如何使用@Value和@PropertySource注入外部资源
1、简介
在Spring Boot进行项目开发的过程中,肯定会有这样一种场景,比如说事件上报,在开发时开发人员可能会模拟在代码中写入一个事件上报Url,然后当部署到生产环境时,该url就需要从外部导入,一般通过修改配置文件的方式达到类似的目的。
在Spring开发中经常涉及调用各种资源的情况,包含普通文件,网址,配置文件,系统环境变量等,这种情况可以使用Spring EL-Spring表达式语言实现资源的注入。

2、实践
程序演示使用IDEA集成开发环境,演示@Value的使用,并通过注解@PropertySource可以注入自定义配置文件或者其他任意新建的文本文件。
注意:以下实践在Spring环境下是通用的,Spring Boot也是可用的的。
2.1项目结构
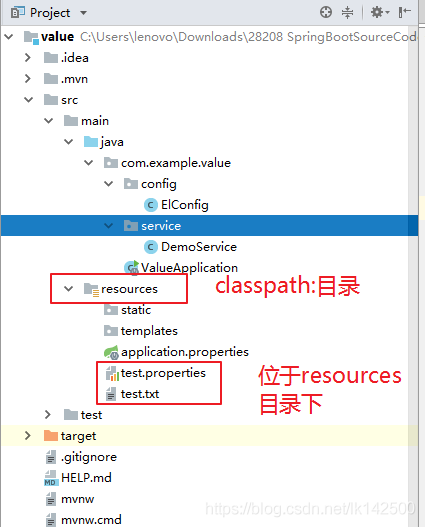
2.2 pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.3.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>value</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>value</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
其中
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.3</version>
</dependency>
依赖可以简化文件相关的操作,本例中使用commons-io将file转换成字符串。
2.3 DemoService
package com.example.value.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* 需被注入的类
*
* @Owner:
* @Time: 2019/3/31-12:35
*/
@Service
public class DemoService {
@Value("其他类的属性")
private String another;
public String getAnother() {
return another;
}
public void setAnother(String another) {
this.another = another;
}
}
其中在上类中使用@Value注解注入了普通字符串“其他类的属性。”
2.4 ElConfig 类
package com.example.value.config;
import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
/**
* 演示@Value的使用
*
* @Owner:
* @Time: 2019/3/31-12:32
*/
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.example.value.service") //扫包
@PropertySource("classpath:test.properties") //注意文件格式的指定
public class ElConfig {
@Value("I Love You!") //1 注入普通字符串
private String normal;
@Value("#{systemProperties['os.name']}") //2 注入操作系统属性
private String osName;
@Value("#{ T(java.lang.Math).random() * 100.0 }") //3 注入表达式结果
private double randomNumber;
@Value("#{demoService.another}") //4 注入其他Bean的属性
private String fromAnother;
@Value("classpath:test.txt") //5 注入了文件资源
private Resource testFile;
@Value("http://www.baidu.com") //6 注入网页资源
private Resource testUrl;
@Value("${book.name}") //7 注入classpath:test.properties中资源项,注意美元符号$
private String bookName;
@Autowired
private Environment environment; //7 属性也可以从environment中获取。
@Bean //7
public static PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer propertyConfigure() {
return new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer();
}
public void outputResource() {
try {
System.out.println(normal);
System.out.println(osName);
System.out.println(randomNumber);
System.out.println(fromAnother);
System.out.println(IOUtils.toString(testFile.getInputStream()));
System.out.println(IOUtils.toString(testUrl.getInputStream()));
System.out.println(bookName);
System.out.println(environment.getProperty("book.author"));
System.out.println(environment.getProperty("book.school"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
注意:注入配置配件使用@PropertySource指定文件地址,若使用@Value注入,则要配置一个PropertySourcePlaceholderConfigure的Bean
2.5 ValueApplication主类
package com.example.value;
import com.example.value.config.ElConfig;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ValueApplication {
@Autowired
private ElConfig config;
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ElConfig.class);
ElConfig resourceService = context.getBean(ElConfig.class);
resourceService.outputResource();
}
}
2.6 resources下两个文件的内容
2.6.1 test.txt
123334455 aaa bbb ccc
2.6.2 test.properties
book.author=sqh book.name=spring boot book.school=NJUST
3、控制台打印结果
I Love You! #直接注入字符串
Windows 8.1 #注入了系统属性
87.12913167952843 # 注入了表达式结果
其他类的属性 # 其他类的属性
123334455 # test.txt
aaa
bbb
ccc
<!DOCTYPE html> # 注入了网页内容
<!--STATUS OK--><html> <head><meta http-equiv=content-type content=text/html;charset=utf-8><meta http-equiv=X-UA-Compatible content=IE=Edge><meta content=always name=referrer><link rel=stylesheet type=text/css href=http://s1.bdstatic.com/r/www/cache/bdorz/baidu.min.css><title>百度一下,你就知道</title></head> <body link=#0000cc> <div id=wrapper> <div id=head> <div class=head_wrapper> <div class=s_form> <div class=s_form_wrapper> <div id=lg> <img hidefocus=true src=//www.baidu.com/img/bd_logo1.png width=270 height=129> </div> <form id=form name=f action=//www.baidu.com/s class=fm> <input type=hidden name=bdorz_come value=1> <input type=hidden name=ie value=utf-8> <input type=hidden name=f value=8> <input type=hidden name=rsv_bp value=1> <input type=hidden name=rsv_idx value=1> <input type=hidden name=tn value=baidu><span class="bg s_ipt_wr"><input id=kw name=wd class=s_ipt value maxlength=255 autocomplete=off autofocus></span><span class="bg s_btn_wr"><input type=submit id=su value=百度一下 class="bg s_btn"></span> </form> </div> </div> <div id=u1> <a href=http://news.baidu.com name=tj_trnews class=mnav>新闻</a> <a href=http://www.hao123.com name=tj_trhao123 class=mnav>hao123</a> <a href=http://map.baidu.com name=tj_trmap class=mnav>地图</a> <a href=http://v.baidu.com name=tj_trvideo class=mnav>视频</a> <a href=http://tieba.baidu.com name=tj_trtieba class=mnav>贴吧</a> <noscript> <a href=http://www.baidu.com/bdorz/login.gif?login&tpl=mn&u=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.baidu.com%2f%3fbdorz_come%3d1 name=tj_login class=lb>登录</a> </noscript> <script>document.write('<a href="http://www.baidu.com/bdorz/login.gif?login&tpl=mn&u='+ encodeURIComponent(window.location.href+ (window.location.search === "" ? "?" : "&")+ "bdorz_come=1")+ '" name="tj_login" class="lb">登录</a>');</script> <a href=//www.baidu.com/more/ name=tj_briicon class=bri style="display: block;">更多产品</a> </div> </div> </div> <div id=ftCon> <div id=ftConw> <p id=lh> <a href=http://home.baidu.com>关于百度</a> <a href=http://ir.baidu.com>About Baidu</a> </p> <p id=cp>©2017 Baidu <a href=http://www.baidu.com/duty/>使用百度前必读</a> <a href=http://jianyi.baidu.com/ class=cp-feedback>意见反馈</a> 京ICP证030173号 <img src=//www.baidu.com/img/gs.gif> </p> </div> </div> </div> </body> </html>spring boot # 配置文件中的三个值
sqh
NJUST
4、总结
通过上述的方式,也附带的阐述了在Spring Boot中不使用application.properties配置文件,而是用其他任意的配置文件来放入程序配置的使用方法,可以看到@Value很灵活,也很方便,作者暂时比较常用的就是在applicaiton.properties中放入类似book.name这样的配置项而使用@Value("${book.name}")直接注入的方式。
Spring的@PropertySource和@Value注解例子
在这篇文章中,我们会利用Spring的@PropertySource和@Value两个注解从配置文件properties中读取值,以及如何从配置文件中的值转换为List对象。
创建Spring配置Class
@Configurable
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.9leg.java.spring")
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:spring/config.properties")
public class AppConfigTest {
@Bean
public PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer propertyConfigInDev() {
return new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer();
}
}
通过@PropertySource注解将properties配置文件中的值存储到Spring的 Environment中,Environment接口提供方法去读取配置文件中的值,参数是properties文件中定义的key值。上面是读取一个配置文件,如果你想要读取多个配置文件,请看下面代码片段:
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:spring/config.properties","classpath:spring/news.properties"})
在Spring 4版本中,Spring提供了一个新的注解——@PropertySources,从名字就可以猜测到它是为多配置文件而准备的。
@PropertySources({
@PropertySource("classpath:config.properties"),
@PropertySource("classpath:db.properties")
})
public class AppConfig {
//something
}
另外在Spring 4版本中,@PropertySource允许忽略不存在的配置文件。先看下面的代码片段:
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:missing.properties")
public class AppConfig {
//something
}
如果missing.properties不存在或找不到,系统则会抛出异常FileNotFoundException。
Caused by: java.io.FileNotFoundException:
class path resource [missiong.properties] cannot be opened because it does not exist
幸好Spring 4为我们提供了ignoreResourceNotFound属性来忽略找不到的文件
@Configuration
@PropertySource(value="classpath:missing.properties", ignoreResourceNotFound=true)
public class AppConfig {
//something
}
@PropertySources({
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:missing.properties", ignoreResourceNotFound=true),
@PropertySource("classpath:config.properties")
})
最上面的AppConfigTest的配置代码等于如下的XML配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.9leg.java.spring"/>
<bean class="org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders" value="true"/>
<property name="locations">
<list>
<value>classpath:spring/config.properties</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
创建properties配置文件
server.name=9leg,spring server.id=10,11,12 server.jdbc=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
创建一个简单的服务
@Component(value = "mockConfigTest")
public class MockConfigTest {
@Value("#{'${server.name}'.split(',')}")
private List<String> servers;
@Value("#{'${server.id}'.split(',')}")
private List<Integer> serverId;
@Value("${server.host:127.0.0.1}")
private String noProKey;
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
public void readValues() {
System.out.println("Services Size : " + servers.size());
for(String s : servers)
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println("ServicesId Size : " + serverId.size());
for(Integer i : serverId)
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println("Server Host : " + noProKey);
String property = environment.getProperty("server.jdbc");
System.out.println("Server Jdbc : " + property);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfigTest.class);
MockConfigTest mockConfigTest = (MockConfigTest) annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("mockConfigTest");
mockConfigTest.readValues();
}
}
首先使用@Component注解声明,接着就是属性字段上的@Value注解,但在这里比较特殊,是通过split()方法,将配置文件中的9leg,spring分割后组成list对象。心细的同学可能注意到了server.host这个key并不存在配置文件中。是的,在这里使用的是默认值,即127.0.0.1,它的格式是这样的。
@value("${key:default}")
private String var;
然后注入了Environment,可以通过getProperty(key)来获取配置文件中的值。 运行main方法,来看下输出结果:
Services Size : 2
9leg
spring
ServicesId Size : 3
10
11
12
Server Host : 127.0.0.1
Server Jdbc : com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
最后要说一点,在main方法中请使用
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfigTest.class)
来代替
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“applicationContext.xml”)
或者
new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(“src/main/resources/applicationContext.xml”)
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

