R语言绘图时输出希腊字符上下标及数学公式实现方法
目录
- 希腊字母
- 上下标
- paste
- 一个复杂的例子
- 进阶
- 数学公式
通常在我们写论文时,所需要的统计图是非常严谨的,里面的希腊字符与上下脚标都必须要严格书写。因此在使用R绘图时,如何在我们目标图中使用希腊字符、上标、下标及一些数学公式呢?在本博客中我们会进行详细的说明。
后面我们都将以一个最简单的绘图为例,只是将其标题进行修改。
希腊字母
使用希腊字符、上标、下标及数学公式,都需要利用一个函数:expression(),具体使用方式如下:
plot(cars) title(main = expression(Sigma))
输出:

上下标
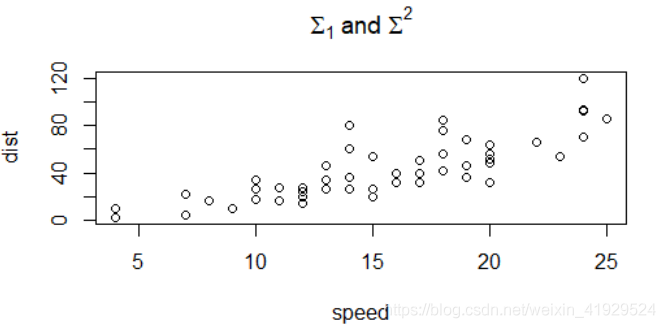
expression()中的下标为[],上标为^,空格为~,连接符为*。示例代码如下:
plot(cars) title(main = expression(Sigma[1]~'a'*'n'*'d'~Sigma^2))
输出:
paste
想达到上面的效果,我们其实可以使用paste()与expression()进行组合,不需要上述繁琐的过程,也能够达到我们上述一模一样的输出,并且方便快捷:
plot(cars) title(main = expression(paste(Sigma[1], ' and ', Sigma^2)))
一个复杂的例子
目标:
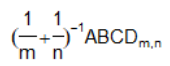
代码:
expression(paste((frac(1, m)+frac(1, n))^-1, ABCD[paste(m, ',', n)]))
进阶
在我们想批量产生大量含有不同变量值的标题时,如果遇到变量与公式的混合输出该如何操作,
可参考前文:R语言绘图公式与变量对象混合拼接实现方法
数学公式
最后的数学公式,只需要在expression()中进行相应的符号连接即可
具体要求可参考:Mathematical Annotation in R
鉴于其很不稳定,这里将里面的细节搬运过来。
(下表也可以直接在 R help 中搜索 plotmath 获取。)
| Syntax | Meaning |
|---|---|
| x + y | x plus y |
| x - y | x minus y |
| x*y | juxtapose x and y |
| x/y | x forwardslash y |
| x %±% y | x plus or minus y |
| x %/% y | x divided by y |
| x %*% y | x times y |
| x %.% y | x cdot y |
| x[i] | x subscript i |
| x^2 | x superscript 2 |
| paste(x, y, z) | juxtapose x, y, and z |
| sqrt(x) | square root of x |
| sqrt(x, y) | yth root of x |
| x == y | x equals y |
| x != y | x is not equal to y |
| x < y | x is less than y |
| x <= y | x is less than or equal to y |
| x > y | x is greater than y |
| x >= y | x is greater than or equal to y |
| !x | not x |
| x %~~% y | x is approximately equal to y |
| x %=~% y | x and y are congruent |
| x %==% y | x is defined as y |
| x %prop% y | x is proportional to y |
| x %~% y | x is distributed as y |
| plain(x) | draw x in normal font |
| bold(x) | draw x in bold font |
| italic(x) | draw x in italic font |
| bolditalic(x) | draw x in bolditalic font |
| symbol(x) | draw x in symbol font |
| list(x, y, z) | comma-separated list |
| … | ellipsis (height varies) |
| cdots | ellipsis (vertically centred) |
| ldots | ellipsis (at baseline) |
| x %subset% y | x is a proper subset of y |
| x %subseteq% y | x is a subset of y |
| x %notsubset% y | x is not a subset of y |
| x %supset% y | x is a proper superset of y |
| x %supseteq% y | x is a superset of y |
| x %in% y | x is an element of y |
| x %notin% y | x is not an element of y |
| hat(x) | x with a circumflex |
| tilde(x) | x with a tilde |
| dot(x) | x with a dot |
| ring(x) | x with a ring |
| bar(xy) | xy with bar |
| widehat(xy) | xy with a wide circumflex |
| widetilde(xy) | xy with a wide tilde |
| x %<->% y | x double-arrow y |
| x %->% y | x right-arrow y |
| x %<-% y | x left-arrow y |
| x %up% y | x up-arrow y |
| x %down% y | x down-arrow y |
| x %<=>% y | x is equivalent to y |
| x %=>% y | x implies y |
| x %<=% y | y implies x |
| x %dblup% y | x double-up-arrow y |
| x %dbldown% y | x double-down-arrow y |
| alpha – omega | Greek symbols |
| Alpha – Omega | uppercase Greek symbols |
| theta1, phi1, sigma1, omega1 | cursive Greek symbols |
| Upsilon1 | capital upsilon with hook |
| aleph | first letter of Hebrew alphabet |
| infinity | infinity symbol |
| partialdiff | partial differential symbol |
| nabla | nabla, gradient symbol |
| 32*degree | 32 degrees |
| 60*minute | 60 minutes of angle |
| 30*second | 30 seconds of angle |
| displaystyle(x) | draw x in normal size (extra spacing) |
| textstyle(x) | draw x in normal size |
| scriptstyle(x) | draw x in small size |
| scriptscriptstyle(x) | draw x in very small size |
| underline(x) | draw x underlined |
| x ~~ y | put extra space between x and y |
| x + phantom(0) + y | leave gap for “0”, but don't draw it |
| x + over(1, phantom(0)) | leave vertical gap for “0” (don't draw) |
| frac(x, y) | x over y |
| over(x, y) | x over y |
| atop(x, y) | x over y (no horizontal bar) |
| sum(x[i], i==1, n) | sum x[i] for i equals 1 to n |
| prod(plain§(X==x), x) | product of P(X=x) for all values of x |
| integral(f(x)*dx, a, b) | definite integral of f(x) wrt x |
| union(A[i], i==1, n) | union of A[i] for i equals 1 to n |
| intersect(A[i], i==1, n) | intersection of A[i] |
| lim(f(x), x %->% 0) | limit of f(x) as x tends to 0 |
| min(g(x), x > 0) | minimum of g(x) for x greater than 0 |
| inf(S) | infimum of S |
| sup(S) | supremum of S |
| x^y + z | normal operator precedence |
| x^(y + z) | visible grouping of operands |
| x^{y + z} | invisible grouping of operands |
| group("(",list(a, b),"]") | specify left and right delimiters |
| bgroup("(",atop(x,y),")") | use scalable delimiters |
| group(lceil, x, rceil) | special delimiters |
| group(lfloor, x, rfloor) | special delimiters |
以上就是R语言绘图时输出希腊字符上下标及数学公式实现方法的详细内容,更多关于R语言绘图输出希腊字符上下标及数学公式的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!
赞 (0)

