OpenCV Python身份证信息识别过程详解
目录
- 前置环境
- 识别过程
- 身份证区域查找
- 原始图像
- 灰度处理
- 中值滤波
- 二值处理
- 边缘检测
- 边缘膨胀
- 轮廓检测
- 轮廓排序
- 透视变换
- 固定图像大小
- 检测身份证文本位置
- 极度膨胀
- 轮廓查找文本区域
- 筛选出文本区域
- 对文本区域进行排序
- 识别文本
- 结语
- 代码
本篇文章使用OpenCV-Python和CnOcr来实现身份证信息识别的案例。想要识别身份证中的文本信息,总共分为三大步骤:一、通过预处理身份证区域检测查找;二、身份证文本信息提取;三、身份证文本信息识别。下面来看一下识别的具体过程CnOcr官网。识别过程视频
前置环境
这里的环境需要安装OpenCV-Python,Numpy和CnOcr。本篇文章使用的Python版本为3.6,OpenCV-Python版本为3.4.1.15,如果是4.x版本的同学,可能会有一些Api操作不同。这些依赖的安装和介绍,我就不在这里赘述了,均是使用Pip进行安装。
识别过程
首先,导入所需要的依赖cv2,numpy,cnocr并创建一个show图像的函数,方便后面使用:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from cnocr import CnOcr
def show(image, window_name):
cv2.namedWindow(window_name, 0)
cv2.imshow(window_name, image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# 加载CnOcr的模型
ocr = CnOcr(model_name='densenet_lite_136-gru')
身份证区域查找
通过对加载图像的灰度处理–>滤波处理–>二值处理–>边缘检测–>膨胀处理–>轮廓查找–>透视变换(校正)–>图像旋转–>固定图像大小一系列处理之后,我们便可以清晰的裁剪出身份证的具体区域。
原始图像
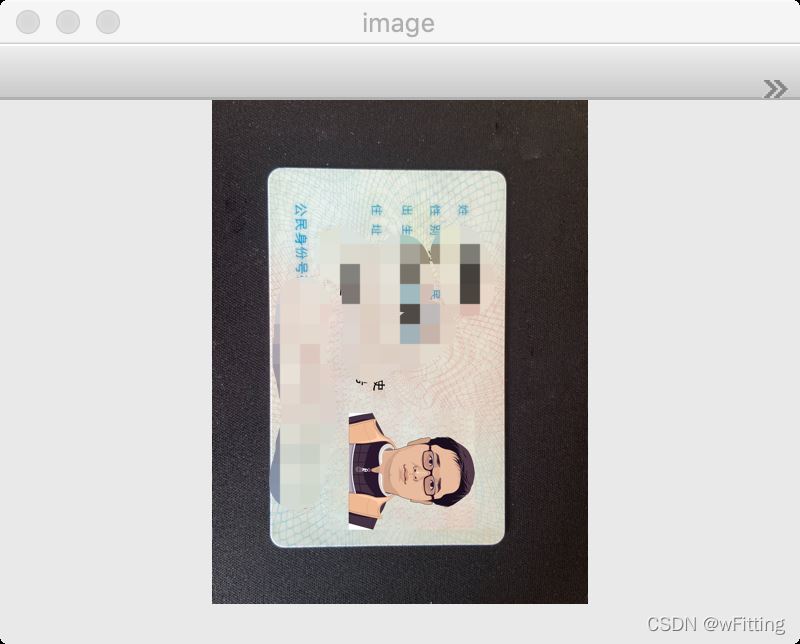
使用OpenCV的imread方法读取本地图片。
image = cv2.imread('card.png')
show(image, "image")

灰度处理
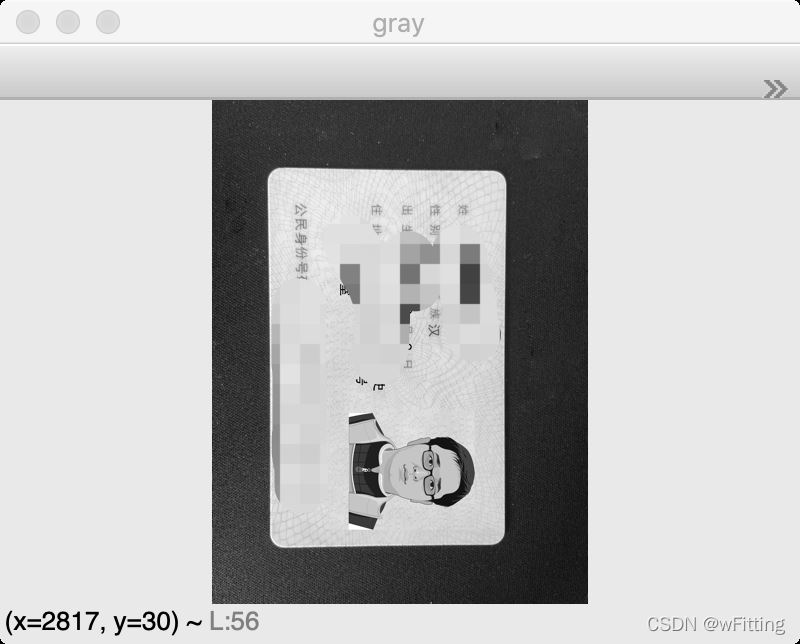
将三通道BGR图像转化为灰度图像,因为一下OpenCV操作都是需要基于灰度图像进行的。
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) show(gray, "gray")

中值滤波
使用滤波处理,也就是模糊处理,这样可以减少一些不需要的噪点。
blur = cv2.medianBlur(gray, 7) show(blur, "blur")

二值处理
二值处理,非黑即白。这里通过cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV + cv2.THRESH_OTSU,使用OpenCV的大津法二值化,对图像进行处理,经过处理后的图像,更加清晰的分辨出了背景和身份证的区域。
threshold = cv2.threshold(blur, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV + cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1] show(threshold, "threshold")

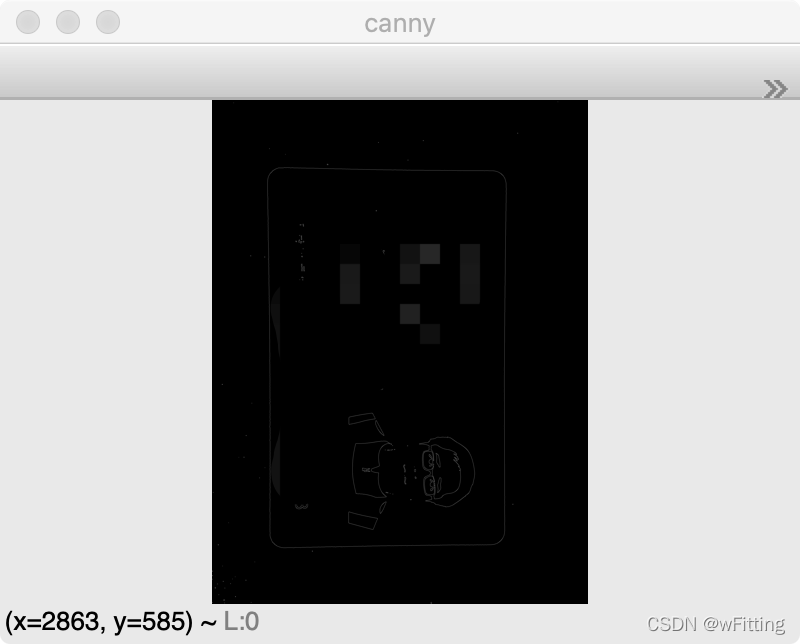
边缘检测
使用OpenCV中最常用的边缘检测方法,Canny,检测出图像中的边缘。
canny = cv2.Canny(threshold, 100, 150) show(canny, "canny")
边缘膨胀
为了使上一步边缘检测的边缘更加连贯,使用膨胀处理,对白色的边缘膨胀,即边缘线条变得更加粗一些。
kernel = np.ones((3, 3), np.uint8) dilate = cv2.dilate(canny, kernel, iterations=5) show(dilate, "dilate")

轮廓检测
使用findContours对边缘膨胀过的图片进行轮廓检测,可以清晰的看到背景部分还是有很多噪点的,所需要识别的身份证部分也被轮廓圈了起来。
binary, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(dilate, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) image_copy = image.copy() res = cv2.drawContours(image_copy, contours, -1, (255, 0, 0), 20) show(res, "res")

轮廓排序
经过对轮廓的面积排序,我们可以准确的提取出身份证的轮廓。
contours = sorted(contours, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse=True)[0] image_copy = image.copy() res = cv2.drawContours(image_copy, contours, -1, (255, 0, 0), 20) show(res, "contours")

透视变换
通过对轮廓近似提取出轮廓的四个顶点,并按顺序进行排序,之后通过warpPerspective对所选图像区域进行透视变换,也就是对所选的图像进行校正处理。
epsilon = 0.02 * cv2.arcLength(contours, True)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(contours, epsilon, True)
n = []
for x, y in zip(approx[:, 0, 0], approx[:, 0, 1]):
n.append((x, y))
n = sorted(n)
sort_point = []
n_point1 = n[:2]
n_point1.sort(key=lambda x: x[1])
sort_point.extend(n_point1)
n_point2 = n[2:4]
n_point2.sort(key=lambda x: x[1])
n_point2.reverse()
sort_point.extend(n_point2)
p1 = np.array(sort_point, dtype=np.float32)
h = sort_point[1][1] - sort_point[0][1]
w = sort_point[2][0] - sort_point[1][0]
pts2 = np.array([[0, 0], [0, h], [w, h], [w, 0]], dtype=np.float32)
# 生成变换矩阵
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(p1, pts2)
# 进行透视变换
dst = cv2.warpPerspective(image, M, (w, h))
# print(dst.shape)
show(dst, "dst")

固定图像大小
将图像变正,通过对图像的宽高进行判断,如果宽<高,就将图像旋转90°。并将图像resize到指定大小。方便之后对图像进行处理。
if w < h:
dst = np.rot90(dst)
resize = cv2.resize(dst, (1084, 669), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
show(resize, "resize")

检测身份证文本位置
经过灰度,二值滤波和开闭运算后,将图像中的文本区域主键显现出来。
temp_image = resize.copy() gray = cv2.cvtColor(resize, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) show(gray, "gray") threshold = cv2.threshold(gray, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV + cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1] show(threshold, "threshold") blur = cv2.medianBlur(threshold, 5) show(blur, "blur") kernel = np.ones((3, 3), np.uint8) morph_open = cv2.morphologyEx(blur, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel) show(morph_open, "morph_open")

极度膨胀
给定一个比较大的卷积盒,进行膨胀处理,使白色的区域加深加大。更加显现出文本的区域。
kernel = np.ones((7, 7), np.uint8) dilate = cv2.dilate(morph_open, kernel, iterations=6) show(dilate, "dilate")

轮廓查找文本区域
使用轮廓查找,将白色块状区域查找出来。
binary, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(dilate, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) resize_copy = resize.copy() res = cv2.drawContours(resize_copy, contours, -1, (255, 0, 0), 2) show(res, "res")

筛选出文本区域
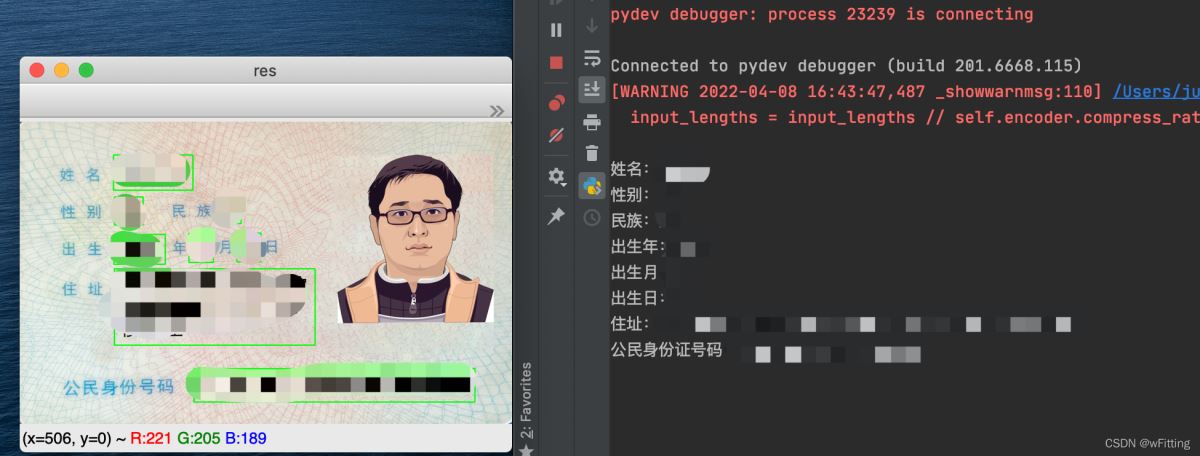
经过上一步轮廓检测,我们发现,选中的轮廓中有一些噪点,通过对图像的观察,使用近似轮廓,然后用以下逻辑筛选出文本区域。并定义文本描述信息,将文本区域位置信息加入到指定集合中。到这一步,可以清晰的看到,所需要的文本区域统统都被提取了出来。
labels = ['姓名', '性别', '民族', '出生年', '出生月', '出生日', '住址', '公民身份证号码']
positions = []
data_areas = {}
resize_copy = resize.copy()
for contour in contours:
epsilon = 0.002 * cv2.arcLength(contour, True)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(contour, epsilon, True)
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(approx)
if h > 50 and x < 670:
res = cv2.rectangle(resize_copy, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
area = gray[y:(y + h), x:(x + w)]
blur = cv2.medianBlur(area, 3)
data_area = cv2.threshold(blur, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV + cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
positions.append((x, y))
data_areas['{}-{}'.format(x, y)] = data_area
show(res, "res")

对文本区域进行排序
发现文本的区域是由下到上的顺序,并且x轴从左到右的的区域是无序的,所以使用以下逻辑,对文本区域进行排序
positions.sort(key=lambda p: p[1])
result = []
index = 0
while index < len(positions) - 1:
if positions[index + 1][1] - positions[index][1] < 10:
temp_list = [positions[index + 1], positions[index]]
for i in range(index + 1, len(positions)):
if positions[i + 1][1] - positions[i][1] < 10:
temp_list.append(positions[i + 1])
else:
break
temp_list.sort(key=lambda p: p[0])
positions[index:(index + len(temp_list))] = temp_list
index = index + len(temp_list) - 1
else:
index += 1
识别文本
对文本区域使用CnOcr一一进行识别,最后将识别结果进行输出。
positions.sort(key=lambda p: p[1])
result = []
index = 0
while index < len(positions) - 1:
if positions[index + 1][1] - positions[index][1] < 10:
temp_list = [positions[index + 1], positions[index]]
for i in range(index + 1, len(positions)):
if positions[i + 1][1] - positions[i][1] < 10:
temp_list.append(positions[i + 1])
else:
break
temp_list.sort(key=lambda p: p[0])
positions[index:(index + len(temp_list))] = temp_list
index = index + len(temp_list) - 1
else:
index += 1
结语
通过以上的步骤,便成功的将身份证信息进行了提取,过程中的一些数字参数,可能会在不同的场景中有些许的调整。
以下放上所有的代码:
代码
import cv2
import numpy as np
from cnocr import CnOcr
def show(image, window_name):
cv2.namedWindow(window_name, 0)
cv2.imshow(window_name, image)
# 0任意键终止窗口
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
ocr = CnOcr(model_name='densenet_lite_136-gru')
image = cv2.imread('card.png')
show(image, "image")
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
show(gray, "gray")
blur = cv2.medianBlur(gray, 7)
show(blur, "blur")
threshold = cv2.threshold(blur, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV + cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
show(threshold, "threshold")
canny = cv2.Canny(threshold, 100, 150)
show(canny, "canny")
kernel = np.ones((3, 3), np.uint8)
dilate = cv2.dilate(canny, kernel, iterations=5)
show(dilate, "dilate")
binary, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(dilate, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
image_copy = image.copy()
res = cv2.drawContours(image_copy, contours, -1, (255, 0, 0), 20)
show(res, "res")
contours = sorted(contours, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse=True)[0]
image_copy = image.copy()
res = cv2.drawContours(image_copy, contours, -1, (255, 0, 0), 20)
show(res, "contours")
epsilon = 0.02 * cv2.arcLength(contours, True)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(contours, epsilon, True)
n = []
for x, y in zip(approx[:, 0, 0], approx[:, 0, 1]):
n.append((x, y))
n = sorted(n)
sort_point = []
n_point1 = n[:2]
n_point1.sort(key=lambda x: x[1])
sort_point.extend(n_point1)
n_point2 = n[2:4]
n_point2.sort(key=lambda x: x[1])
n_point2.reverse()
sort_point.extend(n_point2)
p1 = np.array(sort_point, dtype=np.float32)
h = sort_point[1][1] - sort_point[0][1]
w = sort_point[2][0] - sort_point[1][0]
pts2 = np.array([[0, 0], [0, h], [w, h], [w, 0]], dtype=np.float32)
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(p1, pts2)
dst = cv2.warpPerspective(image, M, (w, h))
# print(dst.shape)
show(dst, "dst")
if w < h:
dst = np.rot90(dst)
resize = cv2.resize(dst, (1084, 669), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
show(resize, "resize")
temp_image = resize.copy()
gray = cv2.cvtColor(resize, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
show(gray, "gray")
threshold = cv2.threshold(gray, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV + cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
show(threshold, "threshold")
blur = cv2.medianBlur(threshold, 5)
show(blur, "blur")
kernel = np.ones((3, 3), np.uint8)
morph_open = cv2.morphologyEx(blur, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel)
show(morph_open, "morph_open")
kernel = np.ones((7, 7), np.uint8)
dilate = cv2.dilate(morph_open, kernel, iterations=6)
show(dilate, "dilate")
binary, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(dilate, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
resize_copy = resize.copy()
res = cv2.drawContours(resize_copy, contours, -1, (255, 0, 0), 2)
show(res, "res")
labels = ['姓名', '性别', '民族', '出生年', '出生月', '出生日', '住址', '公民身份证号码']
positions = []
data_areas = {}
resize_copy = resize.copy()
for contour in contours:
epsilon = 0.002 * cv2.arcLength(contour, True)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(contour, epsilon, True)
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(approx)
if h > 50 and x < 670:
res = cv2.rectangle(resize_copy, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
area = gray[y:(y + h), x:(x + w)]
blur = cv2.medianBlur(area, 3)
data_area = cv2.threshold(blur, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV + cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
positions.append((x, y))
data_areas['{}-{}'.format(x, y)] = data_area
show(res, "res")
positions.sort(key=lambda p: p[1])
result = []
index = 0
while index < len(positions) - 1:
if positions[index + 1][1] - positions[index][1] < 10:
temp_list = [positions[index + 1], positions[index]]
for i in range(index + 1, len(positions)):
if positions[i + 1][1] - positions[i][1] < 10:
temp_list.append(positions[i + 1])
else:
break
temp_list.sort(key=lambda p: p[0])
positions[index:(index + len(temp_list))] = temp_list
index = index + len(temp_list) - 1
else:
index += 1
for index in range(len(positions)):
position = positions[index]
data_area = data_areas['{}-{}'.format(position[0], position[1])]
ocr_data = ocr.ocr(data_area)
ocr_result = ''.join([''.join(result[0]) for result in ocr_data]).replace(' ', '')
# print('{}:{}'.format(labels[index], ocr_result))
result.append('{}:{}'.format(labels[index], ocr_result))
show(data_area, "data_area")
for item in result:
print(item)
show(res, "res")
到此这篇关于OpenCV Python身份证信息识别的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python身份证信息识别内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

