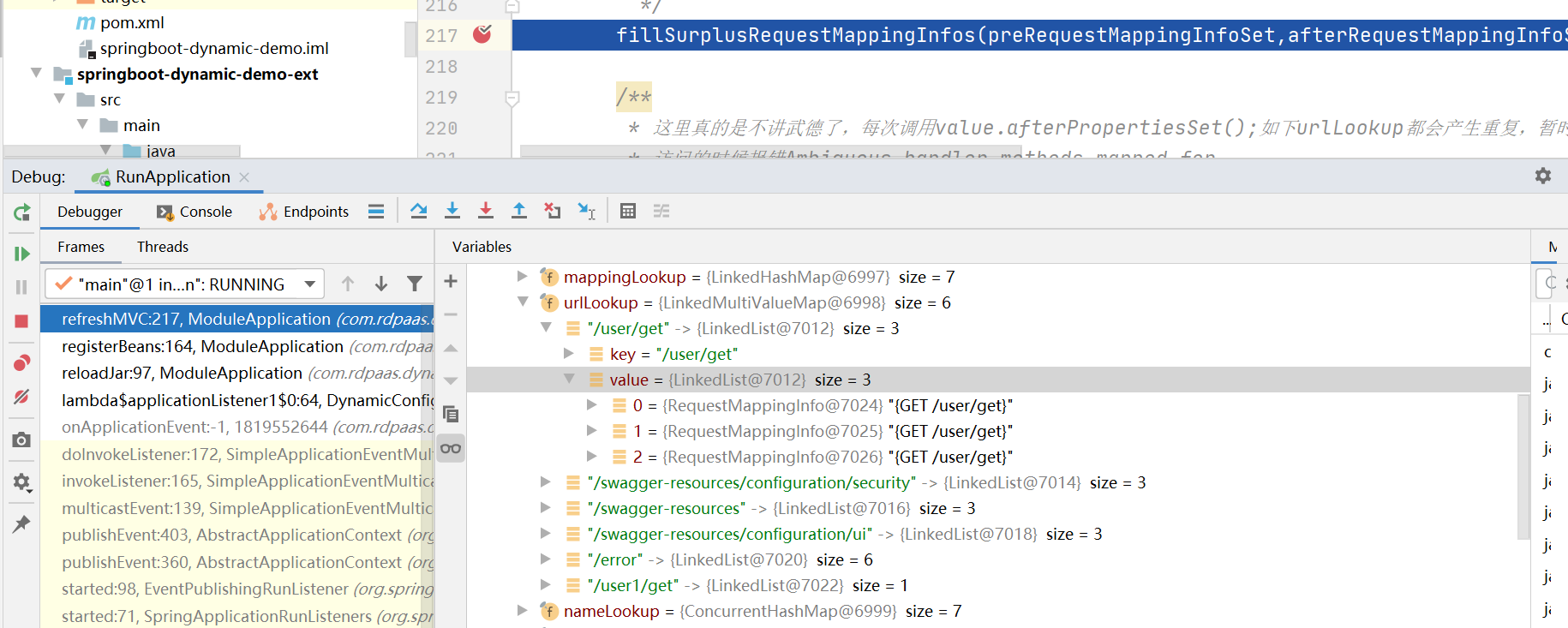
上述是我故意两次加载同一个jar包后第二次走到刷新springmvc之后,可以看到扩展包里的接口,由于unregister所以没有发现重复,那些重复的路径都是本身服务的接口,由于没有unregister所以出现了大把重复,如果这个时候访问重复的接口,会出现如下错误
java.lang.IllegalStateException: Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '/error':
意思就是匹配到了多个相同的路径解决方法有两种,第一种就是所有RequestMappingInfo都先unregister再刷新,第二种就是我调试很久确认就只有urlLookup会发生冲重复,所以如下使用万能的反射强行修改值,其实不要排斥使用反射,spring源码中大量使用反射去强行调用方法,比如org.springframework.cglib.core.ReflectUtils类摘抄如下:
classLoaderDefineClass = (Method) AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction() {
public Object run() throws Exception {
return ClassLoader.class.getDeclaredMethod("defineClass",
String.class, byte[].class, Integer.TYPE, Integer.TYPE, ProtectionDomain.class);
}
});
classLoaderDefineClassMethod = classLoaderDefineClass;
// Classic option: protected ClassLoader.defineClass method
if (c == null && classLoaderDefineClassMethod != null) {
if (protectionDomain == null) {
protectionDomain = PROTECTION_DOMAIN;
}
Object[] args = new Object[]{className, b, 0, b.length, protectionDomain};
try {
if (!classLoaderDefineClassMethod.isAccessible()) {
classLoaderDefineClassMethod.setAccessible(true);
}
c = (Class) classLoaderDefineClassMethod.invoke(loader, args);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new CodeGenerationException(ex.getTargetException());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Fall through if setAccessible fails with InaccessibleObjectException on JDK 9+
// (on the module path and/or with a JVM bootstrapped with --illegal-access=deny)
if (!ex.getClass().getName().endsWith("InaccessibleObjectException")) {
throw new CodeGenerationException(ex);
}
}
}
如上可以看出来像spring这样的名家也一样也很不讲武德,个人认为反射本身就是用来给我们打破规则用的,只有打破规则才会有创新,所以大胆使用反射吧。只要不遇到final的属性,反射是万能的,哈哈!所以我使用反射强行删除重复的代码如下:
/**
* 这里真的是不讲武德了,每次调用value.afterPropertiesSet();如下urlLookup都会产生重复,暂时没找到开放方法去掉重复,这里重复会导致
* 访问的时候报错Ambiguous handler methods mapped for
* 目标是去掉RequestMappingHandlerMapping -> RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping -> AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
* -> mappingRegistry -> urlLookup重复的RequestMappingInfo,这里的.getClass().getSuperclass().getSuperclass()相信会
* 很懵逼,如果单独通过getClass().getDeclaredMethod("getMappingRegistry",new Class[]{})是无论如何都拿不到父类的非public非
* protected方法的,因为这个方法不属于子类,只有父类才可以访问到,只有你拿得到你才有资格不讲武德的使用method.setAccessible(true)强行
* 访问
*/
Method method = ReflectUtil.getMethod(mappingHandlerMapping,"getMappingRegistry",new Class[]{});
method.setAccessible(true);
Object mappingRegistryObj = method.invoke(mappingHandlerMapping,new Object[]{});
Field field = mappingRegistryObj.getClass().getDeclaredField("urlLookup");
field.setAccessible(true);
MultiValueMap<String, RequestMappingInfo> multiValueMap = (MultiValueMap)field.get(mappingRegistryObj);
multiValueMap.forEach((key,list) -> {
clearMultyMapping(list);
});
/**
* 简单的逻辑,删除List里重复的RequestMappingInfo,已经写了toString,直接使用mappingInfo.toString()就可以区分重复了
* @param mappingInfos
*/
private void clearMultyMapping(List<RequestMappingInfo> mappingInfos) {
Set<String> containsList = new HashSet<>();
for(Iterator<RequestMappingInfo> iter = mappingInfos.iterator();iter.hasNext();) {
RequestMappingInfo mappingInfo = iter.next();
String flag = mappingInfo.toString();
if(containsList.contains(flag)) {
iter.remove();
} else {
containsList.add(flag);
}
}
}
还有个虐心的地方是刷新swagger文档的地方,这个swagger只有需要做这个需求时才知道,他封装的有多菜,根本没有刷新相关的方法,也没有可以控制的入口,真的是没办法。下面贴出我解决刷新swagger文档的调试过程,使用过swagger2的朋友们都知道,要想在springboot集成swagger2主要需要编写的配置代码如下
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
//swagger2的配置文件,这里可以配置swagger2的一些基本的内容,比如扫描的包等等
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi() {
List<ResponseMessage> responseMessageList = new ArrayList<>();
responseMessageList.add(new ResponseMessageBuilder().code(200).message("成功").responseModel(new ModelRef("Payload")).build());
Docket docket = new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.globalResponseMessage(RequestMethod.GET,responseMessageList)
.globalResponseMessage(RequestMethod.DELETE,responseMessageList)
.globalResponseMessage(RequestMethod.POST,responseMessageList)
.apiInfo(apiInfo()).select()
//为当前包路径
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.xxx")).paths(PathSelectors.any()).build();
return docket;
}
//构建 api文档的详细信息函数,注意这里的注解引用的是哪个
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
//页面标题
.title("使用 Swagger2 构建RESTful API")
//创建人
.contact(new Contact("rongdi", "https://www.cnblogs.com/rongdi", "495194630@qq.com"))
//版本号
.version("1.0")
//描述
.description("api管理").build();
}
}
而访问swagger的文档请求的是如下接口/v2/api-docs
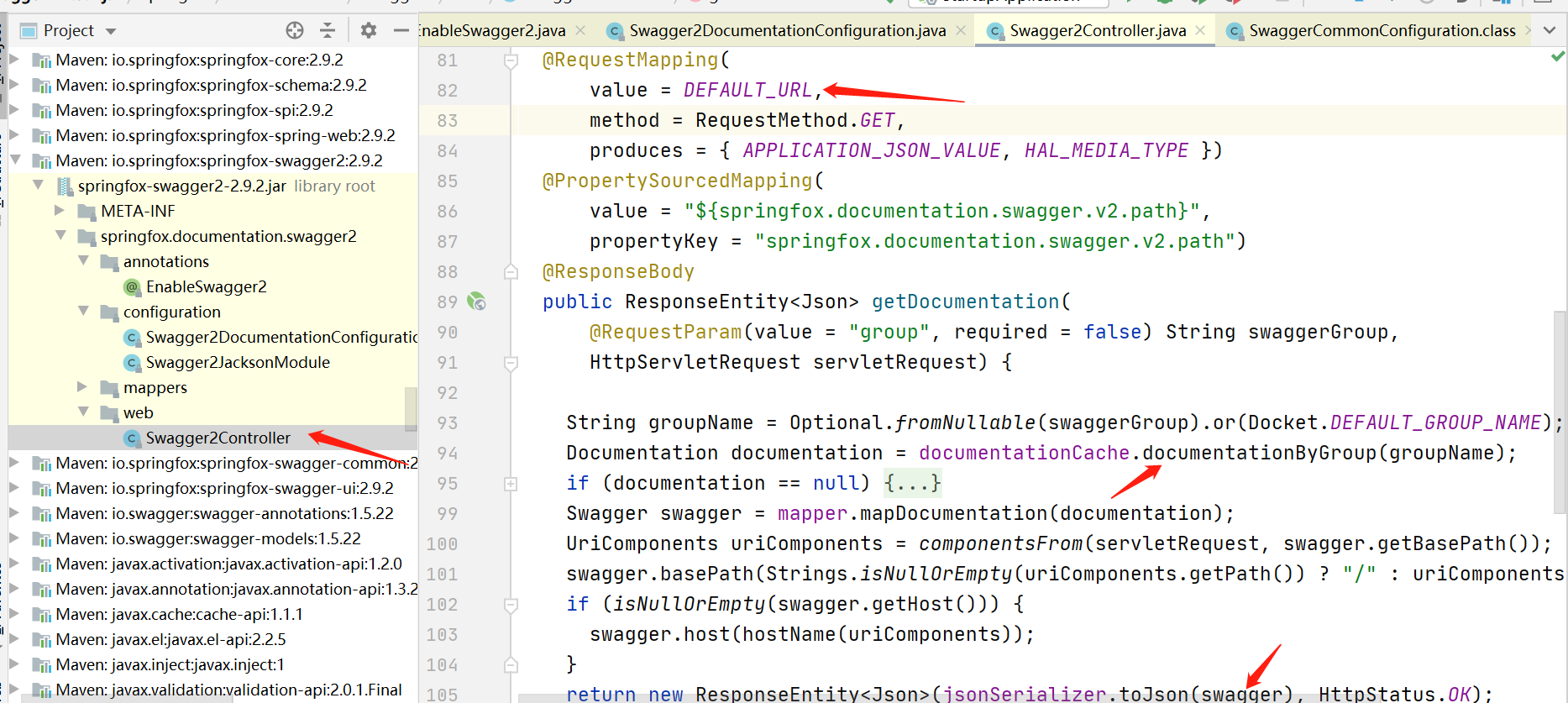
通过调试可以找到swagger2就是通过实现了SmartLifecycle接口的DocumentationPluginsBootstrapper类,当spring容器加载所有bean并完成初始化之后,会回调实现该接口的类(DocumentationPluginsBootstrapper)中对应的方法start()方法,下面会介绍怎么找到这里的。
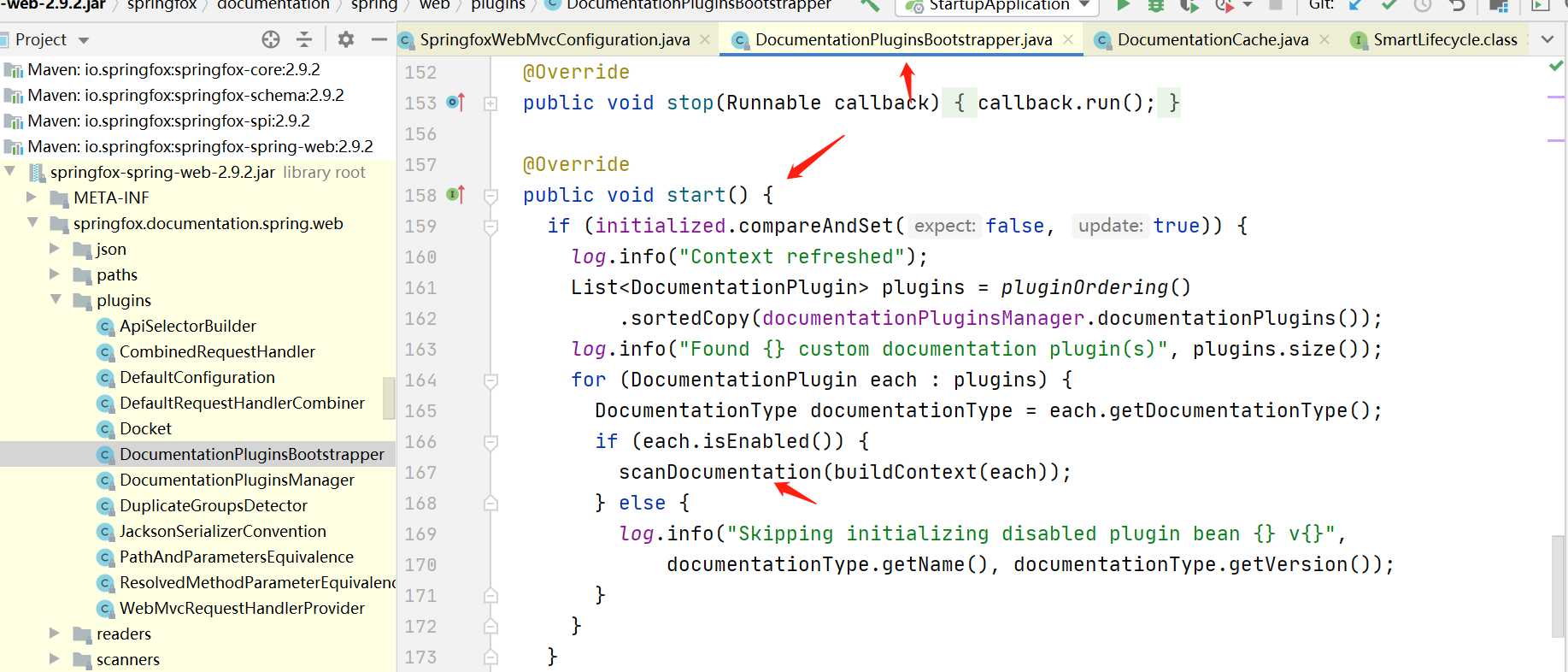
接着循环DocumentationPlugin集合去处理文档
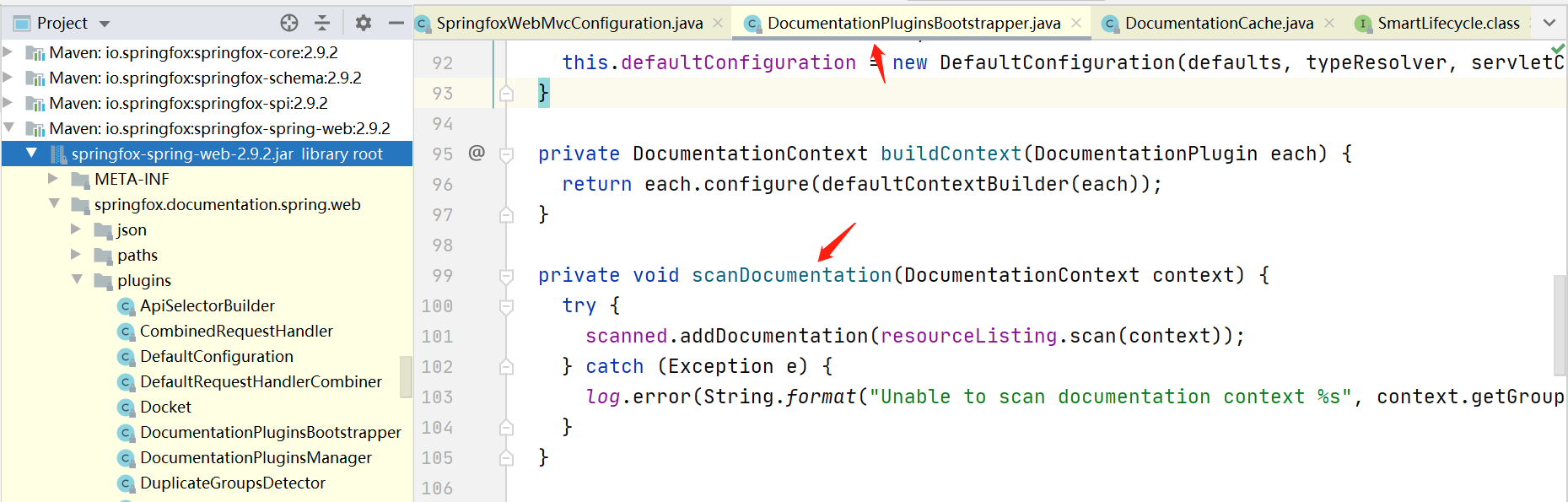
接着放入DocumentationCache中
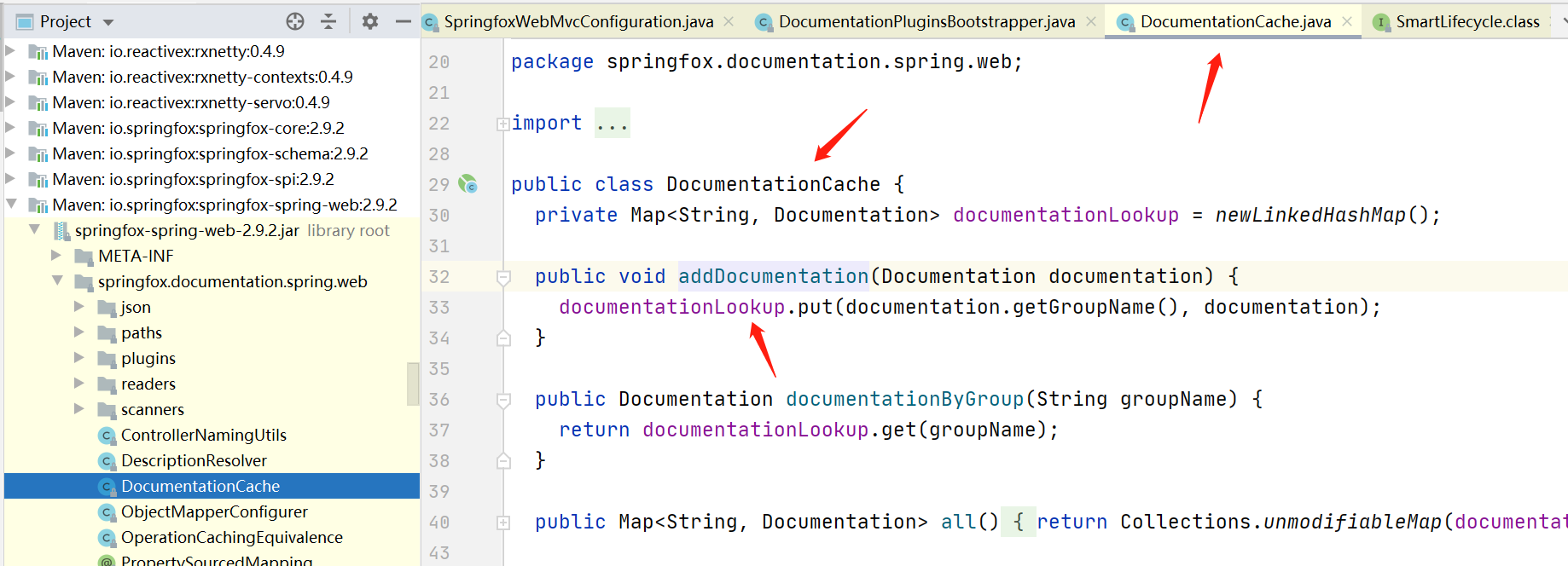
然后再回到swagger接口的类那里,实际上就是从这个DocumentationCache里获取到Documention
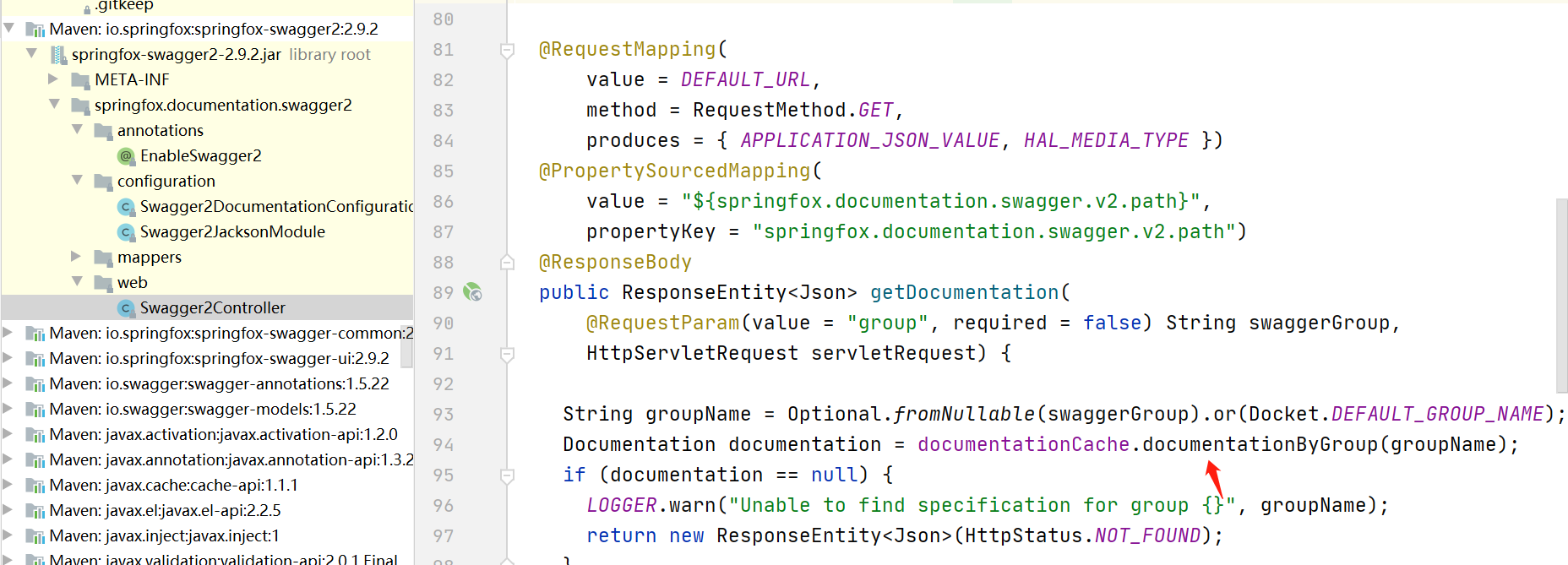
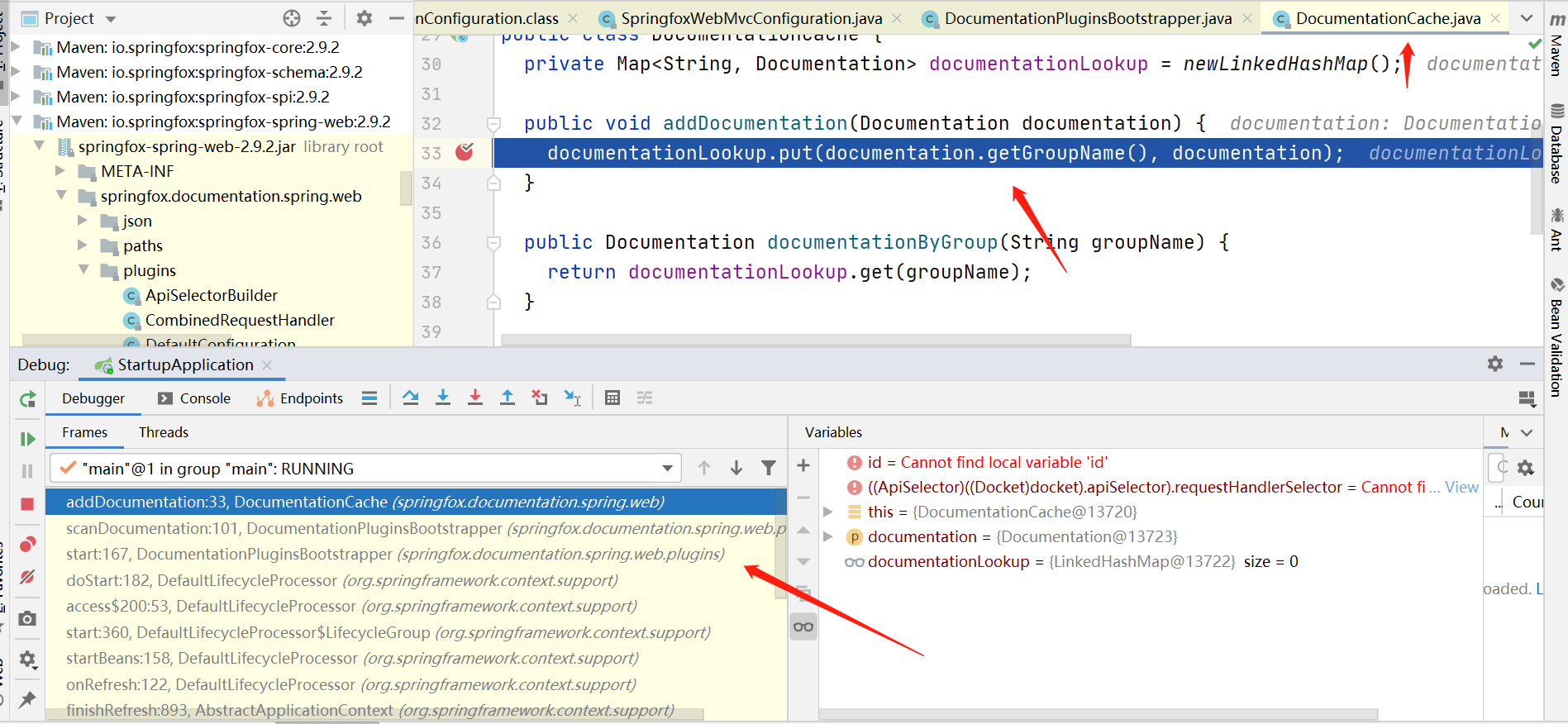
‘如果找不到解决问题的入口,我们至少可以找到访问文档的上面这个接口地址(出口),发现接口返回的文档json内容是从DocumentationCache里获取,那么我们很明显可以想到肯定有地方存放数据到这个DocumentationCache里,然后其实我们可以直接在addDocumentation方法里打个断点,然后看调试左侧的运行方法栈信息,就可以很明确的看到调用链路了
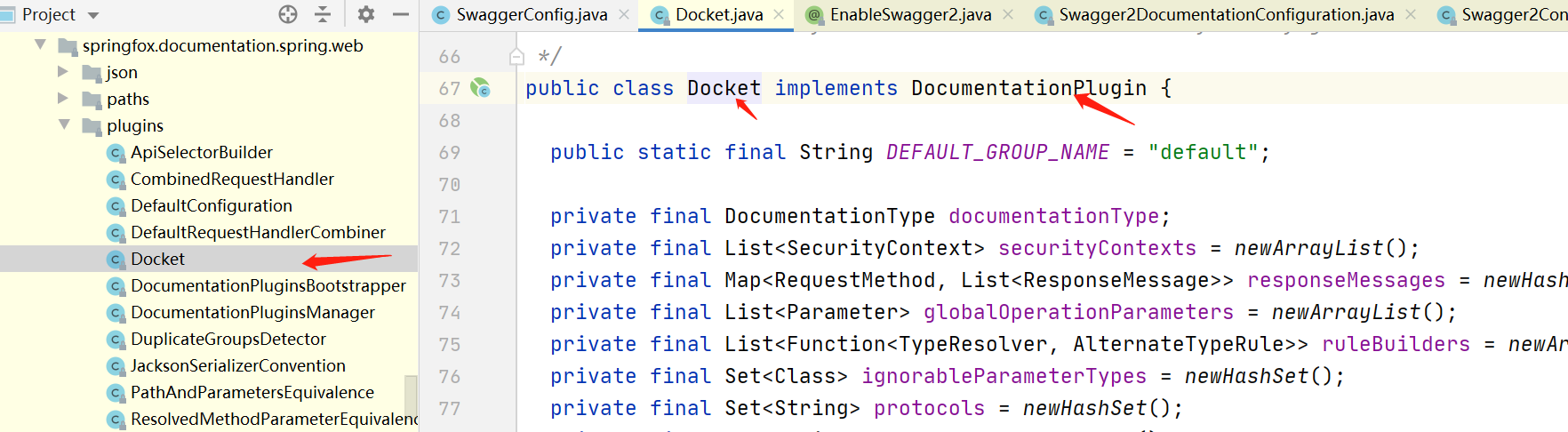
再回看我们接入swagger2的时候写的配置代码
//swagger2的配置文件,这里可以配置swagger2的一些基本的内容,比如扫描的包等等
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi() {
List<ResponseMessage> responseMessageList = new ArrayList<>();
responseMessageList.add(new ResponseMessageBuilder().code(200).message("成功").responseModel(new ModelRef("Payload")).build());
Docket docket = new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.globalResponseMessage(RequestMethod.GET,responseMessageList)
.globalResponseMessage(RequestMethod.DELETE,responseMessageList)
.globalResponseMessage(RequestMethod.POST,responseMessageList)
.apiInfo(apiInfo()).select()
//为当前包路径
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.xxx")).paths(PathSelectors.any()).build();
return docket;
}
然后再看看下图,应该终于知道咋回事了吧,其实Docket对象我们仅仅需要关心的是basePackage,我们扩展jar包大概率接口所在的包和现有包不一样,所以我们需要新增一个Docket插件,并加入DocumentationPlugin集合,然后调用DocumentationPluginsBootstrapper的stop()方法清掉缓存,再调用start()再次开始解析
具体实现代码如下
/**
* 刷新springMVC,这里花了大量时间调试,找不到开放的方法,只能取个巧,在更新RequestMappingHandlerMapping前先记录之前
* 所有RequestMappingInfo,记得这里一定要copy一下,然后刷新后再记录一次,计算出差量存放在成员变量Set中,然后每次开头判断
* 差量那里是否有内容,有就先unregiester掉
*/
private void refreshMVC(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) throws Exception {
Map<String, RequestMappingHandlerMapping> map = applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getBeansOfType(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class);
/**
* 先拿到RequestMappingHandlerMapping对象
*/
RequestMappingHandlerMapping mappingHandlerMapping = map.get("requestMappingHandlerMapping");
/**
* 重新注册mapping前先判断是否存在了,存在了就先unregister掉
*/
if(!extMappingInfos.isEmpty()) {
for(RequestMappingInfo requestMappingInfo:extMappingInfos) {
mappingHandlerMapping.unregisterMapping(requestMappingInfo);
}
}
/**
* 获取刷新前的RequestMappingInfo
*/
Map<RequestMappingInfo, HandlerMethod> preMappingInfoHandlerMethodMap = mappingHandlerMapping.getHandlerMethods();
/**
* 这里注意一定要拿到拷贝,不然刷新后内容就一致了,就没有差量了
*/
Set<RequestMappingInfo> preRequestMappingInfoSet = new HashSet(preMappingInfoHandlerMethodMap.keySet());
/**
* 这里是刷新springmvc上下文
*/
applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getBeansOfType(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class)
.forEach((key,value) ->{
value.afterPropertiesSet();
});
/**
* 获取刷新后的RequestMappingInfo
*/
Map<RequestMappingInfo, HandlerMethod> afterMappingInfoHandlerMethodMap = mappingHandlerMapping.getHandlerMethods();
Set<RequestMappingInfo> afterRequestMappingInfoSet = afterMappingInfoHandlerMethodMap.keySet();
/**
* 填充差量部分RequestMappingInfo
*/
fillSurplusRequestMappingInfos(preRequestMappingInfoSet,afterRequestMappingInfoSet);
/**
* 这里真的是不讲武德了,每次调用value.afterPropertiesSet();如下urlLookup都会产生重复,暂时没找到开放方法去掉重复,这里重复会导致
* 访问的时候报错Ambiguous handler methods mapped for
* 目标是去掉RequestMappingHandlerMapping -> RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping -> AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
* -> mappingRegistry -> urlLookup重复的RequestMappingInfo,这里的.getClass().getSuperclass().getSuperclass()相信会
* 很懵逼,如果单独通过getClass().getDeclaredMethod("getMappingRegistry",new Class[]{})是无论如何都拿不到父类的非public非
* protected方法的,因为这个方法不属于子类,只有父类才可以访问到,只有你拿得到你才有资格不讲武德的使用method.setAccessible(true)强行
* 访问
*/
Method method = ReflectUtil.getMethod(mappingHandlerMapping,"getMappingRegistry",new Class[]{});
method.setAccessible(true);
Object mappingRegistryObj = method.invoke(mappingHandlerMapping,new Object[]{});
Field field = mappingRegistryObj.getClass().getDeclaredField("urlLookup");
field.setAccessible(true);
MultiValueMap<String, RequestMappingInfo> multiValueMap = (MultiValueMap)field.get(mappingRegistryObj);
multiValueMap.forEach((key,list) -> {
clearMultyMapping(list);
});
/**
* 刷新swagger文档
*/
refreshSwagger(applicationContext);
}
/**
* 刷新swagger文档
* @param applicationContext
* @throws Exception
*/
private void refreshSwagger(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) throws Exception {
/**
* 获取扩展包swagger的地址接口扫描包,如果有配置则执行文档刷新操作
*/
String extSwaggerDocPackage = applicationContext.getEnvironment().getProperty(DYNAMIC_DOC_PACKAGE);
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(extSwaggerDocPackage)) {
/**
* 拿到swagger解析文档的入口类,真的不想这样,主要是根本不提供刷新和重新加载文档的方法,只能不讲武德了
*/
DocumentationPluginsBootstrapper bootstrapper = applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getBean(DocumentationPluginsBootstrapper.class);
/**
* 不管愿不愿意,强行拿到属性得到documentationPluginsManager对象
*/
Field field1 = bootstrapper.getClass().getDeclaredField("documentationPluginsManager");
field1.setAccessible(true);
DocumentationPluginsManager documentationPluginsManager = (DocumentationPluginsManager) field1.get(bootstrapper);
/**
* 继续往下层拿documentationPlugins属性
*/
Field field2 = documentationPluginsManager.getClass().getDeclaredField("documentationPlugins");
field2.setAccessible(true);
PluginRegistry<DocumentationPlugin, DocumentationType> pluginRegistrys = (PluginRegistry<DocumentationPlugin, DocumentationType>) field2.get(documentationPluginsManager);
/**
* 拿到最关键的文档插件集合,所有逻辑文档解析逻辑都在插件中
*/
List<DocumentationPlugin> dockets = pluginRegistrys.getPlugins();
/**
* 真的不能怪我,好端端,你还搞个不能修改的集合,强行往父类递归拿到unmodifiableList的list属性
*/
Field unModList = ReflectUtil.getField(dockets,"list");
unModList.setAccessible(true);
List<DocumentationPlugin> modifyerList = (List<DocumentationPlugin>) unModList.get(dockets);
/**
* 这下老实了吧,把自己的Docket加入进去,这里的groupName为dynamic
*/
modifyerList.add(createRestApi(extSwaggerDocPackage));
/**
* 清空罪魁祸首DocumentationCache缓存,不然就算再加载一次,获取文档还是从这个缓存中拿,不会完成更新
*/
bootstrapper.stop();
/**
* 手动执行重新解析swagger文档
*/
bootstrapper.start();
}
}
public Docket createRestApi(String basePackage) {
List<ResponseMessage> responseMessageList = new ArrayList<>();
responseMessageList.add(new ResponseMessageBuilder().code(200).message("成功").responseModel(new ModelRef("Payload")).build());
Docket docket = new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.groupName("dynamic")
.globalResponseMessage(RequestMethod.GET,responseMessageList)
.globalResponseMessage(RequestMethod.DELETE,responseMessageList)
.globalResponseMessage(RequestMethod.POST,responseMessageList)
.apiInfo(apiInfo()).select()
//为当前包路径
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage(basePackage)).paths(PathSelectors.any()).build();
return docket;
}
/**
* 构建api文档的详细信息函数
*/
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
//页面标题
.title("SpringBoot动态扩展")
//创建人
.contact(new Contact("rongdi", "https://www.cnblogs.com/rongdi", "495194630@qq.com"))
//版本号
.version("1.0")
//描述
.description("api管理").build();
}
好了,下面给一下整个扩展功能的入口吧
package com.rdpaas.dynamic.config;
import com.rdpaas.dynamic.core.ModuleApplication;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationStartedEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.net.URL;
/**
* 一切配置的入口
* @author rongdi
* @date 2021-03-06
* @blog https://www.cnblogs.com/rongdi
*/
@Configuration
public class DynamicConfig implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DynamicConfig.class);
@Autowired
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Value("${dynamic.jar:/}")
private String dynamicJar;
@Bean
public ModuleApplication moduleApplication() throws Exception {
return new ModuleApplication();
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
/**
* 随便找个事件ApplicationStartedEvent,用来reload外部的jar,其实直接在moduleApplication()方法也可以做
* 这件事,但是为了验证容器初始化后再加载扩展包还可以生效,所以故意放在了这里。
* @return
*/
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "dynamic",name = "jar")
public ApplicationListener applicationListener1() {
return (ApplicationListener<ApplicationStartedEvent>) event -> {
try {
/**
* 加载外部扩展jar
*/
moduleApplication().reloadJar(new URL(dynamicJar),applicationContext,sqlSessionFactory);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("",e);
}
};
}
}
再给个开关注解
package com.rdpaas.dynamic.anno;
import com.rdpaas.dynamic.config.DynamicConfig;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* 开启动态扩展的注解
* @author rongdi
* @date 2021-03-06
* @blog https://www.cnblogs.com/rongdi
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Documented
@Import({DynamicConfig.class})
public @interface EnableDynamic {
}
好了,至此核心代码和功能都分享完了,详细源码和使用说明见github:https://github.com/rongdi/springboot-dynamic
到此这篇关于springboot运行时新增/更新外部接口的实现方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关springboot外部接口内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

