Python四大金刚之字典详解
目录
- 引言
- 一、字典的创建
- 二、字典元素的操作
- (一)获取
- (二)增删改
- 三、获取字典的视图
- 四、字典的遍历
- 五、字典的特点
- 六、字典生成式
- 总结
- 引言
- 一、字典的创建
- 二、字典元素的操作
- (一)获取
- (二)增删改
- 三、获取字典的视图
- 四、字典的遍历
- 五、字典的特点
- 六、字典生成式
- 总结
引言

列表、字典:可变序列,可以执行增删改排序等
字典:无序的


一、字典的创建
#使用{}创建
scores = {'张三':100 ,'李四':98 ,'王麻子':72}
print(scores)
print(type(scores))
#使用内置函数dict()
student = dict(name = 'jack ', age = 16)
print(student)
print(type(student))
二、字典元素的操作
(一)获取

#获取字典中的元素
#方法一:
print(scores['张三'])
#方法二:
print(scores.get('张三'))
print(scores.get('66'))
#如果查找的不存在,返回none
(二)增删改

删除操作
del scores['张三'] #根据索引删除 key 和value print(scores) scores.clear() #删除所有 print(scores)
新增操作 (直接增加)
scores['赵四'] = 80
三、获取字典的视图
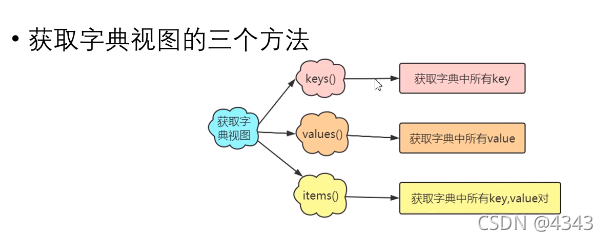
# 获取所有key值 key = scores.keys() print(key) print(type(key)) print(list(key)) #将key组成的视图转成list #获取所有value值 value = scores.values() print(value) print(type(value)) print(list(value)) #将value组成的视图转成list #获取所有的key-value值 items = scores.items() print(items) print(type(items)) print(list(items)) #转换为list后元素由元组组成

四、字典的遍历

for item in scores :
print(item,end=' ') #输出的是字典中的key
#输出key对应的value
print(scores[item],end=' ')
print(scores.get(item))
五、字典的特点

六、字典生成式


students = ['mark','sheep','jerry','tom']
grades = [100,78,60,59]
d={key:price for key,price in zip(students,grades)}
print(d)
总结
本篇文章就到这里了,希望能够给你带来帮助,也希望您能够多多关注我们的更多内容!
引言

列表、字典:可变序列,可以执行增删改排序等
字典:无序的


一、字典的创建
#使用{}创建
scores = {'张三':100 ,'李四':98 ,'王麻子':72}
print(scores)
print(type(scores))
#使用内置函数dict()
student = dict(name = 'jack ', age = 16)
print(student)
print(type(student))
二、字典元素的操作
(一)获取

#获取字典中的元素
#方法一:
print(scores['张三'])
#方法二:
print(scores.get('张三'))
print(scores.get('66'))
#如果查找的不存在,返回none
(二)增删改

删除操作
del scores['张三'] #根据索引删除 key 和value print(scores) scores.clear() #删除所有 print(scores)
新增操作 (直接增加)
scores['赵四'] = 80
三、获取字典的视图

# 获取所有key值 key = scores.keys() print(key) print(type(key)) print(list(key)) #将key组成的视图转成list #获取所有value值 value = scores.values() print(value) print(type(value)) print(list(value)) #将value组成的视图转成list #获取所有的key-value值 items = scores.items() print(items) print(type(items)) print(list(items)) #转换为list后元素由元组组成

四、字典的遍历

for item in scores :
print(item,end=' ') #输出的是字典中的key
#输出key对应的value
print(scores[item],end=' ')
print(scores.get(item))
五、字典的特点

六、字典生成式


students = ['mark','sheep','jerry','tom']
grades = [100,78,60,59]
d={key:price for key,price in zip(students,grades)}
print(d)
总结
本篇文章就到这里了,希望能够给你带来帮助,也希望您能够多多关注我们的更多内容!
赞 (0)

