SpringBoot用配置影响Bean加载@ConditionalOnProperty
目录
- 故事背景
- 调试&解决
- SpringBoot 是怎么做的
- 故事的最后
故事背景
故事发生在几个星期前,自动化平台代码开放给整个测试团队以后,越来越多的同事开始探索平台代码。为了保障自动化测试相关的数据和沉淀能不被污染,把数据库进行了隔离。终于有了2个数据库实例,一个给dev环境用,一个给test环境用。可是随着平台的发展,越来越多的中间件被引用了。所以需要隔离的东西就越来越多了,比如MQ,Redis等。成本越来越高,如果像数据库实例一样全部分开搞一套,那在当下全域降本增效的大潮下,也是困难重重。
通过线下观察和走访发现,这些探索的同学并不是需要全平台的能力,其中有很多模块或者子系统,同学并不关心。因此就产生了一个想法,隔离掉这些类或者不使用这些和中间件相关的类应该就可以了 。而后因为我们的平台是基于springboot开发的,自然而然的想到了@Conditional注解。
调试&解决
以AWS SQS为例,先添加上了注解@ConditionalOnProperty根据配置信息中的coverage.aws.topic属性进行判断,如果存在这个配置就进行CoverageSQSConfig的Spring Bean的加载。
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty(
name = "coverage.aws.topic"
)
public class CoverageSQSConfig {
@Value("${coverage.aws.region}")
private String awsRegion;
@Value("${coverage.aws.access.key}")
private String accessKey;
@Value("${coverage.aws.secret.key}")
private String secretKey;
@Bean(name = "coverageSQSListenerFactory")
public DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory sqsListenerContainerFactory(){
return getDefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory(awsRegion, accessKey, secretKey);
}
private DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory getDefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory(String awsRegion, String accessKey, String secretKey) {
DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory sqsFactory = new DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory();
sqsFactory.setConnectionFactory(new SQSConnectionFactory(
new ProviderConfiguration(),
AmazonSQSClientBuilder.standard()
.withRegion(Region.of(awsRegion).id())
.withCredentials(new AWSStaticCredentialsProvider(new BasicAWSCredentials(accessKey, secretKey)))
.build()));
sqsFactory.setConcurrency("3-10");
sqsFactory.setReceiveTimeout(10*1000L);
sqsFactory.setRecoveryInterval(1000L);
return sqsFactory;
}
}
为调试这个内容的效果,这里列出了2次调试的效果对比:首先是把备注字段全部都注释掉。

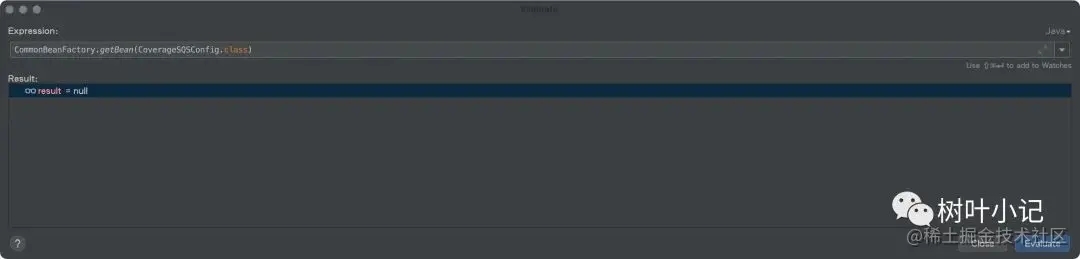
通过上图很明显,当coverage.aws.topic属性不存在的时候,不能找到被Spring统一管理的bean。
第二次是把备注的注释都取消掉,重启后能找到bean。
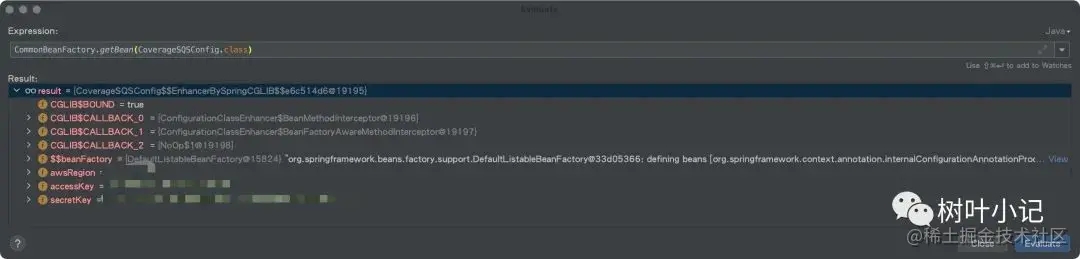
问题解决了吗?当时就想再看下SpringBoot是怎么做的通过这个注解就这么方便的过滤了这个bean的加载,以及是否有什么其他的用法或者特性。
SpringBoot 是怎么做的
通过@ConditionalOnProperty注解,很快能定位到它是位于 autoconfigure模块的特性。**
**

顺藤摸瓜,很快就能找到注解是在哪里进行使用的
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition;
...
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 40)
class OnPropertyCondition extends SpringBootCondition {
@Override
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
// 通过获类原始数据上的ConditionalOnProperty注解的参数值
List<AnnotationAttributes> allAnnotationAttributes = annotationAttributesFromMultiValueMap(
metadata.getAllAnnotationAttributes(ConditionalOnProperty.class.getName()));
List<ConditionMessage> noMatch = new ArrayList<>();
List<ConditionMessage> match = new ArrayList<>();
for (AnnotationAttributes annotationAttributes : allAnnotationAttributes) {
// 通过属性值,逐一判断配置信息中的信息是否满足 , context.getEnvironment() 能获取到所有的配置信息
ConditionOutcome outcome = determineOutcome(annotationAttributes, context.getEnvironment());
(outcome.isMatch() ? match : noMatch).add(outcome.getConditionMessage());
}
if (!noMatch.isEmpty()) {
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage.of(noMatch));
}
return ConditionOutcome.match(ConditionMessage.of(match));
}
private List<AnnotationAttributes> annotationAttributesFromMultiValueMap(
MultiValueMap<String, Object> multiValueMap) {
...
return annotationAttributes;
}
private ConditionOutcome determineOutcome(AnnotationAttributes annotationAttributes, PropertyResolver resolver) {
Spec spec = new Spec(annotationAttributes);
List<String> missingProperties = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonMatchingProperties = new ArrayList<>();
// 通过属性值,判断配置信息中的信息是否满足
spec.collectProperties(resolver, missingProperties, nonMatchingProperties);
if (!missingProperties.isEmpty()) {
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnProperty.class, spec)
.didNotFind("property", "properties").items(Style.QUOTE, missingProperties));
}
if (!nonMatchingProperties.isEmpty()) {
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnProperty.class, spec)
.found("different value in property", "different value in properties")
.items(Style.QUOTE, nonMatchingProperties));
}
return ConditionOutcome
.match(ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnProperty.class, spec).because("matched"));
}
private static class Spec {
private final String prefix;
private final String havingValue;
private final String[] names;
private final boolean matchIfMissing;
Spec(AnnotationAttributes annotationAttributes) {
...
}
private String[] getNames(Map<String, Object> annotationAttributes) {
...
}
private void collectProperties(PropertyResolver resolver, List<String> missing, List<String> nonMatching) {
for (String name : this.names) {
String key = this.prefix + name;
if (resolver.containsProperty(key)) {
// havingValue 默认为 ""
if (!isMatch(resolver.getProperty(key), this.havingValue)) {
nonMatching.add(name);
}
}
else {
if (!this.matchIfMissing) {
missing.add(name);
}
}
}
}
private boolean isMatch(String value, String requiredValue) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(requiredValue)) {
return requiredValue.equalsIgnoreCase(value);
}
// havingValue 默认为 "" ,因此只要对应的属性不为false,在注解中没填havingValue的情况下,都是会match上conditon,即都会被加载
return !"false".equalsIgnoreCase(value);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
...
}
}
}
用这种方式进行SpingBoot扩展的也特别多,SpingBoot自己的autoconfigure模块中有很多模块的增强用的也是这个注解。
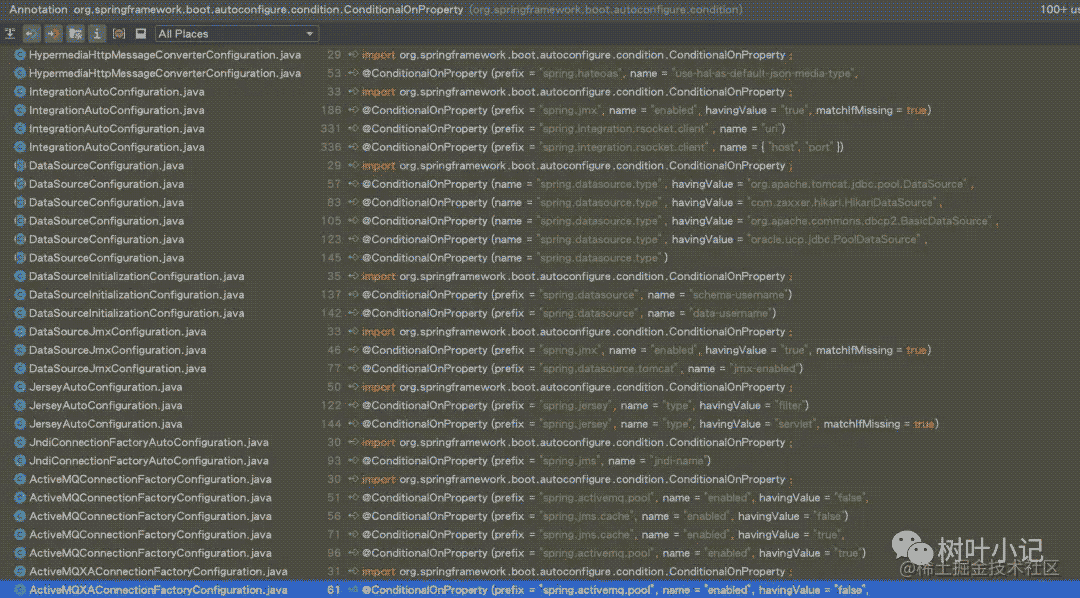
那他是在哪个环节进行的这个condition的判断呢?简单标注如下:
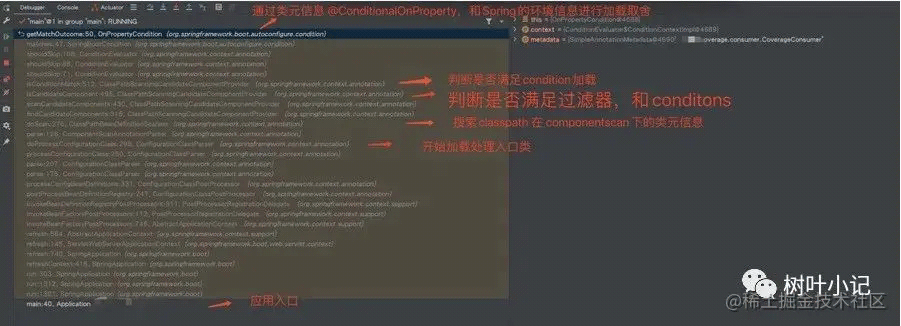
其中判断过滤的总入口:
// org.springframework.context.annotation.ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider
/**
* Determine whether the given class does not match any exclude filter
* and does match at least one include filter.
* @param metadataReader the ASM ClassReader for the class
* @return whether the class qualifies as a candidate component
*/
protected boolean isCandidateComponent(MetadataReader metadataReader) throws IOException {
for (TypeFilter tf : this.excludeFilters) {
if (tf.match(metadataReader, getMetadataReaderFactory())) {
return false;
}
}
for (TypeFilter tf : this.includeFilters) {
if (tf.match(metadataReader, getMetadataReaderFactory())) {
// conditons 相关的入口,
return isConditionMatch(metadataReader);
}
}
return false;
}
环顾整个流程,这里比较好的一点就是一旦条件过滤后,那就对类元文件里面的其他内容也不进行加载,像下面的@Value和@Bean的填充也不会进行,能优雅高效的解决掉当前的问题。
@Value("${coverage.aws.region}")
private String awsRegion;
@Value("${coverage.aws.access.key}")
private String accessKey;
@Value("${coverage.aws.secret.key}")
private String secretKey;
@Bean(name = "coverageSQSListenerFactory")
public DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory sqsListenerContainerFactory(){
return getDefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory(awsRegion, accessKey, secretKey);
}
故事的最后
做完这个改动以后,就提交了代码,妈妈再也不用担心因为其他人不小心使用某些只有一个实例的中间件导致数据污染了。用注解方式解决这个通过配置就能控制加载bean的这个能力确实很方便很Boot。比如中间件团队提供组件能力给团队,用condtion的这个特性也是能方便落地的。当然condition里面还有其他的一些特性,这里只是抛砖引玉,简单的梳理一下最近的一个使用场景。
以上就是SpringBoot用配置影响Bean加载@ConditionalOnProperty的详细内容,更多关于SpringBoot Bean加载@ConditionalOnProperty的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!

