C# ThreadPool之QueueUserWorkItem使用案例详解
先看代码:
//设置可以同时处于活动状态的线程池的请求数目。
bool pool = ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(8, 8);
if (pool) {
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数1"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数2"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数3"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数4"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数5"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数6"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数7"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数8"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数9"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数10"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数11"));
};
上面代码先设置线程池中最大并发量为8个,然后通过QueueUserWorkItem向线程池中添加11个方法,运行,输出结果:
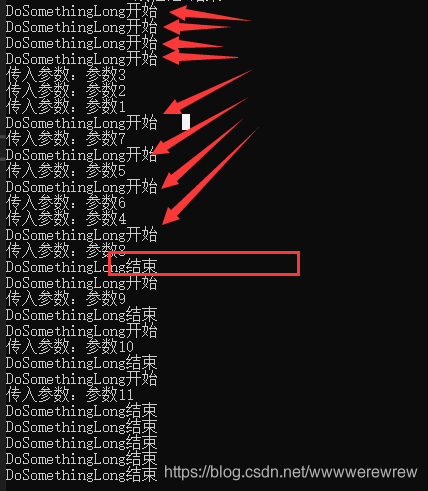
可以看出,先运行了8个,当有一个任务结束后线程池中有空闲线程时,排队的下一个任务才会执行,
把最大并发量改成9试试:
{
//设置可以同时处于活动状态的线程池的请求数目。
bool pool = ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(9, 9);
if (pool) {
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数1"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数2"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数3"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数4"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数5"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数6"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数7"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数8"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数9"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数10"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数11"));
};
}
运行结果:
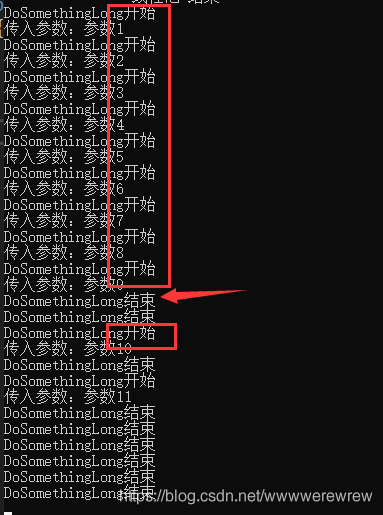
果然没错,这次是先执行9个,当有空闲线程时再执行下一个
总结一下
QueueUserWorkItem:将方法排入队列以便执行。 此方法在有线程池线程变得可用时执行。
到此这篇关于C# ThreadPool之QueueUserWorkItem使用案例详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C# ThreadPool之QueueUserWorkItem内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!
赞 (0)

