python中elasticsearch_dsl模块的使用方法
目录
- 前言
- 连接elasticsearch
- elasticsearch_dsl.Search
- query方法
- filter方法
- index方法
- elasticsearch_dsl.query
- elasticsearch_dsl.Q
- 嵌套类型
- 查询
- 排序
- 分页
- 聚合
- 高亮显示
- source限制返回字段
- 删除
- 案例分析
前言
elasticsearch-dsl是基于elasticsearch-py封装实现的,提供了更简便的操作elasticsearch的方法。
安装:
install elasticsearch_dsl

连接elasticsearch
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20) print(es)
还可以通过alias给连接设置别名,后续可以通过别名来引用该连接,默认别名为default。
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search # 方式一:连接es es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20) print(es) # 方式二:连接es connections.create_connection(alias="my_new_connection", hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
elasticsearch_dsl.Search
search对象代表整个搜索请求,包括:queries、filters、aggregations、sort、pagination、additional parameters、associated client。
API被设置为可链接的即和用.连续操作。search对象是不可变的,除了聚合,对对象的所有更改都将导致创建包含该更改的浅表副本。
当初始化Search对象时,传递elasticsearch客户端作为using的参数
示例代码1:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search
# 方式一:连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
# 方式二:连接es
connections.create_connection(alias="my_new_connection", hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# 不使用别名使用
res = Search(using=es).index("test_index").query()
# print(res)
for data in res:
print(data.to_dict())
print("*" * 100)
# 使用别名后这样使用
res2 = Search(using="my_new_connection").index('test_index').query()
# print(e)
for data in res2:
print(data.to_dict())
运行结果:

示例代码2:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search
# 方式一:连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
# 不使用别名使用
res = Search(using=es).index("test_index").query()
# print(res)
for data in res:
print(data.to_dict())
print("*" * 100)
# 书写方式一:按条件查询数据
res2 = Search(using=es).index("test_index").query("match", name="张三") # 查询时注意分词器的使用
for data in res2:
print(data.to_dict())
print("*" * 100)
# 书写方式二:按条件查询数据
res3 = Search(using=es).index("test_index").query({"match": {"name": "张三"}})
for data in res3:
print(data.to_dict())
运行结果:

在上述执行execute方法将请求发送给elasticsearch:
response = res.execute()不需要执行execute()方法,迭代后可以通过to_dict()方法将Search对象序列化为一个dict对象,这样可以方便调试。
query方法
查询,参数可以是Q对象,也可以是query模块中的一些类,还可以是自已写上如何查询。
示例代码1:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q import time # 方式一:连接es es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20) # print(es) res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").query().query() # 当调用.query()方法多次时,内部会使用&操作符 print(res.to_dict())
运行结果:

filter方法
在过滤上下文中添加查询,可以使用filter()函数来使之变的简单。
示例代码1:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
# 方式一:连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
# res = Search(using=es).index("test_index").filter({"match": {"name": "北"}})
# res = Search(using=es).index("test_index").filter("terms", tags=["name", "id"])
res = Search(using=es).index("test_index").query("bool", filter=[
Q("terms", tags=["name", "id"])]) # 上面代码在背后会产生一个bool查询,并将指定的条件查询放入到filter分支
print(res)
for data in res:
print(data.to_dict())
示例代码2:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
import time
# 方式一:连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
# 范围查询
# res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").filter("range", timestamp={"gte": 0, "lt": time.time()}).query({"match": {"name": "北"}})
res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").filter("range", id={"gte": 1, "lte": 4}).query({"match": {"name": "北"}})
print(res)
for data in res:
print(data.to_dict())
# 普通过滤
res2 = Search(using=es, index="test_index").filter("terms", id=["2", "4"]).execute()
print(res2)
for data in res2:
print(data.to_dict())
运行结果:

示例代码3:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
# 方式一:连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
# 方式一
q = Q('range', age={"gte": 25, "lte": 27})
res = Search(using=es, index="account_info").query(q)
print(res.to_dict())
for data in res:
print(data.to_dict())
print("*" * 100)
# 方式二
q2 = Q('range', **{"age": {"gte": 25, "lte": 27}})
res2 = Search(using=es, index="account_info").query(q2)
print(res2.to_dict())
for data in res2:
print(data.to_dict())
运行结果:

index方法
指定索引
usring方法
指定哪个elasticsearch
elasticsearch_dsl.query
该库为所有的Elasticsearch查询类型都提供了类。以关键字参数传递所有的参数,最终会把参数序列化后传递给Elasticsearch,这意味着在原始查询和它对应的dsl之间有这一个清理的一对一的映射。
示例代码:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
from elasticsearch_dsl.query import MultiMatch, Match
# 方式一:连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
# 相对与{"multi_match": {"query": "ha", "fields": ["firstname", "lastname"]}}
m1 = MultiMatch(query="Ha", fields=["firstname", "lastname"])
res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").query(m1)
print(res)
for data in res:
print(data.to_dict())
# 相当于{"match": {"firstname": {"query": "Hughes"}}}
m2 = Match(firstname={"query": "Hughes"})
res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").query(m2)
print(res)
for data in res:
print(data.to_dict())
elasticsearch_dsl.Q
使用快捷方式Q通过命名参数或者原始dict类型数据来构建一个查询实例。Q的格式一般是Q("查询类型", 字段="xxx")或Q("查询类型", query="xxx", fields=["字段1", "字段2"])
示例代码1:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
from elasticsearch_dsl.query import MultiMatch, Match
# 方式一:连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
# q = Q("match", city="Summerfield")
q = Q("multi_match", query="Summerfield", fields=["city", "firstname"])
res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").query(q)
print(res)
for data in res:
print(data.to_dict())
查询对象可以通过逻辑运算符组合起来:
Q("match", title="python") | Q("match", title="django")
# {"bool": {"should": [...]}}
Q("match", title="python") & Q("match", title="django")
# {"bool": {"must": [...]}}
~Q("match", title="python")
# {"bool": {"must_not": [...]}}
示例代码2:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
# 方式一:连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
# q = Q("multi_match", query="123.244.101.255", fields=["clientip", "timestamp"])
q = Q('match', name='张') | Q("match", name="北")
res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").query(q)
# print(res)
for data in res:
print(data.to_dict(), data.name)
print("*" * 100)
q = Q('match', name='张') & Q("match", name="北")
res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").query(q)
# print(res)
for data in res:
print(data.to_dict(), data.name)
print("*" * 100)
q = ~Q('match', name='张')
res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").query(q)
# print(res)
for data in res:
print(data.to_dict(), data.name)
运行结果:

示例代码3:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
s = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
# constant_score内置属性
q = Q({"constant_score": {"filter": {"term": {"age": 25}}}})
res = s.query(q).execute()
for hit in res:
print(hit.to_dict())
print("*" * 100)
q2 = Q("bool", must=[Q("match", address="山")], should=[Q("match", gender="男"), Q("match", emplyer="AAA")], minimum_should_match=1)
res2 = s.query(q2).execute()
for hit in res2:
print(hit.to_dict())
运行结果:

嵌套类型
有时候需要引用一个在其他字段中的字段,例如多字段(title.keyword)或者在一个json文档中的address.city。为了方便,Q允许你使用双下划线‘__’代替关键词参数中的‘.’
示例代码:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
# 方式一:连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
# res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").query("match", address__city="北京")
res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").filter("term", address__city="北京")
# print(res)
for data in res:
print(data.to_dict(), data.name)
查询
示例代码:
from elasticsearch_dsl import Search
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
# 连接es
es = Elasticsearch(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], sniffer_timeout=60, timeout=30)
# 获取es中所有的索引
# 返回类型为字典,只返回索引名
index_name = es.cat.indices(format="json", h="index")
print(index_name)
# 查询多个索引
es_multi_index = Search(using=es, index=["personal_info_5000000", "grade", "test_index"])
print(es_multi_index.execute())
# 查询一个索引
es_one_index = Search(using=es, index="test_index")
print(es_one_index.execute())
print("*" * 100)
# 条件查询1
es_search1 = es_one_index.filter("range", id={"gte": 1, "lt": 5})
print(es_search1.execute())
# 条件查询2
es_search2 = es_one_index.filter("term", name="张")
print(es_search2.execute())
print("*" * 100)
# 结果转换为字典
es_search3 = es_search2.to_dict()
print(es_search3)
es_search4 = es_search2.execute().to_dict()
print(es_search4)
运行结果:

排序
示例代码:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, A
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
s = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
res = s.query().sort('-age').execute()
# print(res)
for data in res:
print(data.to_dict())
运行结果:

分页
要指定from、size
示例代码:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, A
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
s = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
res = s.query()[2: 5].execute() # {"from": 2, "size": 5}
# print(res)
for data in res:
print(data.to_dict())
运行结果:

要访问匹配的所有文档,可以使用scan()函数,scan()函数使用scan、scroll elasticsearch API,需要注意的是这种情况下结果是不会被排序的。
示例代码:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
s = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
res = s.query()
# print(res)
for hit in res.scan():
print(hit.age, hit.address)
运行结果:

聚合
使用A快捷方式来定义一个聚合。为了实现聚合嵌套,你可以使用.bucket()、.metirc()以及.pipeline()方法。
bucket 即为分组,其中第一个参数是分组的名字,自己指定即可,第二个参数是方法,第三个是指定的field。
metric 也是同样,metric的方法有sum、avg、max、min等等,但是需要指出的是有两个方法可以一次性返回这些值,stats和extended_stats,后者还可以返回方差等值。
示例代码1:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, A
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
s = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
a = A("terms", field="gender")
s.aggs.bucket("gender_terms", a)
res = s.execute()
# print(res)
for hit in res.aggregations.gender_terms:
print(hit.to_dict())
运行结果:

示例代码2:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, A
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
s = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
s.aggs.bucket("per_gender", "terms", field="gender")
s.aggs["per_gender"].metric("sum_age", "sum", field="age")
s.aggs["per_gender"].bucket("terms_balance", "terms", field="balance")
res = s.execute()
# print(res)
for hit in res.aggregations.per_gender:
print(hit.to_dict())
运行结果:


示例代码3:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
s = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
res = s.aggs.bucket("aaa", "terms", field="gender").metric("avg_age", "avg", field="age")
print(res.to_dict())
运行结果:

示例代码4: 【聚合,内置排序】
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
"""
{
'terms': {
'field': 'age',
'order': {
'_count': 'desc'
}
}
}
"""
s = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
res = s.aggs.bucket("agg_age", "terms", field="age", order={"_count": "desc"})
print(res.to_dict())
response = s.execute()
for hit in response.aggregations.agg_age:
print(hit.to_dict())
"""
{
'terms': {
'field': 'age',
'order': {
'_count': 'asc'
}
},
'aggs': {
'avg_age': {
'avg': {
'field': 'age'
}
}
}
}
"""
s2 = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
res2 = s2.aggs.bucket("agg_age", "terms", field="age", order={"_count": "asc"}).metric("avg_age", "avg", field="age")
print(res2.to_dict())
response = s2.execute()
for hit in response.aggregations.agg_age:
print(hit.to_dict())
运行结果:

示例代码5:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
"""
{
'aggs': {
'avg_age': {
'avg': {
'field': 'age'
}
}
}
}
"""
s = Search(using=es, index="account_info").query("range", age={"gte": 28})
res = s.aggs.metric("avg_age", "avg", field="age")
print(res.to_dict())
response = s.execute()
print(response)
for hit in response:
print(hit.to_dict())
运行结果:

高亮显示
示例代码:【目前似乎没有效果,待验证】
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
s = Search(using=es, index="test_index")
res = s.highlight("id").execute().to_dict()
print(res)
运行结果:

source限制返回字段
示例代码:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
s = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
res = s.query().execute()
for hit in res:
print(hit.to_dict())
# 限制返回字段
s2 = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
res2 = s2.query().source(['account_number', 'address']).execute()
for hit in res2:
print(hit.to_dict())
运行结果:

删除
调用Search对象上的delete方法而不是execute来实现删除匹配查询的文档
示例代码:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
s = Search(using=es, index="test_index")
res = s.query("match", name="张").delete()
print(res)
运行结果:

案例分析
创建索引:
from elasticsearch_dsl import Search
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
# 连接es
es = Elasticsearch(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], sniffer_timeout=60, timeout=30)
body = {
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"account_number": {
"type": "integer"
},
"balance": {
"type": "integer"
},
"firstname": {
"type": "text"
},
"lastname": {
"type": "text"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"gender": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"address": {
"type": "text"
},
"employer": {
"type": "text"
},
"email": {
"type": "text"
},
"province": {
"type": "text"
},
"state": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
# 创建 index
es.indices.create(index="account_info", body=body)
查看索引:

使用kibana批量生成数据:
POST account_info/_bulk
{"index": {"_index":"account_info"}}
{"account_number":1,"balance":20,"firstname":"三","lastname":"张","age":25,"gender":"男","address":"北京朝阳","employer":"AAA","email":"123@qq.com","province":"北京","state":"正常"}
{"index": {"_index":"account_info"}}
{"account_number":2,"balance":70,"firstname":"二","lastname":"张","age":26,"gender":"男","address":"北京海淀","employer":"AAA","email":"123@qq.com","province":"北京","state":"正常"}
{"index": {"_index":"account_info"}}
{"account_number":3,"balance":80,"firstname":"四","lastname":"张","age":27,"gender":"女","address":"辽宁朝阳","employer":"BBB","email":"123@qq.com","province":"辽宁","state":"正常"}
{"index": {"_index":"account_info"}}
{"account_number":4,"balance":60,"firstname":"五","lastname":"张","age":28,"gender":"男","address":"山东青岛","employer":"AAA","email":"123@qq.com","province":"山东","state":"正常"}
{"index": {"_index":"account_info"}}
{"account_number":5,"balance":40,"firstname":"六","lastname":"张","age":29,"gender":"女","address":"山东济南","employer":"AAA","email":"123@qq.com","province":"山东","state":"正常"}
{"index": {"_index":"account_info"}}
{"account_number":6,"balance":50,"firstname":"七","lastname":"张","age":30,"gender":"男","address":"河北唐山","employer":"BBB","email":"123@qq.com","province":"河北","state":"正常"}
{"index": {"_index":"account_info"}}
{"account_number":7,"balance":30,"firstname":"一","lastname":"张","age":31,"gender":"女","address":"河北石家庄","employer":"AAA","email":"123@qq.com","province":"河北","state":"正常"}
查看生成的数据:


根据条件查询:
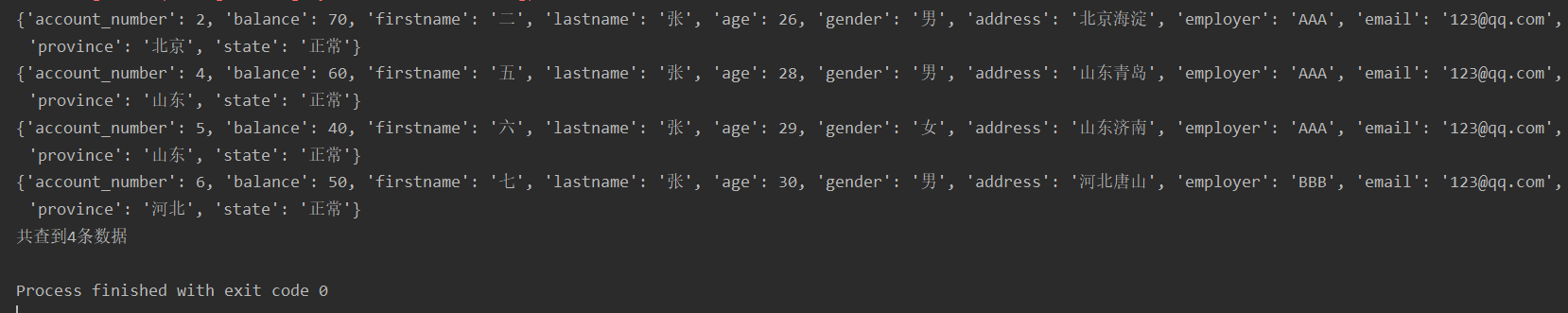
1.查询balance在40~70的信息
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
s = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
# 查询balance在40~70的信息
q = Q("range", balance={"gte": 40, "lte": 70})
res = s.query(q)
for data in res:
print(data.to_dict())
print("共查到%d条数据" % res.count())
2.查询balance在40~70的男性信息
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
s = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
# 查询balance在40~70的信息
q1 = Q("range", balance={"gte": 40, "lte": 70})
# 男性
q2 = Q("term", gender="男")
# and
q = q1 & q2
res = s.query(q)
for data in res:
print(data.to_dict())
print("共查到%d条数据" % res.count())

3.省份为北京、25或30岁的男性信息
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
s = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
# 方式一:
# 省份为北京
q1 = Q("match", province="北京")
# 25或30岁的男性信息
q2 = Q("bool", must=[Q("terms", age=[25, 30]), Q("term", gender="男")])
# and
q = q1 & q2
res = s.query(q)
for data in res:
print(data.to_dict())
print("共查到%d条数据" % res.count())
print("*" * 100)
# 方式二
# 省份为北京
q1 = Q("match", province="北京")
# 25或30岁的信息
# q2 = Q("bool", must=[Q("terms", age=[25, 30]), Q("term", gender="男")])
q2 = Q("term", age=25) | Q("term", age=30)
# 男性
q3 = Q("term", gender="男")
res = s.query(q1).query(q2).query(q3) # 多次query就是& ==> and 操作
for data in res:
print(data.to_dict())
print("共查到%d条数据" % res.count())

4.地址中有“山”字,年龄不在25~28岁的女性信息
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
s = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
# 地址中有“山”字且为女性
q1 = Q("match", address="山") & Q("match", gender="女")
# 年龄在25~28岁
q2 = ~Q("range", age={"gte": 25, "lte": 28})
# 使用filter过滤
# query和filter的前后关系都行
res = s.filter(q2).query(q1)
for data in res:
print(data.to_dict())
print("共查到%d条数据" % res.count())

5.根据年龄进行聚合,然后计算每个年龄的评价balance数值
示例代码:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, A
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
s = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
# 先用年龄聚合,然后拿到返平均数
# size指定最大返回多少条数据,默认10条
# 实质上account的数据中,age分组没有100个这么多
q = A("terms", field="age", size=100).metric("age_per_balance", "avg", field="balance")
s.aggs.bucket("res", q)
# 执行并拿到返回值
response = s.execute()
# res是bucket指定的名字
# response.aggregations.to_dict是一个{'key': 25, 'doc_count': 1, 'age_per_balance': {'value': 20.0}}的数据,和用restful查询的一样
for data in response.aggregations.res:
print(data.to_dict())
运行结果:

6.根据年龄聚合,求25~28岁不同性别的balance值。
示例代码:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, A
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["127.0.0.1:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
s = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
# 这次就用这种方法
# range 要注意指定ranges参数和from to
a1 = A("range", field="age", ranges={"from": 25, "to": 28})
a2 = A("terms", field="gender")
a3 = A("avg", field="balance")
s.aggs.bucket("res", a1).bucket("gender_group", a2).metric("balance_avg", a3)
# 执行并拿到返回值
response = s.execute()
# res是bucket指定的名字
for data in response.aggregations.res:
print(data.to_dict())
运行结果: 【注意:不包含年龄28的值】

总结:
假如是数组,如:bool的must、terms,那么就要字段=[ ]假如是字典,如:range,那么就要字段={xxx: yyy, .... }假如是单值,如:term、match,那么就要字段=值假如查的是多个字段,如:multi_mathc,那么就要加上query="要查的值", fields=["字段1", "字段2", ...]然后各个条件的逻辑关系,可以通过多次query和filter或直接用Q("bool", must=[Q...], should=[Q...])再加上& | ~表示
到此这篇关于python中elasticsearch_dsl模块的使用方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python elasticsearch_dsl模块内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

