关于Spring Cache 缓存拦截器( CacheInterceptor)
目录
- Spring Cache 缓存拦截器( CacheInterceptor)
- spring cache常用的三种缓存操作
- 具体整个流程是这样的
- CacheInterceptor.java
- 定义Cacheable注解
- 定义Rediskey.java
- Cache.java
- RedisCache.java
- CacheManager.java
- AbstractCacheManager.java
- RedisCacheManager.java
- 实现CacheInterceptor.java
- 配置Spring.xml
- 测试使用
Spring Cache 缓存拦截器( CacheInterceptor)
打开Spring Cache的核心缓存拦截器CacheInterceptor,可以看到具体实现:
public class CacheInterceptor extends CacheAspectSupport implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
@Override
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Method method = invocation.getMethod();
CacheOperationInvoker aopAllianceInvoker = new CacheOperationInvoker() {
@Override
public Object invoke() {
try {
return invocation.proceed();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ThrowableWrapper(ex);
}
}
};
try {
return execute(aopAllianceInvoker, invocation.getThis(), method, invocation.getArguments());
}
catch (CacheOperationInvoker.ThrowableWrapper th) {
throw th.getOriginal();
}
}
}
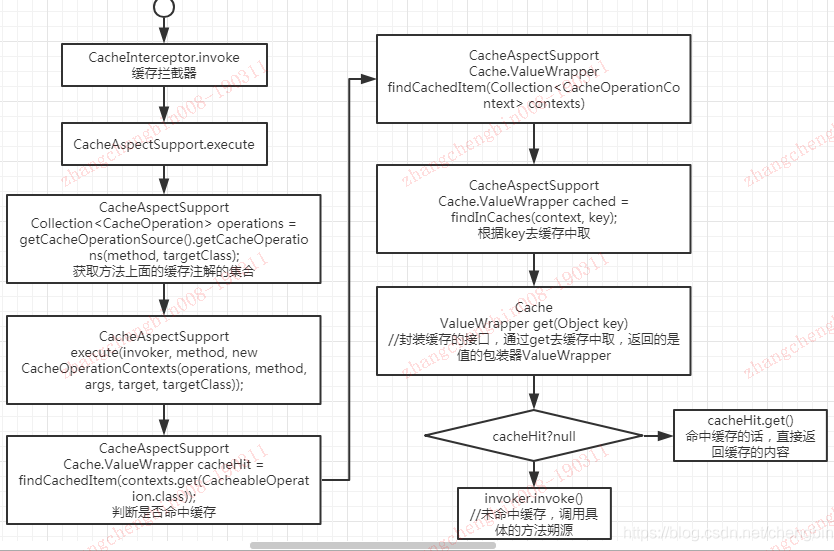
CacheInterceptor默认实现了Spring aop的MethodInterceptor接口,MethodInterceptor的功能是做方法拦截。拦截的方法都会调用invoke方法,在invoke方法里面主要缓存逻辑是在execute方法里面,该方法是继承了父类CacheAspectSupport。
protected Object execute(CacheOperationInvoker invoker, Object target, Method method, Object[] args) {
// Check whether aspect is enabled (to cope with cases where the AJ is pulled in automatically)
if (this.initialized) {
Class<?> targetClass = getTargetClass(target);
//获取执行方法上所有的缓存操作集合。如果有缓存操作则执行到execute(...),如果没有就执行invoker.invoke()直接调用执行方法了
Collection<CacheOperation> operations = getCacheOperationSource().getCacheOperations(method, targetClass);
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(operations)) {
return execute(invoker, method, new CacheOperationContexts(operations, method, args, target, targetClass));
}
}
return invoker.invoke();
}
集合Collection operations中存放了所有的缓存操作CachePutOperation、CacheableOperation、CacheEvictOperation
spring cache常用的三种缓存操作
@CachePut:执行方法后,将方法返回结果存放到缓存中。不管有没有缓存过,执行方法都会执行,并缓存返回结果(unless可以否决进行缓存)。(当然,这里说的缓存都要满足condition条件)@Cacheable:如果没有缓存过,获取执行方法的返回结果;如果缓存过,则直接从缓存中获取,不再执行方法。@CacheEvict:如果设置了beforeIntercepte则在方法执行前进行缓存删除操作,如果没有,则在执行方法调用完后进行缓存删除操作。
private Object execute(final CacheOperationInvoker invoker, Method method, CacheOperationContexts contexts) {
// Special handling of synchronized invocation
if (contexts.isSynchronized()) {
CacheOperationContext context = contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class).iterator().next();
if (isConditionPassing(context, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT)) {
Object key = generateKey(context, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT);
Cache cache = context.getCaches().iterator().next();
try {
return wrapCacheValue(method, cache.get(key, new Callable<Object>() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
return unwrapReturnValue(invokeOperation(invoker));
}
}));
}
catch (Cache.ValueRetrievalException ex) {
// The invoker wraps any Throwable in a ThrowableWrapper instance so we
// can just make sure that one bubbles up the stack.
throw (CacheOperationInvoker.ThrowableWrapper) ex.getCause();
}
}
else {
// No caching required, only call the underlying method
return invokeOperation(invoker);
}
}
// 处理beforeIntercepte=true的缓存删除操作
processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), true,
CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT);
// 从缓存中查找,是否有匹配@Cacheable的缓存数据
Cache.ValueWrapper cacheHit = findCachedItem(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class));
// 如果@Cacheable没有被缓存,那么就需要将数据缓存起来,这里将@Cacheable操作收集成CachePutRequest集合,以便后续做@CachePut缓存数据存放。
List<CachePutRequest> cachePutRequests = new LinkedList<CachePutRequest>();
if (cacheHit == null) {
collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class),
CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT, cachePutRequests);
}
Object cacheValue;
Object returnValue;
//如果没有@CachePut操作,就使用@Cacheable获取的结果(可能也没有@Cableable,所以result可能为空)。
if (cacheHit != null && cachePutRequests.isEmpty() && !hasCachePut(contexts)) {
//如果没有@CachePut操作,并且cacheHit不为空,说明命中缓存了,直接返回缓存结果
cacheValue = cacheHit.get();
returnValue = wrapCacheValue(method, cacheValue);
}
else {
// 否则执行具体方法内容,返回缓存的结果
returnValue = invokeOperation(invoker);
cacheValue = unwrapReturnValue(returnValue);
}
// Collect any explicit @CachePuts
collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CachePutOperation.class), cacheValue, cachePutRequests);
// Process any collected put requests, either from @CachePut or a @Cacheable miss
for (CachePutRequest cachePutRequest : cachePutRequests) {
cachePutRequest.apply(cacheValue);
}
// Process any late evictions
processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), false, cacheValue);
return returnValue;
}
//根据key从缓存中查找,返回的结果是ValueWrapper,它是返回结果的包装器
private Cache.ValueWrapper findCachedItem(Collection<CacheOperationContext> contexts) {
Object result = CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT;
for (CacheOperationContext context : contexts) {
if (isConditionPassing(context, result)) {
Object key = generateKey(context, result);
Cache.ValueWrapper cached = findInCaches(context, key);
if (cached != null) {
return cached;
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No cache entry for key '" + key + "' in cache(s) " + context.getCacheNames());
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
private Cache.ValueWrapper findInCaches(CacheOperationContext context, Object key) {
for (Cache cache : context.getCaches()) {
Cache.ValueWrapper wrapper = doGet(cache, key);
if (wrapper != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Cache entry for key '" + key + "' found in cache '" + cache.getName() + "'");
}
return wrapper;
}
}
return null;
}
具体整个流程是这样的
CacheInterceptor.java
项目中基本上都需要使用到Cache的功能, 但是Spring提供的Cacheable并不能很好的满足我们的需求, 所以这里自己借助Spring思想完成自己的业务逻辑.
定义Cacheable注解
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface Cacheable {
RedisKey value();
String key();
}
定义Rediskey.java
public enum RedisKeyEnum {
TEST_CACHE("test:", 24, TimeUnit.HOURS, "Test");
/**
* 缓存Key的前缀
*/
private String keyPrefix;
/**
* 过期时间
*/
private long timeout;
/**
* 过期时间单位
*/
private TimeUnit timeUnit;
/**
* 描述
*/
private String desc;
private static final String REDIS_KEY_DEFUALT_SEPARATOR = ":";
RedisKey(String keyPrefix, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit, String desc){
this.keyPrefix = keyPrefix;
this.timeout = timeout;
this.timeUnit = timeUnit;
this.desc = desc;
}
public long getTimeout() {
return timeout;
}
public TimeUnit getTimeUnit() {
return timeUnit;
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
/**
* 获取完整的缓存Key
* @param keys
* @return
*/
public String getKey(String... keys) {
if(keys == null || keys.length <= 0){
return this.keyPrefix;
}
String redisKey = keyPrefix;
for (int i = 0, length = keys.length; i < length; i++) {
String key = keys[i];
redisKey += key;
if (i < length - 1) {
redisKey += REDIS_KEY_DEFUALT_SEPARATOR;
}
}
return redisKey;
}
}
Cache.java
public interface Cache<K, V> {
/**
* 返回缓存名称
* @return
*/
String getName();
/**
* 添加一个缓存实例
*
* @param key
* @param value
*/
V put(K key, V value);
/**
* 添加一个可过期的缓存实例
* @param key
* @param value
* @param expire
* @param timeUnit
* @return
*/
V put(K key, V value, long expire, TimeUnit timeUnit);
/**
* 返回缓存数据
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
V get(K key);
/**
* 删除一个缓存实例, 并返回缓存数据
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
void remove(K key);
/**
* 获取所有的缓存key
* @return
*/
Set<K> keys();
/**
* 获取所有的缓存key
* @return
*/
Set<K> keys(K pattern);
/**
* 获取所有的缓存数据
* @return
*/
Collection<V> values();
/**
* 清空所有缓存
*/
void clear();
}
RedisCache.java
public class RedisCache<K, V> implements Cache<K, V> {
public static final String DEFAULT_CACHE_NAME = RedisCache.class.getName() + "_CACHE_NAME";
private RedisTemplate<K, V> redisTemplate;
private ValueOperations<K, V> valueOperations;
public RedisCache(RedisTemplate redisTemplate) {
this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate;
this.valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
DataType dataType = redisTemplate.type("a");
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return DEFAULT_CACHE_NAME;
}
@Override
public V put(K key, V value) {
valueOperations.set(key, value);
return value;
}
@Override
public V put(K key, V value, long expire, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
valueOperations.set(key, value, expire, timeUnit);
return value;
}
@Override
public V get(K key) {
return valueOperations.get(key);
}
@Override
public void remove(K key) {
// V value = valueOperations.get(key);
redisTemplate.delete(key);
}
@Override
public Set<K> keys() {
return null;
}
@Override
public Set<K> keys(K pattern) {
return redisTemplate.keys(pattern);
}
@Override
public Collection<V> values() {
return null;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
}
}
CacheManager.java
public interface CacheManager {
/**
* 获取缓存
* @return
*/
Cache getCache(String name);
/**
* 获取所有的缓存名称
*/
Collection<String> getCacheNames();
}
AbstractCacheManager.java
public abstract class AbstractCacheManager implements CacheManager, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AbstractCacheManager.class);
private final Map<String, Cache> cacheMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
private volatile Set<String> cacheNames = Collections.emptySet();
private static final String DEFAULT_CACHE_NAME_SUFFIX = "_CACHE_NAME";
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
initlalizingCache();
}
private void initlalizingCache(){
Collection<? extends Cache> caches = loadCaches();
synchronized (this.cacheMap) {
this.cacheNames = Collections.emptySet();
this.cacheMap.clear();
Set<String> cacheNames = new LinkedHashSet<String>(caches.size());
for (Cache cache : caches) {
String name = cache.getName();
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(name)){
name = cache.getClass().getName() + DEFAULT_CACHE_NAME_SUFFIX;
}
this.cacheMap.put(name, cache);
cacheNames.add(name);
}
this.cacheNames = Collections.unmodifiableSet(cacheNames);
}
}
@Override
public Cache getCache(String name) {
Cache cache = cacheMap.get(name);
if(cache != null){
return cache;
}
return null;
}
protected abstract Collection<? extends Cache> loadCaches();
@Override
public Collection<String> getCacheNames() {
return this.cacheNames;
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
cacheMap.clear();
}
}
RedisCacheManager.java
public class RedisCacheManager extends AbstractCacheManager {
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
public RedisCacheManager(RedisTemplate redisTemplate) {
this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate;
}
@Override
protected Collection<? extends Cache> loadCaches() {
Collection<Cache<String, Object>> caches = new ArrayList<>();
RedisCache<String, Object> redisCache = new RedisCache<>(redisTemplate);
caches.add(redisCache);
return caches;
}
}
实现CacheInterceptor.java
/**
* 缓存数据过滤器, 缓存到redis数据中的数据是ServiceResult.getDateMap()数据
* 使用: 在service方法上添加com.chinaredstar.urms.annotations.Cacheable注解, 并指定RedisKeyEunm和cache key, cache key支持Spel表达式
* 以下情况不缓存数据:
* 1: 返回状态为fasle时, 不缓存数据
* 2: 返回dataMap为空时, 不缓存数据
* 3: 返回数据结构不是ServiceReslut实例时, 不缓存数据
*
* 当缓存问题时, 不影响正常业务, 但所有的请求都会打到DB上, 对DB有很大的冲击
*/
public class CacheInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CacheInterceptor.class);
private static final ParameterNameDiscoverer parameterNameDiscoverer = new DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer();
private CacheManager cacheManager;
public void setCacheManager(CacheManager cacheManager) {
this.cacheManager = cacheManager;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
Method method = methodInvocation.getMethod();
Object[] args = methodInvocation.getArguments();
Cacheable cacheable = method.getAnnotation(Cacheable.class);
if (cacheable == null) {
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}
String key = parseCacheKey(method, args, cacheable.key());
logger.info(">>>>>>>> -- 获取缓存key : {}", key);
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(key)){
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}
RedisKey redisKey = cacheable.value();
Cache cache = cacheManager.getCache(RedisCache.DEFAULT_CACHE_NAME);
Object value = null;
try{
value = cache.get(redisKey.getKey(key));
} catch (Exception e){
logger.info(">>>>>>>> -- 从缓存中获取数据异常 : {}", ExceptionUtil.exceptionStackTrace(e));
}
if (value != null) {
logger.info(">>>>>>>> -- 从缓存中获取数据 : {}", JsonUtil.toJson(value));
return ServiceResult.newInstance(true, value);
}
value = methodInvocation.proceed();
logger.info(">>>>>>>> -- 从接口中获取数据 : {}", JsonUtil.toJson(value));
if ( value != null && value instanceof ServiceResult ) {
ServiceResult result = (ServiceResult) value;
if(!result.isSuccess() || result.getDataMap() == null){
return value;
}
try{
cache.put(redisKey.getKey(key), result.getDataMap(), redisKey.getTimeout(), redisKey.getTimeUnit());
} catch (Exception e){
logger.info(">>>>>>>> -- 将数据放入缓存异常 : {}", ExceptionUtil.exceptionStackTrace(e));
}
}
return value;
}
/**
* 使用SpeL解析缓存key
* @param method
* @param args
* @param expressionString
* @return
*/
private String parseCacheKey(Method method, Object[] args, String expressionString) {
String[] parameterNames = parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(method);
EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
if (parameterNames != null && parameterNames.length > 0
&& args != null && args.length > 0
&& args.length == parameterNames.length ) {
for (int i = 0, length = parameterNames.length; i < length; i++) {
context.setVariable(parameterNames[i], args[i]);
}
}
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
Expression expression = parser.parseExpression(expressionString);
return (String) expression.getValue(context);
}
}
配置Spring.xml
<bean id="redisCacheManager" class="com.package.cache.RedisCacheManager">
<constructor-arg ref="cacheRedisTemplate" />
</bean>
<bean id="cacheInterceptor" class="com.package.interceptor.CacheInterceptor" p:cacheManager-ref="redisCacheManager"/>
<!-- 方法拦截器 MethodInterceptor -->
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<aop:pointcut id="cacheInterceptorPointcut" expression="execution(* com.package..*(..))
and @annotation(com.package.annotations.Cacheable)"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="cacheInterceptor" pointcut-ref="cacheInterceptorPointcut" order="2" />
</aop:config>
测试使用
@Cacheable(value = RedisKey.TEST_CACHE, key = "#code + ':' + #user.id")
public ServiceResult<String> test(String code, User user){
return new ServiceResult("success");
}
说明
Cacheable其中的参数key拼接的规则支持Spring SpeL表达式。其规则和Spring Cacheable使用方法一致。
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。
赞 (0)

