详解spring boot rest例子
简介:本文将帮助您使用 Spring Boot 创建简单的 REST 服务。
你将学习
- 什么是 REST 服务?
- 如何使用 Spring Initializr 引导创建 Rest 服务应用程序?
- 如何创建获取 REST 服务以检索学生注册的课程?
- 如何为学生注册课程创建 Post REST 服务?
- 如何利用 postman 执行 rest 服务?
本教程使用的 rest 服务
在本教程中,我们将使用适当的 URI 和 HTTP 方法创建三个服务:
@GetMapping(“/ students / {studentId} / courses”):您可以使用请求方法 Get 和示例 uri / students / Student1 / courses 来查询特定学生已注册的课程。
@GetMapping(“/students/{studentId}/courses/{courseId}”):您可以使用请求方法 Get 和示例 uri / students / Student1 / courses / Course1 获取特定学生的特定课程。
@PostMapping(“/students/{studentId}/courses”) :您可以通过向 UURI /students/Student1/courses 发送 POST 请求来为学生注册一门课程
您将需要的工具
- Maven 3.0+ 是您的构建工具
- 你最喜欢的 IDE。我们使用 Eclipse。
- JDK 1.8+
完整的 spring booot rest Maven 项目代码示例子
我们的 Github 存储库包含所有代码示例 - https://github.com/in28minutes/in28minutes.github.io/tree/master/code-zip-files
带有单元和集成测试的 REST 服务
Website-springbootrestservices-simplerestserviceswithunitandintegrationtests.zip
什么是 REST?
REST 代表 REpresentational State Transfer。REST 指定了一组体系结构约束。任何满足以下这些条件的服务都称为 RESTful 服务。
RESTful Web Service 的五个重要条件:
- 客户端 - 服务器:应该有一个服务生产者和一个服务使用者。
- 接口(URL)是统一的并且暴露资源。
- 该服务是无状态的。
- 服务结果应该是可缓存的。例如 HTTP 缓存。
- 服务应该采用分层架构。客户端不应该直接连接到服务器 - 它可能从中间层获取信息 - 缓存。
理查森成熟度模型
Richardson 成熟度模型用于识别 Restful Web Service 的成熟度级别。以下是不同级别和特点:
级别 0:以 REST 风格公开 SOAP Web 服务。公开的操作使用 REST 服务(http:// server / getPosts,http:// server / deletePosts,http:// server / doThis,http:// server / doThat 等)。
级别 1:使用正确的 URI(使用名词)公开资源。例如:http:// server / accounts,http:// server / accounts / 10。但是,HTTP 方法并未使用。
级别 2:资源使用正确的 URI + HTTP 方法。例如,要更新一个账户,你需要做一个 PUT。创建一个帐户,你做一个 POST。Uri 看起来像 posts/1/comments/5 和 accounts/1/friends/1.
等级 3:HATEOAS (Hypermedia as the engine of application state)。您不仅可以了解所请求的信息,还可以了解服务消费者可以采取的下一个可能的操作。当请求有关 Facebook 用户的信息时,REST 服务可以返回用户详细信息以及有关如何获取他最近的帖子,如何获取他最近的评论以及如何检索他朋友的列表的信息。
使用适当的请求方法
始终使用 HTTP 方法。有关每种 HTTP 方法的最佳做法如下所述:
GET:不应该更新任何东西。应该是幂等的(多次调用相同的结果)。可能的返回码 200(OK)+ 404(NOT FOUND)+400(BAD REQUEST)
POST:应该创建新的资源。理想情况下返回 JSON 和链接到新创建的资源。尽可能使用相同的返回码。另外:返回码 201(创建)是可能的。
PUT:更新已知资源。例如:更新客户详细信息。可能的返回码:200(OK)
DELETE:用于删除资源。
项目结构
以下屏幕截图显示了我们将创建的项目的结构。

一些细节:
- StudentController.java - rest 控制器提供上面讨论的所有三种服务方法。
- Course.java, Student.java, StudentService.java - 应用程序的业务逻辑。StudentService 提供了一些我们从 Rest 控制器中消耗的方法。
- StudentControllerIT.java - rest 服务的集成测试。
- StudentControllerTest.java - test 服务的单元测试。
- StudentServicesApplication.java - Spring Boot 应用程序的启动器。要运行该应用程序,只需将该文件作为 Java 应用程序启动。
- pom.xml - 包含构建此项目所需的所有依赖。我们将使用 Spring Boot Starter Web。
使用 Spring Initializr 引导创建 REST 服务
用 Spring Initializr 创建一个 REST 服务是非常的容易小菜一碟。我们将使用 Spring Web MVC 作为我们的 web 层框架。
Spring Initializr http://start.spring.io/ 是引导创建 Spring Boot 项目的好工具。
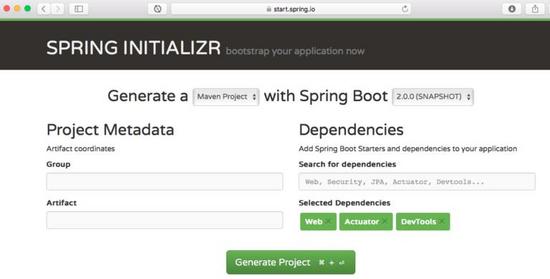
如上图所示,必须执行以下步骤
启动 Spring Initializr 并选择以下内容
选择 com.in28minutes.springboot 为 Group
选择 student-services 为 Artifact
选择以下依赖项
- Web
- Actuator
- DevTools
点击生成项目。
将项目导入 Eclipse。文件 - > 导入 - > 现有的 Maven 项目。
如果你想了解这个项目的所有文件,你可以继续向下阅读。
应用业务层实现
所有应用都需要数据。我们将使用 ArrayList 这种内存数据存储,而不是与真实数据库交互。
一名学生可以参加多门课程。课程有一个 ID,名称,说明和完成课程需要完成的步骤列表。学生有一个身份证,姓名,说明和他 / 她目前注册的课程列表。StudentService 提供以下公开方法
public List retrieveAllStudents() - 检索所有学生的详细信息
public Student retrieveStudent(String studentId) - 检索特定的学生详细信息
public List retrieveCourses(String studentId) - 检索学生注册的所有课程
public Course retrieveCourse(String studentId, String courseId) - 检索学生注册的特定课程的详细信息
public Course addCourse(String studentId, Course course) - 为现有学生添加课程
请参阅下面这些文件,具体的实现服务类 StudentService 和模型类 Course 和 Student。
- src/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/model/Course.java
- src/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/model/Student.java
- src/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/service/StudentService.java
添加几个 GET Rest 服务
Rest 服务 StudentController 暴露了几个 get 服务。
- @Autowired private StudentService studentService :我们使用 Spring Autowiring 将 student 服务自动注入到 StudentController。
- @GetMapping(“/students/{studentId}/courses”):以 studentId 作为路径变量公开获取服务
- @GetMapping(“/students/{studentId}/courses/{courseId}”):公开获取服务以检索学生的特定课程。
- @PathVariable String studentId:来自 uri 的 studentId 的值将映射到此参数。
package com.in28minutes.springboot.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.in28minutes.springboot.model.Course;
import com.in28minutes.springboot.service.StudentService;
@RestController
public class StudentController {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@GetMapping("/students/{studentId}/courses")
public List<Course> retrieveCoursesForStudent(@PathVariable String studentId) {
return studentService.retrieveCourses(studentId);
}
@GetMapping("/students/{studentId}/courses/{courseId}")
public Course retrieveDetailsForCourse(@PathVariable String studentId,
@PathVariable String courseId) {
return studentService.retrieveCourse(studentId, courseId);
}
}
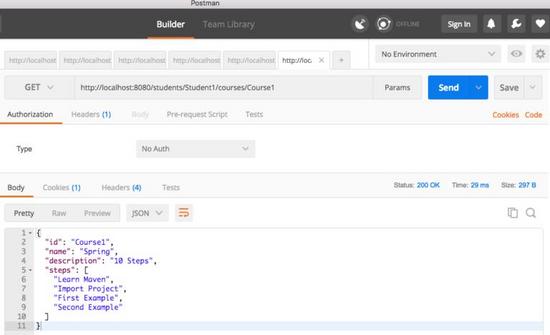
使用 Postman 执行获取服务
我们将向 http:// localhost:8080 / students / Student1 / courses / Course1 发起请求以测试该服务。回应如下所示。
{
"id": "Course1",
"name": "Spring",
"description": "10 Steps",
"steps": [
"Learn Maven",
"Import Project",
"First Example",
"Second Example"
]
}
下面的图片显示了我们如何执行 Postman 的 Get Service - 我最喜欢的运行 rest 服务的工具。
添加 POST Rest 服务
当资源创建成功时,POST 服务应该返回创建的状态(201)。
- @PostMapping(“/students/{studentId}/courses”):为 POST 请求映射 URL
- @RequestBody Course newCourse:使用绑定将请求正文绑定到课程对象。
- ResponseEntity.created(location).build():返回已创建的状态。还将创建资源的位置作为响应标题返回。
@PostMapping("/students/{studentId}/courses")
public ResponseEntity<Void> registerStudentForCourse(
@PathVariable String studentId, @RequestBody Course newCourse) {
Course course = studentService.addCourse(studentId, newCourse);
if (course == null)
return ResponseEntity.noContent().build();
URI location = ServletUriComponentsBuilder.fromCurrentRequest().path(
"/{id}").buildAndExpand(course.getId()).toUri();
return ResponseEntity.created(location).build();
}
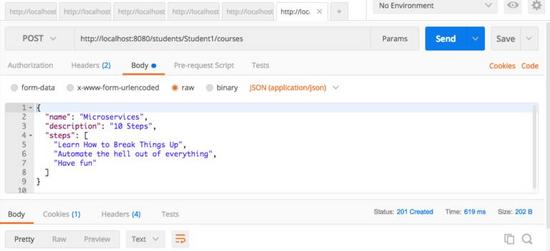
执行 POST Rest 服务
示例请求如下所示。它包含了学生注册课程的所有细节。
{
"name": "Microservices",
"description": "10 Steps",
"steps": [
"Learn How to Break Things Up",
"Automate the hell out of everything",
"Have fun"
]
}
下图显示了我们如何从 Postman 执行 Post 服务 - 我最喜欢的运行 rest 服务的工具。确保你去 Body 选项卡并选择 raw。从下拉菜单中选择 JSON。将上述请求复制到 body 中。
我们使用的 URL 是 http:// localhost:8080 / students / Student1 / courses。
完整的代码示例
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.in28minutes.springboot</groupId> <artifactId>student-services</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>student-services</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.4.4.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
src/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/controller/StudentController.java
import java.net.URI;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.ServletUriComponentsBuilder;
import com.in28minutes.springboot.model.Course;
import com.in28minutes.springboot.service.StudentService;
@RestController
public class StudentController {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@GetMapping("/students/{studentId}/courses")
public List<Course> retrieveCoursesForStudent(@PathVariable String studentId) {
return studentService.retrieveCourses(studentId);
}
@GetMapping("/students/{studentId}/courses/{courseId}")
public Course retrieveDetailsForCourse(@PathVariable String studentId,
@PathVariable String courseId) {
return studentService.retrieveCourse(studentId, courseId);
}
@PostMapping("/students/{studentId}/courses")
public ResponseEntity<Void> registerStudentForCourse(
@PathVariable String studentId, @RequestBody Course newCourse) {
Course course = studentService.addCourse(studentId, newCourse);
if (course == null)
return ResponseEntity.noContent().build();
URI location = ServletUriComponentsBuilder.fromCurrentRequest().path(
"/{id}").buildAndExpand(course.getId()).toUri();
return ResponseEntity.created(location).build();
}
}
src/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/model/Course.java
import java.util.List;
public class Course {
private String id;
private String name;
private String description;
private List<String> steps;
// Needed by Caused by: com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonMappingException:
// Can not construct instance of com.in28minutes.springboot.model.Course:
// no suitable constructor found, can not deserialize from Object value
// (missing default constructor or creator, or perhaps need to add/enable
// type information?)
public Course() {
}
public Course(String id, String name, String description, List<String> steps) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
this.steps = steps;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public List<String> getSteps() {
return steps;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format(
"Course [id=%s, name=%s, description=%s, steps=%s]", id, name,
description, steps);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((id == null) ? 0 : id.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Course other = (Course) obj;
if (id == null) {
if (other.id != null)
return false;
} else if (!id.equals(other.id))
return false;
return true;
}
}
src/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/model/Student.java
package com.in28minutes.springboot.model;
import java.util.List;
public class Student {
private String id;
private String name;
private String description;
private List<Course> courses;
public Student(String id, String name, String description,
List<Course> courses) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
this.courses = courses;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public List<Course> getCourses() {
return courses;
}
public void setCourses(List<Course> courses) {
this.courses = courses;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format(
"Student [id=%s, name=%s, description=%s, courses=%s]", id,
name, description, courses);
}
}
src/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/service/StudentService.java
package com.in28minutes.springboot.service;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.security.SecureRandom;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.in28minutes.springboot.model.Course;
import com.in28minutes.springboot.model.Student;
@Component
public class StudentService {
private static List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
static {
//Initialize Data
Course course1 = new Course("Course1", "Spring", "10 Steps", Arrays
.asList("Learn Maven", "Import Project", "First Example",
"Second Example"));
Course course2 = new Course("Course2", "Spring MVC", "10 Examples",
Arrays.asList("Learn Maven", "Import Project", "First Example",
"Second Example"));
Course course3 = new Course("Course3", "Spring Boot", "6K Students",
Arrays.asList("Learn Maven", "Learn Spring",
"Learn Spring MVC", "First Example", "Second Example"));
Course course4 = new Course("Course4", "Maven",
"Most popular maven course on internet!", Arrays.asList(
"Pom.xml", "Build Life Cycle", "Parent POM",
"Importing into Eclipse"));
Student ranga = new Student("Student1", "Ranga Karanam",
"Hiker, Programmer and Architect", new ArrayList<>(Arrays
.asList(course1, course2, course3, course4)));
Student satish = new Student("Student2", "Satish T",
"Hiker, Programmer and Architect", new ArrayList<>(Arrays
.asList(course1, course2, course3, course4)));
students.add(ranga);
students.add(satish);
}
public List<Student> retrieveAllStudents() {
return students;
}
public Student retrieveStudent(String studentId) {
for (Student student : students) {
if (student.getId().equals(studentId)) {
return student;
}
}
return null;
}
public List<Course> retrieveCourses(String studentId) {
Student student = retrieveStudent(studentId);
if (student == null) {
return null;
}
return student.getCourses();
}
public Course retrieveCourse(String studentId, String courseId) {
Student student = retrieveStudent(studentId);
if (student == null) {
return null;
}
for (Course course : student.getCourses()) {
if (course.getId().equals(courseId)) {
return course;
}
}
return null;
}
private SecureRandom random = new SecureRandom();
public Course addCourse(String studentId, Course course) {
Student student = retrieveStudent(studentId);
if (student == null) {
return null;
}
String randomId = new BigInteger(130, random).toString(32);
course.setId(randomId);
student.getCourses().add(course);
return course;
}
}
src/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/StudentServicesApplication.java
package com.in28minutes.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class StudentServicesApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(StudentServicesApplication.class, args);
}
}
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。
您可能感兴趣的文章:
- SpringBoot构建Restful service完成Get和Post请求
- Spring Boot(四)之使用JWT和Spring Security保护REST API
- Spring Boot集成springfox-swagger2构建restful API的方法教程
- SpringBoot集成Swagger2实现Restful(类型转换错误解决办法)
- 详解Spring Boot实战之Rest接口开发及数据库基本操作
- 详解使用Spring Boot开发Restful程序
- 详解SpringBoot restful api的单元测试
- Spring Boot 实现Restful webservice服务端示例代码
- 使用SpringBoot开发Restful服务实现增删改查功能

