SpringBoot整合ip2region实现使用ip监控用户访问城市的详细过程
目录
- 举个栗子
- 快速上手
- 第一步,将整个项目down下来,找到data目录,进入
- 第二步,创建maven项目,引入依赖
- 第三步,编写测试类
- 项目实现
- 1、思路分析
- 2、配置文件
- SpringBoot项目pom.xml文件
- 3、项目代码
- 项目结构
- SpringbootIpApplication.java
- TestController.java
- Ip.java
- IpAspect.java
- AddressUtil.java
- HttpContextUtil.java
- IPUtil.java
- 打印结果
举个栗子
最近,多平台都上线了展示近期发帖所在地功能,比如抖音、微博、百度,像下面那样:


那么这个功能都是如何实现的呢?
一般有两个方法:GPS 定位的信息和用户 IP 地址。
由于每个手机都不一定会打开 GPS,而且有时并不太需要太精确的位置(到城市这个级别即可),所以根据 IP 地址入手来分析用户位置是个不错的选择。
所以ip2region框架应运而生,GitHub上️已经10.6K,值得一用。
GitHub地址:github.com/lionsoul201…
快速上手
第一步,将整个项目down下来,找到data目录,进入
这里有三份ip地址库,我们将ip2region.xdb复制出来,等下我们的java项目中需要使用到。
第二步,创建maven项目,引入依赖
pom.xml依赖如下:
<!-- ip2region -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.lionsoul</groupId>
<artifactId>ip2region</artifactId>
<version>2.6.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 用于读取ip2region.xdb文件使用 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.6</version>
</dependency>
加好依赖后,在resources目录下创建ip2region文件夹,把上面的ip2region.xdb文件放进去。
第三步,编写测试类
package com.example.springbootip.util;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import org.lionsoul.ip2region.xdb.Searcher;
import java.io.File;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
import java.util.Objects;
public class AddressUtil {
/**
* 当前记录地址的本地DB
*/
private static final String TEMP_FILE_DIR = "/home/admin/app/";
/**
* 根据IP地址查询登录来源
*
* @param ip
* @return
*/
public static String getCityInfo(String ip) {
try {
// 获取当前记录地址位置的文件
String dbPath = Objects.requireNonNull(AddressUtil.class.getResource("/ip2region/ip2region.xdb")).getPath();
File file = new File(dbPath);
//如果当前文件不存在,则从缓存中复制一份
if (!file.exists()) {
dbPath = TEMP_FILE_DIR + "ip.db";
System.out.println(MessageFormat.format("当前目录为:[{0}]", dbPath));
file = new File(dbPath);
FileUtils.copyInputStreamToFile(Objects.requireNonNull(AddressUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("classpath:ip2region/ip2region.xdb")), file);
}
//创建查询对象
Searcher searcher = Searcher.newWithFileOnly(dbPath);
//开始查询
return searcher.searchByStr(ip);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//默认返回空字符串
return "";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(getCityInfo("1.2.3.4"));
}
}
输出结果如下:

项目实现
1、思路分析
通过上面简单的例子我们已经可以通过ip获取地域了,那么接下来将实现如何监控Controller接口的访问地址。
首先,在一个项目中肯定有很多接口,所以我们不能直接在接口中写代码的方式去实现,这样代码复杂度、耦合度太高。所以我打算在这里使用注解切面的方式实现,只需要在接口方法上加上 @Ip 注解就可以实现。不知道切面是什么的同学可以参考这篇文章:SpringBoot整合aspectj实现面向切面编程(即AOP)
其次,有些项目中会使用Nginx等反向代理软件,则不能通过 request.getRemoteAddr()获取 IP地址,如果使用了多级反向代理的话,X-Forwarded-For的值并不止一个,而是一串IP地址,X-Forwarded-For中第一个非 unknown的有效IP字符串,则为真实IP地址。
最后,让我们来实现这个功能吧!
2、配置文件
SpringBoot项目pom.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.1</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-ip</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springboot-ip</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- ip2region -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.lionsoul</groupId>
<artifactId>ip2region</artifactId>
<version>2.6.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- aop切面 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
3、项目代码
项目结构

SpringbootIpApplication.java
package com.example.springbootip;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootIpApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootIpApplication.class, args);
}
}
TestController.java
package com.example.springbootip.controller;
import com.example.springbootip.ip2region.Ip;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
@Ip
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
}
Ip.java
package com.example.springbootip.ip2region;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Ip {
}
IpAspect.java
package com.example.springbootip.ip2region;
import com.example.springbootip.util.AddressUtil;
import com.example.springbootip.util.HttpContextUtil;
import com.example.springbootip.util.IPUtil;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
@Aspect
@Component
public class IpAspect {
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.example.springbootip.ip2region.Ip)")
public void pointcut() {
// do nothing
}
@Around("pointcut()")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {
HttpServletRequest request = HttpContextUtil.getHttpServletRequest();
String ip = IPUtil.getIpAddr(request);
System.out.println(MessageFormat.format("当前IP为:[{0}];当前IP地址解析出来的地址为:[{1}]", ip, AddressUtil.getCityInfo(ip)));
return point.proceed();
}
}
AddressUtil.java
package com.example.springbootip.util;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import org.lionsoul.ip2region.xdb.Searcher;
import java.io.File;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
import java.util.Objects;
public class AddressUtil {
/**
* 当前记录地址的本地DB
*/
private static final String TEMP_FILE_DIR = "/home/admin/app/";
/**
* 根据IP地址查询登录来源
*
* @param ip
* @return
*/
public static String getCityInfo(String ip) {
try {
// 获取当前记录地址位置的文件
String dbPath = Objects.requireNonNull(AddressUtil.class.getResource("/ip2region/ip2region.xdb")).getPath();
File file = new File(dbPath);
//如果当前文件不存在,则从缓存中复制一份
if (!file.exists()) {
dbPath = TEMP_FILE_DIR + "ip.db";
System.out.println(MessageFormat.format("当前目录为:[{0}]", dbPath));
file = new File(dbPath);
FileUtils.copyInputStreamToFile(Objects.requireNonNull(AddressUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("classpath:ip2region/ip2region.xdb")), file);
}
//创建查询对象
Searcher searcher = Searcher.newWithFileOnly(dbPath);
//开始查询
return searcher.searchByStr(ip);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//默认返回空字符串
return "";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(getCityInfo("1.2.3.4"));
}
}
HttpContextUtil.java
package com.example.springbootip.util;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* @desc 全局获取HttpServletRequest、HttpServletResponse
*/
public class HttpContextUtil {
private HttpContextUtil() {
}
public static HttpServletRequest getHttpServletRequest() {
return ((ServletRequestAttributes) Objects.requireNonNull(RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes())).getRequest();
}
public static HttpServletResponse getHttpServletResponse() {
return ((ServletRequestAttributes) Objects.requireNonNull(RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes())).getResponse();
}
}
IPUtil.java
package com.example.springbootip.util;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
/**
* @desc 查询当前访问的IP地址
*/
public class IPUtil {
private static final String UNKNOWN = "unknown";
protected IPUtil() {
}
/**
* 获取 IP地址
* 使用 Nginx等反向代理软件, 则不能通过 request.getRemoteAddr()获取 IP地址
* 如果使用了多级反向代理的话,X-Forwarded-For的值并不止一个,而是一串IP地址,
* X-Forwarded-For中第一个非 unknown的有效IP字符串,则为真实IP地址
*/
public static String getIpAddr(HttpServletRequest request) {
String ip = request.getHeader("x-forwarded-for");
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || UNKNOWN.equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getHeader("Proxy-Client-IP");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || UNKNOWN.equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getHeader("WL-Proxy-Client-IP");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || UNKNOWN.equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getRemoteAddr();
}
return "0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1".equals(ip) ? "127.0.0.1" : ip;
}
}
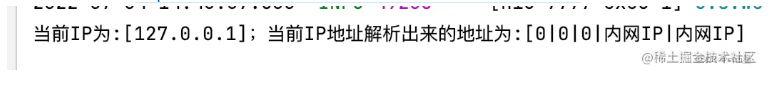
打印结果
由于访问路径是:http://127.0.0.1:8080/test/hello,所以本地解析出来的是内网
到此这篇关于SpringBoot整合ip2region实现使用ip监控用户访问城市的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot整合ip2region内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

