详谈@Cacheable不起作用的原因:bean未序列化问题
目录
- @Cacheable不起作用的原因:bean未序列化
- 是返回的Blogger自定义实体类没有实现序列化接口
- @Cacheable注解式缓存不起作用的情形
- 使用注解式缓存的正确方式
@Cacheable不起作用的原因:bean未序列化
SpringMVC中将serviceImpl的方法返回值缓存在redis中,发现@Cacheable失效
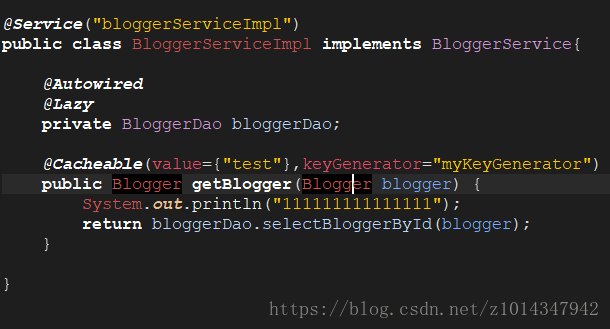
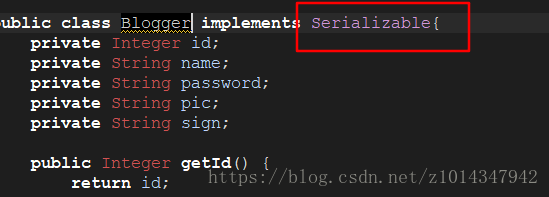
是返回的Blogger自定义实体类没有实现序列化接口
无法存入到redis中。implements一下Serializable接口即可!
@Cacheable注解式缓存不起作用的情形
@Cacheable注解式缓存使用的要点:正确的注解式缓存配置,注解对象为spring管理的hean,调用者为另一个对象。有些情形下注解式缓存是不起作用的:同一个bean内部方法调用,子类调用父类中有缓存注解的方法等。后者不起作用是因为缓存切面必须走代理才有效,这时可以手动使用CacheManager来获得缓存效果。
使用注解式缓存的正确方式
<cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="springCacheManager" proxy-target-class="false"/> <bean id="ehcacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManagerFactoryBean"> <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:ehcache.xml"/> <property name="cacheManagerName" value="ehcache"/> </bean> <bean id="springCacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheCacheManager"> <property name="cacheManager" ref="ehcacheManager"/> </bean>
要点:@Cacheable(value="必须使用ehcache.xml已经定义好的缓存名称,否则会抛异常")
@Component
public class CacheBean {
@Cacheable(value="passwordRetryCache",key="#key")
public String map(String key) {
System.out.println("get value for key: "+key);
return "value: "+key;
}
public String map2(String key) {
return map(key);
}
}
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = { "classpath:cache.xml" })
public class CacheTester {
@Autowired CacheManager cacheManager;
@Autowired CacheBean cacheBean;
@Test public void cacheManager() {
System.out.println(cacheManager);
}
@Test public void cacheAnnotation() {
cacheBean.map("a");
cacheBean.map("a");
cacheBean.map("a");
cacheBean.map("a");
System.out.println(cacheManager.getCacheNames());
}
}
输出:
get value for key: a
[authorizationCache, authenticationCache, shiro-activeSessionCache, passwordRetryCache]
稍微改造一下,让ehcache支持根据默认配置自动添加缓存空间,这里提供自定义的MyEhCacheCacheManager即可
<bean id="springCacheManager" class="com.itecheast.ite.domain.util.MyEhCacheCacheManager"> <property name="cacheManager" ref="ehcacheManager"/> </bean>
另一种改造方式,找不到已定义的缓存空间时不缓存,或者关闭全部缓存。把cacheManagers配置去掉就可以关闭圈闭缓存。
<bean id="springCacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.support.CompositeCacheManager"> <property name="cacheManagers"> <list> <bean class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheCacheManager"></bean> <!-- <bean class="com.itecheast.ite.domain.util.MyEhCacheCacheManager"></bean> 这个会自动创建缓存空间 --> </list> </property> <property name="fallbackToNoOpCache" value="true"/> </bean>
调用相同类或父类方法没有缓存效果:这时可以选择手动使用CacheManager。
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = { "classpath:cache.xml" })
public class CacheTester {
@Test public void cacheAnnotation() {
this.map("a");
this.map("a");
}
@Cacheable(value="passwordRetryCache",key="#key")
public String map(String key) {
System.out.println("get value for key: "+key);
return "value: "+key;
}
}
或者再换一种方式:手动使用代理方式调用同类方法也是可以的
public class CacheBean {
@Autowired ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Cacheable(value="passwordRetryCache",key="#key")
public String map(String key) { //方法不能为private,否则也没有缓存效果
System.out.println("get value for key: "+key);
return "value: "+key;
}
public String map2(String key) {
CacheBean proxy = applicationContext.getBean(CacheBean.class);
return proxy.map(key); //这里使用proxy调用map就可以缓存,而直接调用map则没有缓存
}
}
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。
赞 (0)

