springboot的缓存技术的实现
引子
我门知道一个程序的瓶颈在于数据库,我门也知道内存的速度是大大快于硬盘的速度的。当我门需要重复的获取相同的数据的时候,我门一次又一次的请求数据库或者远程服务,导致大量的时间耗费在数据库查询或者远程方法的调用上,导致程序性能的恶化,这更是数据缓存要解决的问题。
spring 缓存支持
spring定义了 org.springframework.cache.CacheManager和org.springframework.cache.Cache接口来统一不同的缓存技术。其中,CacheManager是Spring提供的各种缓存技术抽象接口,Cache接口包含了缓存的各种操作(增加、删除获得缓存,我门一般不会直接和此接口打交道)
spring 支持的CacheManager
针对不同的缓存技术,需要实现不同的CacheManager ,spring 定义了如下表的CacheManager实现。

实现任意一种CacheManager 的时候,需要注册实现CacheManager的bean,当然每种缓存技术都有很多额外的配置,但配置CacheManager 是必不可少的。
声明式缓存注解
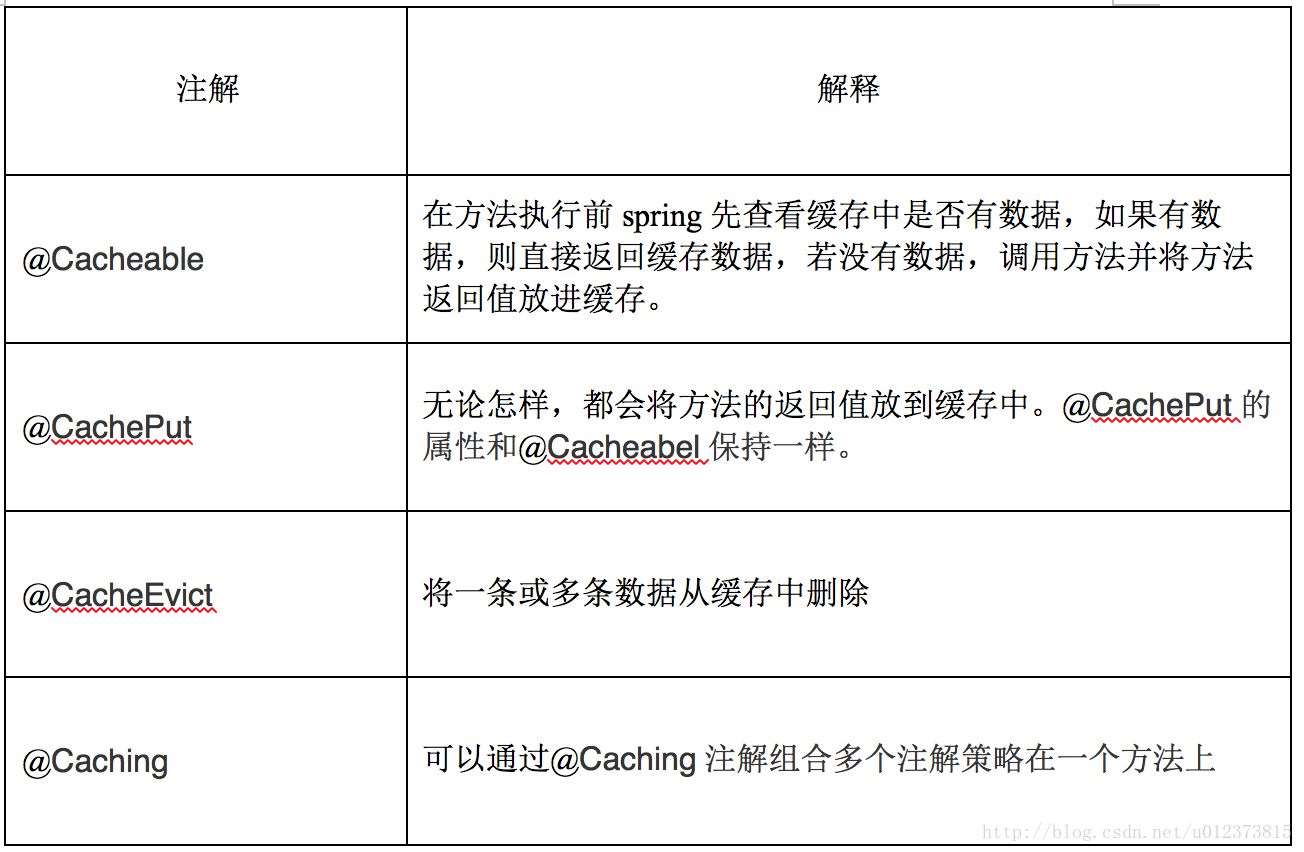
spring提供了4个注解来声明缓存规则(又是使用注解式的AOP的一个生动例子),如表。
开启声明式缓存
开启声明式缓存支持非常简单,只需要在配置类上使用@EnabelCaching 注解即可。
springBoot 的支持
在spring中国年使用缓存技术的关键是配置CacheManager 而springbok 为我门自动配置了多个CacheManager的实现。在spring boot 环境下,使用缓存技术只需要在项目中导入相关缓存技术的依赖包,并配置类使用@EnabelCaching开启缓存支持即可。
小例子
小例子是使用 springboot+jpa +cache 实现的。
实例步骤目录
- 创建maven项目
- 数据库配置
- jpa配置和cache配置
- 编写bean 和dao层
- 编写service层
- 编写controller
- 启动cache
- 测试校验
1.创建maven项目
新建maven 项目pom.xml文件如下内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.us</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-Cache</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.3.0.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<properties>
<start-class>com.us.Application</start-class>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
</properties>
<!-- Add typical dependencies for a web application -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--db-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>6.0.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mchange</groupId>
<artifactId>c3p0</artifactId>
<version>0.9.5.2</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
2.数据库配置
在src/main/esouces目录下新建application.properties 文件,内容为数据库连接信息,如下:
application.properties
ms.db.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver ms.db.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/cache?prepStmtCacheSize=517&cachePrepStmts=true&autoReconnect=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&allowMultiQueries=true ms.db.username=root ms.db.password=xxxxxx ms.db.maxActive=500
新建DBConfig.java 配置文件,配置数据源
package com.us.example.config;
/**
* Created by yangyibo on 17/1/13.
*/
import java.beans.PropertyVetoException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
@Configuration
public class DBConfig {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@Bean(name="dataSource")
public ComboPooledDataSource dataSource() throws PropertyVetoException {
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClass(env.getProperty("ms.db.driverClassName"));
dataSource.setJdbcUrl(env.getProperty("ms.db.url"));
dataSource.setUser(env.getProperty("ms.db.username"));
dataSource.setPassword(env.getProperty("ms.db.password"));
dataSource.setMaxPoolSize(20);
dataSource.setMinPoolSize(5);
dataSource.setInitialPoolSize(10);
dataSource.setMaxIdleTime(300);
dataSource.setAcquireIncrement(5);
dataSource.setIdleConnectionTestPeriod(60);
return dataSource;
}
}
数据库设计,数据库只有一张Person表,设计如下:

3.jpa配置
spring-data- jpa 配置文件如下:
package com.us.example.config;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaVendorAdapter;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
/**
* Created by yangyibo on 17/1/13.
*/
@Configuration
@EnableJpaRepositories("com.us.example.dao")
@EnableTransactionManagement
@ComponentScan
public class JpaConfig {
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
@Bean
public EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory() {
HibernateJpaVendorAdapter vendorAdapter = new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter();
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean factory = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean();
factory.setJpaVendorAdapter(vendorAdapter);
factory.setPackagesToScan("com.us.example.bean");
factory.setDataSource(dataSource);
Map<String, Object> jpaProperties = new HashMap<>();
jpaProperties.put("hibernate.ejb.naming_strategy","org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy");
jpaProperties.put("hibernate.jdbc.batch_size",50);
factory.setJpaPropertyMap(jpaProperties);
factory.afterPropertiesSet();
return factory.getObject();
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager() {
JpaTransactionManager txManager = new JpaTransactionManager();
txManager.setEntityManagerFactory(entityManagerFactory());
return txManager;
}
}
4.编写bean 和dao层
实体类 Person.java
package com.us.example.bean;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
/**
* Created by yangyibo on 17/1/13.
*/
@Entity
@Table(name = "Person")
public class Person {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String address;
public Person() {
super();
}
public Person(Long id, String name, Integer age, String address) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.address = address;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
dao层,PersonRepository.java
package com.us.example.dao;
import com.us.example.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
/**
* Created by yangyibo on 17/1/13.
*/
public interface PersonRepository extends JpaRepository<Person, Long> {
}
5.编写service层
service 接口
package com.us.example.service;
import com.us.example.bean.Person;
/**
* Created by yangyibo on 17/1/13.
*/
public interface DemoService {
public Person save(Person person);
public void remove(Long id);
public Person findOne(Person person);
}
实现:(重点,此处加缓存)
package com.us.example.service.Impl;
import com.us.example.bean.Person;
import com.us.example.dao.PersonRepository;
import com.us.example.service.DemoService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* Created by yangyibo on 17/1/13.
*/
@Service
public class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService {
@Autowired
private PersonRepository personRepository;
@Override
//@CachePut缓存新增的或更新的数据到缓存,其中缓存名字是 people 。数据的key是person的id
@CachePut(value = "people", key = "#person.id")
public Person save(Person person) {
Person p = personRepository.save(person);
System.out.println("为id、key为:"+p.getId()+"数据做了缓存");
return p;
}
@Override
//@CacheEvict 从缓存people中删除key为id 的数据
@CacheEvict(value = "people")
public void remove(Long id) {
System.out.println("删除了id、key为"+id+"的数据缓存");
//这里不做实际删除操作
}
@Override
//@Cacheable缓存key为person 的id 数据到缓存people 中,如果没有指定key则方法参数作为key保存到缓存中。
@Cacheable(value = "people", key = "#person.id")
public Person findOne(Person person) {
Person p = personRepository.findOne(person.getId());
System.out.println("为id、key为:"+p.getId()+"数据做了缓存");
return p;
}
}
6.编写controller
为了测试方便请求方式都用了get
package com.us.example.controller;
import com.us.example.bean.Person;
import com.us.example.service.DemoService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* Created by yangyibo on 17/1/13.
*/
@RestController
public class CacheController {
@Autowired
private DemoService demoService;
//http://localhost:8080/put?name=abel&age=23&address=shanghai
@RequestMapping("/put")
public Person put(Person person){
return demoService.save(person);
}
//http://localhost:8080/able?id=1
@RequestMapping("/able")
@ResponseBody
public Person cacheable(Person person){
return demoService.findOne(person);
}
//http://localhost:8080/evit?id=1
@RequestMapping("/evit")
public String evit(Long id){
demoService.remove(id);
return "ok";
}
}
7.启动cache
启动类中要记得开启缓存配置。
package com.us.example;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import static org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.*;
/**
* Created by yangyibo on 17/1/13.
*/
@ComponentScan(basePackages ="com.us.example")
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = run(Application.class, args);
}
}
8.测试校验检验able:
启动Application 类,启动后在浏览器输入:http://localhost:8080/able?id=1(首先要在数据库中初始化几条数据。)
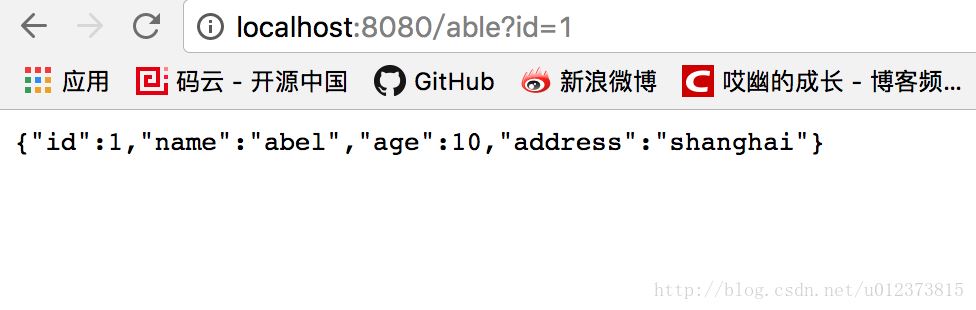
控制台输出:
“为id、key为:1数据做了缓存“ 此时已经为此次查询做了缓存,再次查询该条数据将不会出现此条语句,也就是不查询数据库了。
检验put
在浏览器输入:http://localhost:8080/put?name=abel&age=23&address=shanghai(向数据库插入一条数据,并将数据放入缓存。)

此时控制台输出为该条记录做了缓存:

然后再次调用able 方法,查询该条数据,将不再查询数据库,直接从缓存中读取数据。
测试evit
在浏览器输入:http://localhost:8080/evit?id=1(将该条记录从缓存中清楚,清除后,在次访问该条记录,将会重新将该记录放入缓存。)
控制台输出:

切换缓存
1.切换为EhCache作为缓存
pom.xml 文件中添加依赖
<dependency> <groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId> <artifactId>ehcache</artifactId> </dependency>
在resource 文件夹下新建ehcache的配置文件ehcache.xml 内容如下,此文件spring boot 会自动扫描
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <ehcache> <!--切换为ehcache 缓存时使用--> <cache name="people" maxElementsInMemory="1000" /> </ehcache>
2.切换为Guava作为缓存
只需要在pom中添加依赖
<dependency> <groupId>com.google.guava</groupId> <artifactId>guava</artifactId> <version>18.0</version> </dependency>
3.切换为redis作为缓存
请看下篇博客
本文参考:《JavaEE开发的颠覆者:Spring Boot实战 》
本文源代码:https://github.com/527515025/springBoot.git
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。

