SpringBoot+ShardingSphereJDBC实现读写分离详情
目录
- 1 概述
- 2 环境
- 3 一些基础理论
- 3.1 读写分离
- 3.2 主从复制
- 3.3 数据库中间件简介
- 4MySQL主从复制环境准备
- 4.1 主库操作
- 4.1.1 拉取镜像并创建容器运行
- 4.1.2 修改配置文件
- 4.1.3 准备数据源
- 4.1.4 创建一个复制操作的用户(可选但推荐)
- 4.1.5 数据备份(可选)
- 4.1.6 查看主库状态
- 4.2 从库操作
- 4.2.1 拉取镜像并创建容器运行
- 4.2.2 修改配置文件
- 4.2.3 查看ip地址
- 4.2.4 导入数据(可选)
- 4.2.5 准备数据源
- 4.2.6 设置主库
- 4.2.7 开启从库
- 4.3 测试
- 5 搭建Spring Boot环境
- 5.1 新建项目并引入依赖
- 5.2 使用生成器
- 5.3 配置文件
- 5.3.1 模式
- 5.3.2 数据源配置
- 5.3.3 读写分离规则配置
- 5.3.3.1 数据源配置
- 5.3.3.2 负载均衡配置
- 5.3.4 属性配置
- 5.4 准备Controller
- 6 测试
1 概述
本文讲述了如何使用MyBatisPlus+ShardingSphereJDBC进行读写分离,以及利用MySQL进行一主一从的主从复制。
具体步骤包括:
MySQL主从复制环境准备(Docker)- 搭建
ShardingShpereJDBC+MyBatisPlus+Druid环境 - 测试
2 环境
OpenJDK 17.0.3Spring Boot 2.7.0MyBatis Plus 3.5.1MyBatis Plus Generator 3.5.2Druid 1.2.10ShardingSphereJDBC 5.1.1MySQL 8.0.29(Docker)
3 一些基础理论
3.1 读写分离
读写分离,顾名思义就是读和写分开,更具体来说,就是:
- 写操作在主数据库进行
- 读操作在从数据库进行
使用读写分离的根本目的就是为了提高并发性能,如果读写都在同一台MySQL上实现,相信会不如一台MySQL写,另外两台MySQL读这样的配置性能高。另一方面,在很多时候都是读操作的请求要远远高于写操作,这样就显得读写分离非常有必要了。
3.2 主从复制
主从复制,顾名思义就是把主库的数据复制到从库中,因为读写分离之后,写操作都在主库进行,但是读操作是在从库进行的,也就是说,主库上的数据如果不能复制到从库中,那么从库就不会读到主库中的数据。严格意义上说,读写分离并不要求主从复制,只需要在主库写从库读即可,但是如果没有了主从复制,读写分离将失去了它的意义。因此读写分离通常与主从复制配合使用。
因为本示例使用的是MySQL,这里就说一下MySQL主从复制的原理,如下图所示:
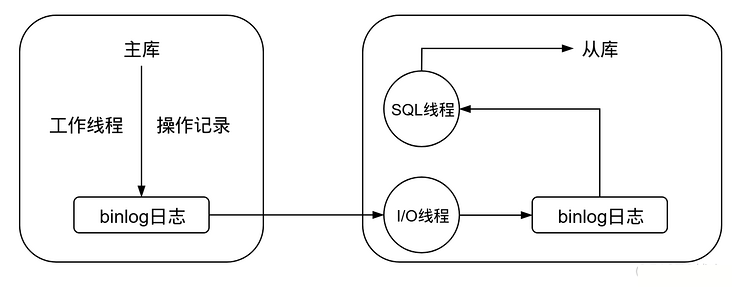
工作流程如下:
- 主库修改数据后,将修改日志写入
binlog - 从库的
I/O线程读取主库的binlog,并拷贝到从库本地的binlog中 - 从库本地的
binlog被SQL线程读取,执行其中的内容并同步到从库中
3.3 数据库中间件简介
数据库中间件可以简化对读写分离以及分库分表的操作,并隐藏底层实现细节,可以像操作单库单表那样操作多库多表,主流的设计方案主要有两种:
- 服务端代理:需要独立部署一个代理服务,该代理服务后面管理多个数据库实例,在应用中通过一个数据源与该代理服务器建立连接,由该代理去操作底层数据库,并返回相应结果。优点是支持多语言,对业务透明,缺点是实现复杂,实现难度大,同时代理需要确保自身高可用
- 客户端代理:在连接池或数据库驱动上进行一层封装,内部与不同的数据库建立连接,并对
SQL进行必要的操作,比如读写分离选择走主库还是从库,分库分表select后如何聚合结果。优点是实现简单,天然去中心化,缺点是支持语言较少,版本升级困难
一些常见的数据库中间件如下:
Cobar:阿里开源的关系型数据库分布式服务中间件,已停更DRDS:脱胎于Cobar,全称分布式关系型数据库服务MyCat:开源数据库中间件,目前更新了MyCat2版本Atlas:Qihoo 360公司Web平台部基础架构团队开发维护的一个基于MySQL协议的数据中间层项目,同时还有一个NoSQL的版本,叫Pikatddl:阿里巴巴自主研发的分布式数据库服务Sharding-JDBC:ShardingShpere的一个子产品,一个轻量级Java框架
4MySQL主从复制环境准备
看完了一些基础理论就可以进行动手了,本小节先准备好MySQL主从复制的环境,基于Docker+MySQL官方文档搭建。
4.1 主库操作
4.1.1 拉取镜像并创建容器运行
docker pull mysql docker run -itd -p 3306:3306 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456 --name master mysql docker exec -it master /bin/bash
在主库中进行更新镜像源,安装vim以及net-tools的操作:
cd /etc/apt echo deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian/ buster main non-free contrib deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian/ buster main non-free contrib deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian-security buster/updates main deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian-security buster/updates main deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian/ buster-updates main non-free contrib deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian/ buster-updates main non-free contrib deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian/ buster-backports main non-free contrib deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian/ buster-backports main non-free contrib > sources.list apt update && apt upgrade apt install vim net-tools
4.1.2 修改配置文件
vim /etc/mysql/my.cnf
添加下面两行数据:
[mysqld] server-id=1 # 全局唯一,取值[1,2^32-1],默认为1 binlog-do-db=test # 表示需要复制的是哪个库
修改完成后重启。
4.1.3 准备数据源
CREATE DATABASE test; USE test; CREATE TABLE user( id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, );
4.1.4 创建一个复制操作的用户(可选但推荐)
注意创建用户需要加上mysql_native_password,否则会导致从库一直处于连接状态:
CREATE USER 'repl'@'172.17.0.3' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY '123456'; GRANT REPLICATION slave ON *.* TO 'repl'@'172.17.0.3';
具体的地址请根据从库的地址修改,可以先看后面的从库配置部分。
4.1.5 数据备份(可选)
如果原来的主库中是有数据的,那么这部分数据需要手动同步到从库中:
FLUSH TABLES WITH READ LOCK;
开启主库的另一个终端,使用mysqldump导出:
mysqldump -u root -p --all-databases --master-data > dbdump.db
导出完成后,解除读锁:
UNLOCK TABLES;
4.1.6 查看主库状态
SHOW MASTER STATUS;
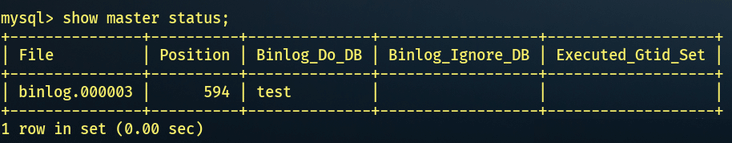
需要把File以及Position记录下来,后面从库的配置需要用到。
4.2 从库操作
4.2.1 拉取镜像并创建容器运行
docker pull mysql docker run -itd -p 3307:3306 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456 --name slave mysql docker exec -it slave /bin/bash
进入容器后,像主库一样更新源然后安装vim和net-tools:
cd /etc/apt echo deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian/ buster main non-free contrib deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian/ buster main non-free contrib deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian-security buster/updates main deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian-security buster/updates main deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian/ buster-updates main non-free contrib deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian/ buster-updates main non-free contrib deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian/ buster-backports main non-free contrib deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian/ buster-backports main non-free contrib > sources.list apt update && apt upgrade apt install vim net-tools
4.2.2 修改配置文件
vim /etc/mysql/my.cnf
添加如下两行:
[mysqld] server-id=2 # 全局唯一,不能与主库相同 replicate-do-db=test # 与主库相同,表示对该库进行复制
修改完成后重启。
4.2.3 查看ip地址
查看从库的ip地址,用于给主库设置同步的用户:
ifconfig
输出:
inet 172.17.0.3 netmask 255.255.0.0 broadcast 172.17.255.255
那么主库中用于复制的用户就可以是repl@172.17.0.3。
4.2.4 导入数据(可选)
如果主库有数据可以先导入到从库:
mysqldump -u root -p --all-databases < dbdump.db
4.2.5 准备数据源
CREATE DATABASE test; USE test; CREATE TABLE user( id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, );
4.2.6 设置主库
可以使用change master to/change replication source to(8.0.23+)命令:
CHANGE REPLICATION SOURCE TO source_host='172.17.0.2', # 可以使用ifconfig查看主库ip source_user='repl', # 之前主库创建的用户 source_password='123456', # 密码 source_log_file='binlog.000003', # 之前在主库上使用show master status查看的日志文件 source_log_pos=594; # 同样使用show master status查看
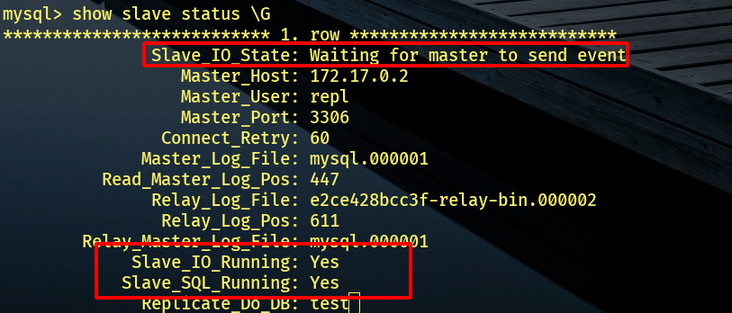
4.2.7 开启从库
START SLAVE; SHOW SLAVE STATUS\G
新版本(8.0.22+)可使用:
START REPLICA; SHOW REPLICA STATUS\G
需要IO和SQL线程显示Yes才算成功:
4.3 测试
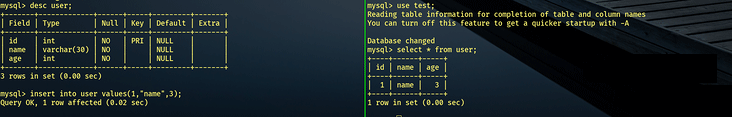
主库选择插入一条数据:
INSERT INTO user VALUES(1,"name",3);
然后从库就能select到了:
5 搭建Spring Boot环境
5.1 新建项目并引入依赖
新建Spring Boot项目,并引入如下依赖:
implementation 'com.alibaba:druid:1.2.10' implementation 'com.baomidou:mybatis-plus-boot-starter:3.5.1' implementation 'org.freemarker:freemarker:2.3.31' implementation 'com.baomidou:mybatis-plus-generator:3.5.2' implementation 'org.apache.shardingsphere:shardingsphere-jdbc-core-spring-boot-starter:5.1.1'
Maven版本:
<dependency> <groupId>com.baomidou</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>3.5.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.baomidou</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-plus-generator</artifactId> <version>3.5.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.freemarker</groupId> <artifactId>freemarker</artifactId> <version>2.3.31</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.2.10</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId> <artifactId>sharding-jdbc-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>5.1.1</version> </dependency>
5.2 使用生成器
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.FastAutoGenerator;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.engine.FreemarkerTemplateEngine;
public class Generator {
public static void main(String[] args){
FastAutoGenerator.create("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test", "root", "123456")
.globalConfig(builder ->
builder.author("author").outputDir(System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/src/main/java").build())
.packageConfig(builder ->
builder.parent("com.example.demo").moduleName("user").build())
.strategyConfig(builder ->
builder.addInclude("user").entityBuilder().enableLombok().disableSerialVersionUID().build())
.templateEngine(new FreemarkerTemplateEngine())
.execute();
}
}
直接运行main方法即可生成代码,配置请根据个人需要进行更改。
5.3 配置文件
spring: shardingsphere: mode: type: Memory # 内存模式,元数据保存在当前进程中 datasource: names: master,slave # 数据源名称,这里有两个 master: # 跟上面的数据源对应 type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource # 连接池 url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test # 连接url username: root password: 123456 slave: # 跟上面的数据源对应 type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test username: root password: 123456 rules: readwrite-splitting: # 读写分离规则 data-sources: # 数据源配置 random: # 这个名字随便起 type: Static # 静态类型 load-balancer-name: round_robin # 负载均衡算法名字 props: write-data-source-name: master # 写数据源 read-data-source-names: slave # 读数据源 load-balancers: # 负载均衡配置 round_robin: # 跟上面负载均衡算法的名字对应 type: ROUND_ROBIN # 负载均衡算法 props: sql-show: true # 打印SQL
因为配置文件的内容比较多,以下进行分开说明。
5.3.1 模式
spring.shardingsphere.mode.type,模式有三种:
Memory:内存模式,初始化配置或执行SQL等操作均在当前进程生效Standalone:单机模式,可以将数据源和规则等元数据信息持久化,但是这些元数据不会在集群中同步Cluster:集群模式,提供了多个Apache ShardingSphere实例之间元数据共享以及分布式场景下的状态协调的能力,也提供水平扩展以及高可用的能力
这里使用内存模式,如果想将元数据等信息持久化,请使用单机模式,单机模式需要配置以下属性:
- spring.shardingsphere.mode.type=Standalone:设置单机模式
- spring.shardingsphere.mode.repository.type=:持久化仓库的类型,单机模式适用类型为File
- spring.shardingsphere.mode.repository.props.path=:元数据存储路径,默认.shardingsphere
- spring.shardingsphere.mode.overwrite=:是否覆盖
而采用集群模式,需要配置以下属性:
- spring.shardingsphere.mode.type=Cluster:设置集群模式
- spring.shardingsphere.mode.repository.type=:持久化仓库类型,集群模式支持ZooKeeper以及Etcd持久化
- spring.shardingsphere.mode.repository.props.namespace=:注册中心命名空间
- spring.shardingsphere.mode.repository.props.server-lists=:注册中心服务器列表
- spring.shardingsphere.mode.overwrite=:是否覆盖
- spring.shardingsphere.mode.repository.props.<key>=:注册中心的属性配置,对于ZooKeeper,可以配置retryIntervalMilliseconds(重试间隔毫秒)、maxRetries(客户端连接最大重试数)、timeToLiveSeconds(临时数据存活秒数)、operationTimeoutMilliseconds(客户端操作超时毫秒数)、digest(登录密码),对于Etcd,可以配置timeToLiveSeconds(临时数据存活秒数)、connectionTimeout(连接超时秒数)
5.3.2 数据源配置
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names,后面接数据源的名称,使用,分隔,比如此处有两个数据源:
masterslave
然后每个数据源可以配置:
type:数据库连接池类型,这里使用的是Druidusername:用户名password:密码jdbc-url:连接url,注意,对于此处使用的Druid连接池,需要使用url而不是jdbc-url
5.3.3 读写分离规则配置
spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting,需要配置其中的数据源以及负载均衡类型:
- spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.data-sources
- spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.load-balancers
5.3.3.1 数据源配置
数据源配置首先需要添加一个数据源的名字,随便起一个,比如这里是random,然后需要配置三个属性:
- spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.data-sources.random.type:读写分离的类型,可选值为Static与Dynamic,这里选择Static,如果选择Dynamic,也就是动态数据源,请配合dynamic-datasource-spring-boot-starter使用
- spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.data-sources.random.props.write-data-source-name:写数据源
- spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.data-sources.random.props.read-data-source-name:读数据源
- spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.data-sources.random.load-balancer-name:负载均衡算法的名称,这里写的是round_robin
5.3.3.2 负载均衡配置
负载均衡配置需要与上面的spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.data-sources.random.load-balancer-name属性对应,比如这里是round_robin,那么需要配置的就是spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.load-balancers.round_robin。然后下一步就是配置具体的负载均衡算法。
内置的负载均衡算法有三个:
- 轮询算法:
ROUND_ROBIN,配置type=ROUND_ROBIN即可,也就是spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.load-balancers.round_robin.type=ROUND_ROBIN - 随机访问算法:
RANDOM,配置type=RANDOM - 权重访问算法:
WEIGHT,配置type=WEIGHT,同时需要配置props,在其中配置各个读节点的权重
5.3.4 属性配置
属性的话这里只配置了一个spring.shardingsphere.props.sql-show=true,也就是打印SQL,其他支持的属性有:
- spring.shardingsphere.props.sql-simple:是否打印简单风格的SQL,默认为false
- spring.shardingsphere.props.kernel-exector-size:设置任务处理线程池大小,默认为infinite
- spring.shardingsphere.props.max-connections-size-per-query:每次查询所能使用的最多数据库连接数,默认为1
- spring.shardingsphere.props.check-table-metadata-enabled:启动时是否检查分片元数据的一致性,默认为false
- spring.shardingsphere.props.check-duplicate-table-enabled:启动时是否检查重复表,默认为false
- spring.shardingsphere.props.sql-federation-enabled:是否开启联邦查询,默认为false
5.4 准备Controller
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
@RequiredArgsConstructor(onConstructor = @__(@Autowired))
public class UserController {
private final UserServiceImpl userService;
@GetMapping("/select")
public User select(){
return userService.getById(1);
}
@GetMapping("/insert")
public boolean insert(){
return userService.saveOrUpdate(User.builder().id(3L).name("name3").build());
}
}
6 测试
访问http://localhost:8080/user/insert,可以看到写操作在主库进行:

访问http://localhost:8080/user/select,可以看到读操作在从库进行:
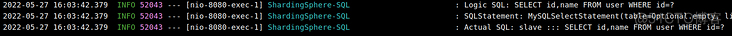
这样读写分离就算是完成了。
到此这篇关于SpringBoot+ShardingSphereJDBC实现读写分离详情的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot读写分离内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

